Unveiling The Dynamics Of Wisconsin’s Snow Cover: A Comprehensive Exploration
Unveiling the Dynamics of Wisconsin’s Snow Cover: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Dynamics of Wisconsin’s Snow Cover: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Dynamics of Wisconsin’s Snow Cover: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Dynamics of Wisconsin’s Snow Cover: A Comprehensive Exploration

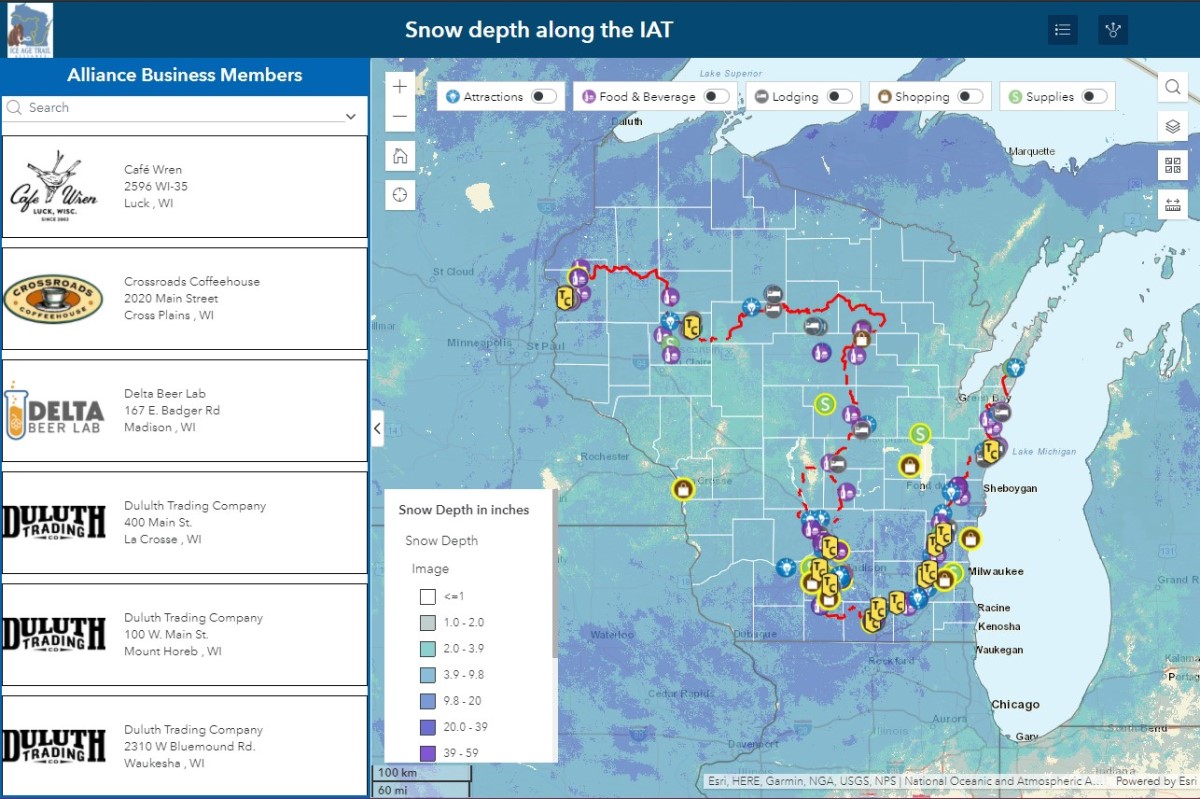
Wisconsin, a state renowned for its picturesque landscapes and distinct seasons, experiences a significant annual snowfall. Understanding the spatial distribution and temporal evolution of snow cover is crucial for numerous sectors, ranging from agriculture and transportation to water resources management and public safety. The Wisconsin Snow Cover Map, a valuable tool developed and maintained by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), provides a detailed visual representation of snow depth across the state. This article delves into the significance of this map, exploring its intricacies, applications, and the vital role it plays in various aspects of Wisconsin’s life.
Understanding the Wisconsin Snow Cover Map: A Visual Chronicle of Winter’s Grip
The Wisconsin Snow Cover Map, a dynamic visualization updated regularly, offers a snapshot of snow depth across the state. Utilizing data from various sources, including satellite imagery and ground-based observations, the map depicts snow cover in a clear and concise manner. Each pixel on the map represents a specific location within Wisconsin, with its color indicating the estimated snow depth.
The Significance of Snow Cover: A Multifaceted Impact
Snow cover, a seemingly simple phenomenon, plays a pivotal role in shaping Wisconsin’s environment and influencing various aspects of human activity. Its impact extends far beyond the picturesque winter landscapes, influencing:
1. Water Resources Management: Snow acts as a natural reservoir, accumulating and storing water during the winter months. As temperatures rise in the spring, snowmelt replenishes rivers, lakes, and groundwater, providing a crucial water source for agriculture, industry, and domestic use. Understanding the extent and distribution of snow cover is vital for water resource managers to anticipate water availability and plan for potential shortages.
2. Agriculture and Forestry: Snow cover provides insulation for crops and trees, protecting them from extreme cold temperatures and frost damage. Snowmelt also provides a vital source of water for plant growth, particularly during the spring months. Farmers and foresters rely on accurate snow cover information to assess crop health, plan irrigation schedules, and predict potential risks to their operations.
3. Transportation and Infrastructure: Snow accumulation can significantly impact transportation systems, leading to road closures, flight delays, and disruptions in supply chains. The Wisconsin Snow Cover Map helps transportation authorities anticipate potential challenges, allowing them to implement preventive measures such as snow removal and road closures, ensuring safe and efficient transportation.
4. Wildlife and Ecology: Snow cover plays a crucial role in the ecology of Wisconsin’s diverse ecosystems. It provides habitat for various wildlife species, offering insulation and protection from harsh winter conditions. Snowmelt also contributes to the replenishment of wetlands and aquatic habitats, supporting the delicate balance of ecosystems.
5. Public Safety and Emergency Response: Heavy snowfall can create hazardous conditions, increasing the risk of accidents, power outages, and other emergencies. The Wisconsin Snow Cover Map aids emergency responders in anticipating potential challenges and allocating resources effectively. It helps them understand the severity of snow conditions and prioritize areas requiring immediate attention.
Navigating the Data: A Deeper Dive into the Map’s Insights
The Wisconsin Snow Cover Map offers a wealth of information beyond simply depicting snow depth. Users can access various data layers and visualizations, providing a more comprehensive understanding of snow cover dynamics. These include:
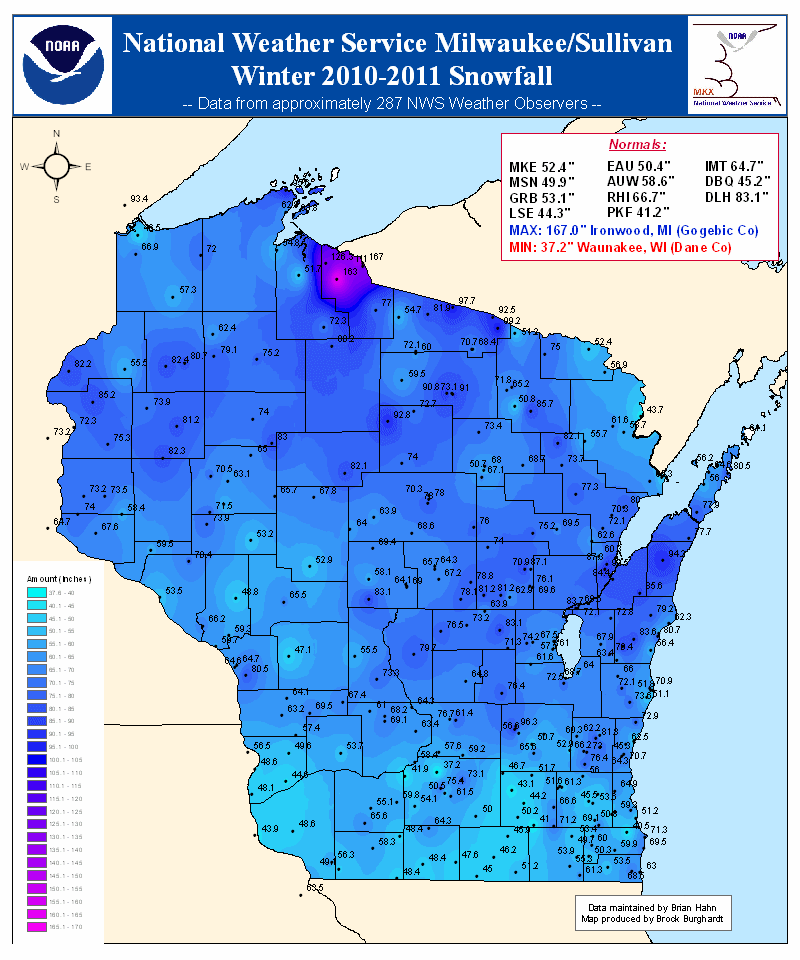
1. Historical Data: The map provides access to historical snow cover data, allowing users to track long-term trends and patterns. This information is crucial for understanding the impacts of climate change on snow cover and its implications for various sectors.
2. Snow Depth Anomalies: The map highlights areas where snow depth deviates significantly from historical averages. This information helps identify regions experiencing unusual snowfall patterns, potentially indicating climate change impacts or localized weather events.
3. Snow Water Equivalent (SWE): The map displays the amount of water contained within the snowpack. This data is essential for water resource managers, as it directly relates to the amount of water available for replenishing rivers and lakes during snowmelt.
4. Snow Cover Duration: The map tracks the duration of snow cover at different locations, providing valuable insights into the timing of snowmelt and its influence on various natural processes.
5. Real-time Updates: The Wisconsin Snow Cover Map is regularly updated, providing users with access to the most current snow cover information. This real-time data is crucial for decision-making in various sectors, particularly those sensitive to changing snow conditions.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about Wisconsin’s Snow Cover
1. How is the Wisconsin Snow Cover Map created?
The Wisconsin Snow Cover Map utilizes data from various sources, including:
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites equipped with specialized sensors capture images of the Earth’s surface, providing information on snow cover extent and depth.
- Ground-Based Observations: Weather stations across Wisconsin record snow depth measurements, providing accurate ground-truth data for validating satellite observations.
- Numerical Weather Models: Weather models generate predictions of snow accumulation and distribution, providing valuable information for forecasting snow cover patterns.
2. How accurate is the Wisconsin Snow Cover Map?
The accuracy of the Wisconsin Snow Cover Map varies depending on the data sources used and the specific location. However, the map is generally considered reliable, particularly when utilizing data from multiple sources.
3. What are the limitations of the Wisconsin Snow Cover Map?
While the Wisconsin Snow Cover Map provides valuable information, it has certain limitations:
- Spatial Resolution: The map’s resolution may not be sufficient to accurately depict snow cover in highly localized areas, such as small valleys or forested regions.
- Data Availability: Data availability may be limited in remote or sparsely populated areas, impacting the accuracy of snow cover estimates.
- Snow Depth Variability: Snow depth can vary significantly within a small area, making it challenging to capture precise measurements using satellite imagery.
4. How can I access the Wisconsin Snow Cover Map?
The Wisconsin Snow Cover Map is publicly available through the NOAA website. Users can access the map through a web interface, allowing them to view, download, and analyze the data.
5. What are the potential impacts of climate change on Wisconsin’s snow cover?
Climate change is expected to significantly impact Wisconsin’s snow cover, with potential consequences for various sectors:
- Reduced Snowfall: Warmer temperatures are predicted to lead to reduced snowfall, impacting water resources, agriculture, and transportation systems.
- Earlier Snowmelt: Increased temperatures are expected to cause earlier snowmelt, altering the timing of water availability and potentially impacting ecosystems and water resources management.
- Increased Snow Depth Variability: Climate change may lead to more extreme weather events, resulting in increased variability in snow depth and potential challenges for various sectors.
Tips for Utilizing the Wisconsin Snow Cover Map
- Familiarize yourself with the map’s features: Understand the data layers, visualization options, and how to navigate the map effectively.
- Consider your specific needs: Determine the type of information you require, such as snow depth, SWE, or snow cover duration.
- Compare data with historical trends: Use the map’s historical data feature to identify long-term patterns and potential anomalies.
- Integrate data with other resources: Combine snow cover information with other relevant data sources, such as weather forecasts, to gain a more comprehensive understanding.
- Share information and collaborate: Communicate snow cover information with relevant stakeholders, fostering collaboration and informed decision-making.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Navigating Wisconsin’s Winter Landscape
The Wisconsin Snow Cover Map stands as a vital tool for understanding and managing the impacts of snow cover on the state’s environment and various sectors. By providing detailed visualizations and data analysis capabilities, the map empowers decision-makers in agriculture, transportation, water resources management, and public safety to anticipate challenges, plan effectively, and mitigate potential risks. As climate change continues to influence snow cover patterns, the importance of this valuable resource will only grow, ensuring a more informed and resilient approach to managing Wisconsin’s unique winter landscape.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Dynamics of Wisconsin’s Snow Cover: A Comprehensive Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!