Understanding Blastomycosis In Wisconsin: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Blastomycosis in Wisconsin: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Blastomycosis in Wisconsin: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Blastomycosis in Wisconsin: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Blastomycosis in Wisconsin: A Comprehensive Guide
Blastomycosis, a fungal infection caused by the organism Blastomyces dermatitidis, is a serious health concern, particularly in certain regions of the United States, including Wisconsin. This article provides a comprehensive overview of blastomycosis in Wisconsin, focusing on its prevalence, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Prevalence and Geographic Distribution
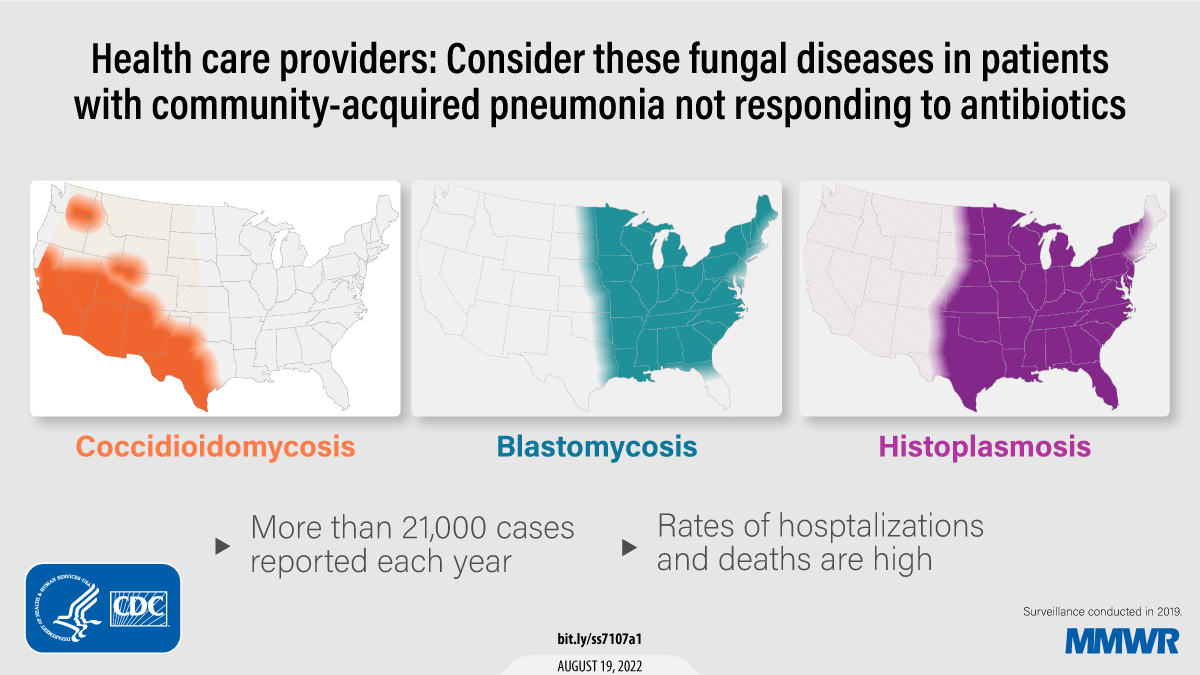
Wisconsin is considered an endemic area for blastomycosis, meaning the fungus is naturally present in the environment. The disease is most commonly found in the northern and central regions of the state, particularly in areas with decaying wood, moist soil, and forested landscapes. This is due to the fungus’s preference for decaying wood, particularly oak and maple trees.
The Importance of Mapping Blastomycosis Cases
Understanding the geographic distribution of blastomycosis cases is crucial for public health officials and healthcare providers. Maps illustrating the prevalence of the disease help to:
- Identify high-risk areas: This allows for targeted public health interventions and education campaigns to raise awareness and promote prevention measures.
- Track disease trends: Monitoring the incidence of blastomycosis over time can reveal patterns and potential outbreaks, facilitating timely responses.
- Guide research efforts: Maps can help pinpoint areas where further research on the fungus’s ecology, transmission, and treatment is most needed.
Risk Factors for Blastomycosis
While anyone can contract blastomycosis, certain individuals are at higher risk. These include:
- Outdoor workers: Individuals engaged in activities such as logging, farming, construction, and landscaping are more likely to inhale fungal spores.
- Individuals with weakened immune systems: People with conditions like HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or who are undergoing chemotherapy are more susceptible to infection.
- Smokers: Smoking can impair the immune system, increasing the risk of developing blastomycosis.
- People living in endemic areas: Residents of areas where the fungus is prevalent have a higher chance of exposure.
Symptoms of Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis can manifest in various ways, ranging from mild, flu-like symptoms to severe, life-threatening complications. Common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Muscle aches
- Joint pain
- Skin lesions
- Weight loss
In severe cases, blastomycosis can lead to pneumonia, meningitis, or even death. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications.
Diagnosis of Blastomycosis
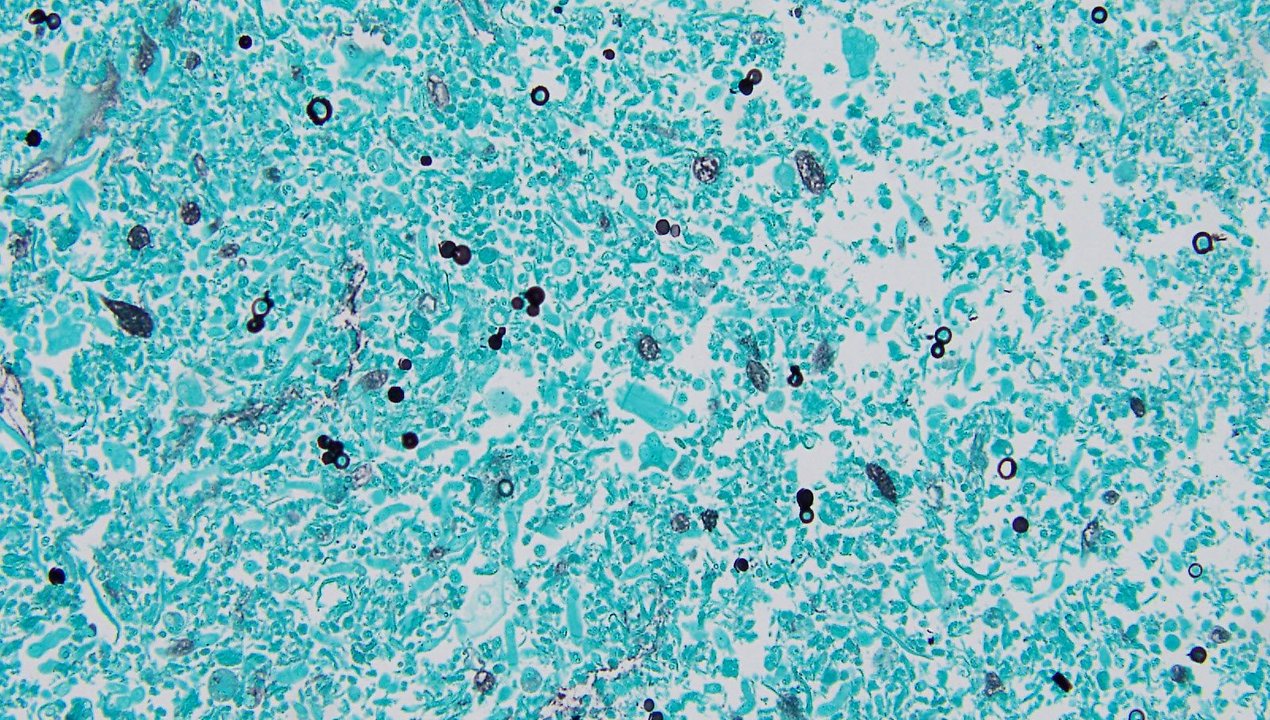
Diagnosing blastomycosis can be challenging as its symptoms often mimic other respiratory infections. A combination of diagnostic methods is typically employed:
- Medical history and physical exam: Assessing the patient’s symptoms, occupation, and exposure history.
- Sputum culture: Analyzing a sample of the patient’s phlegm for the presence of Blastomyces dermatitidis.
- Blood tests: Detecting the presence of antibodies against the fungus.
- Imaging tests: Chest X-rays or CT scans to visualize any lung abnormalities.
- Biopsy: Obtaining a tissue sample from a lesion or lung for microscopic examination.
Treatment of Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis is typically treated with antifungal medications, primarily itraconazole or amphotericin B. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the infection and the patient’s overall health.
- Itraconazole: This oral medication is generally well-tolerated and is often the first-line treatment for blastomycosis.
- Amphotericin B: This intravenous medication is used for severe infections or when oral medications are ineffective.
Prevention of Blastomycosis
While eliminating exposure to Blastomyces dermatitidis is impossible, certain measures can help reduce the risk of infection:
- Avoid disturbing soil and decaying wood: Wear a mask and gloves when working in areas with potential exposure.
- Maintain good ventilation: Ensure adequate airflow in enclosed spaces where work is being done.
- Wash hands frequently: After working outdoors, wash hands thoroughly with soap and water.
- Be aware of symptoms: Seek medical attention if experiencing any of the symptoms associated with blastomycosis.
FAQs about Blastomycosis in Wisconsin
Q: What are the most common symptoms of blastomycosis?
A: The most common symptoms of blastomycosis include fever, cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, muscle aches, joint pain, and skin lesions.
Q: How is blastomycosis diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical exam, sputum culture, blood tests, imaging tests, and biopsy.
Q: What are the treatment options for blastomycosis?
A: Treatment typically involves antifungal medications such as itraconazole or amphotericin B.
Q: Is blastomycosis contagious?
A: Blastomycosis is not contagious from person to person. It is spread through inhalation of fungal spores from the environment.
Q: What are some tips for preventing blastomycosis?
A: Tips for preventing blastomycosis include avoiding disturbing soil and decaying wood, maintaining good ventilation, washing hands frequently, and being aware of symptoms.
Conclusion
Blastomycosis is a serious fungal infection that can cause significant health problems. Understanding its prevalence, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention is crucial for protecting individuals and communities. By utilizing maps to track the distribution of cases, public health officials and healthcare providers can better target interventions, educate the public, and promote preventative measures. Continued research and awareness are essential to mitigate the impact of blastomycosis and ensure the well-being of individuals living in endemic areas like Wisconsin.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Blastomycosis in Wisconsin: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
