The Wisconsin Assembly District Map: A Foundation For Representation
The Wisconsin Assembly District Map: A Foundation for Representation
Related Articles: The Wisconsin Assembly District Map: A Foundation for Representation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Wisconsin Assembly District Map: A Foundation for Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Wisconsin Assembly District Map: A Foundation for Representation

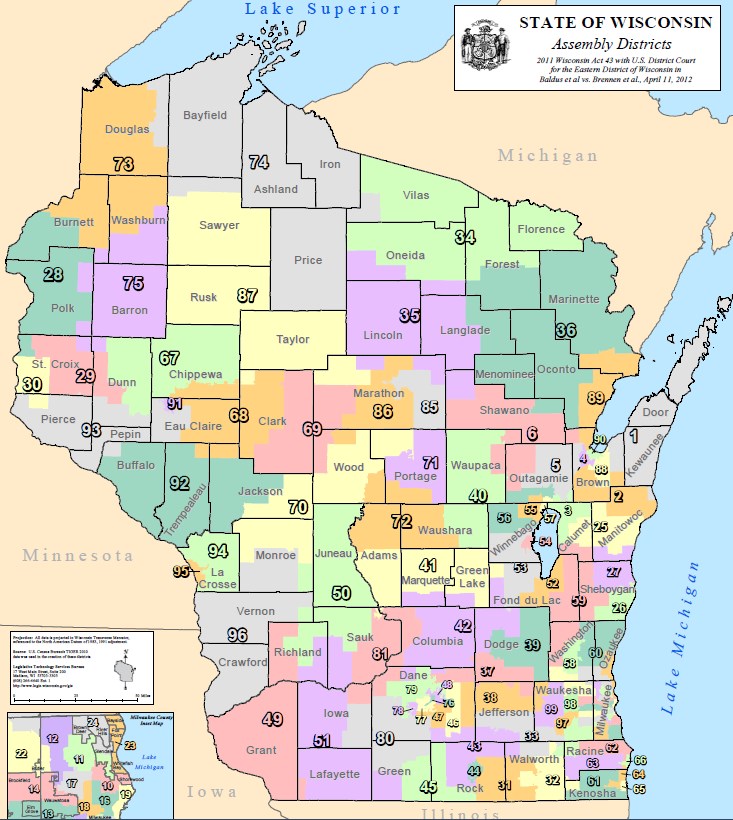
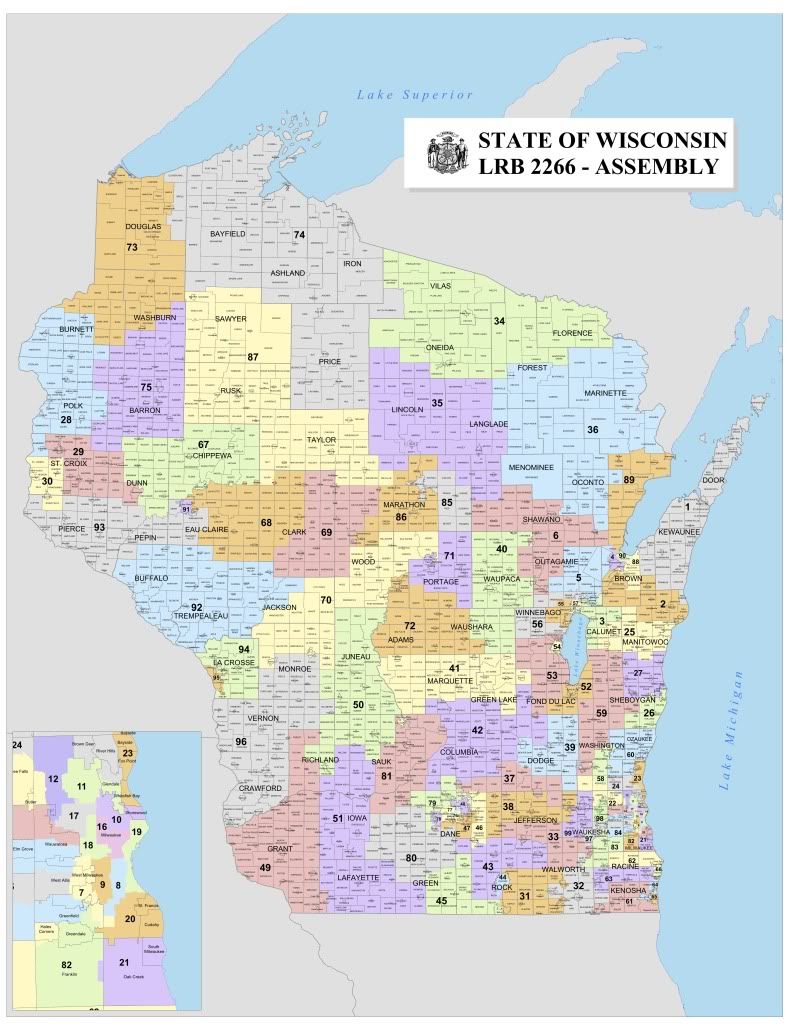
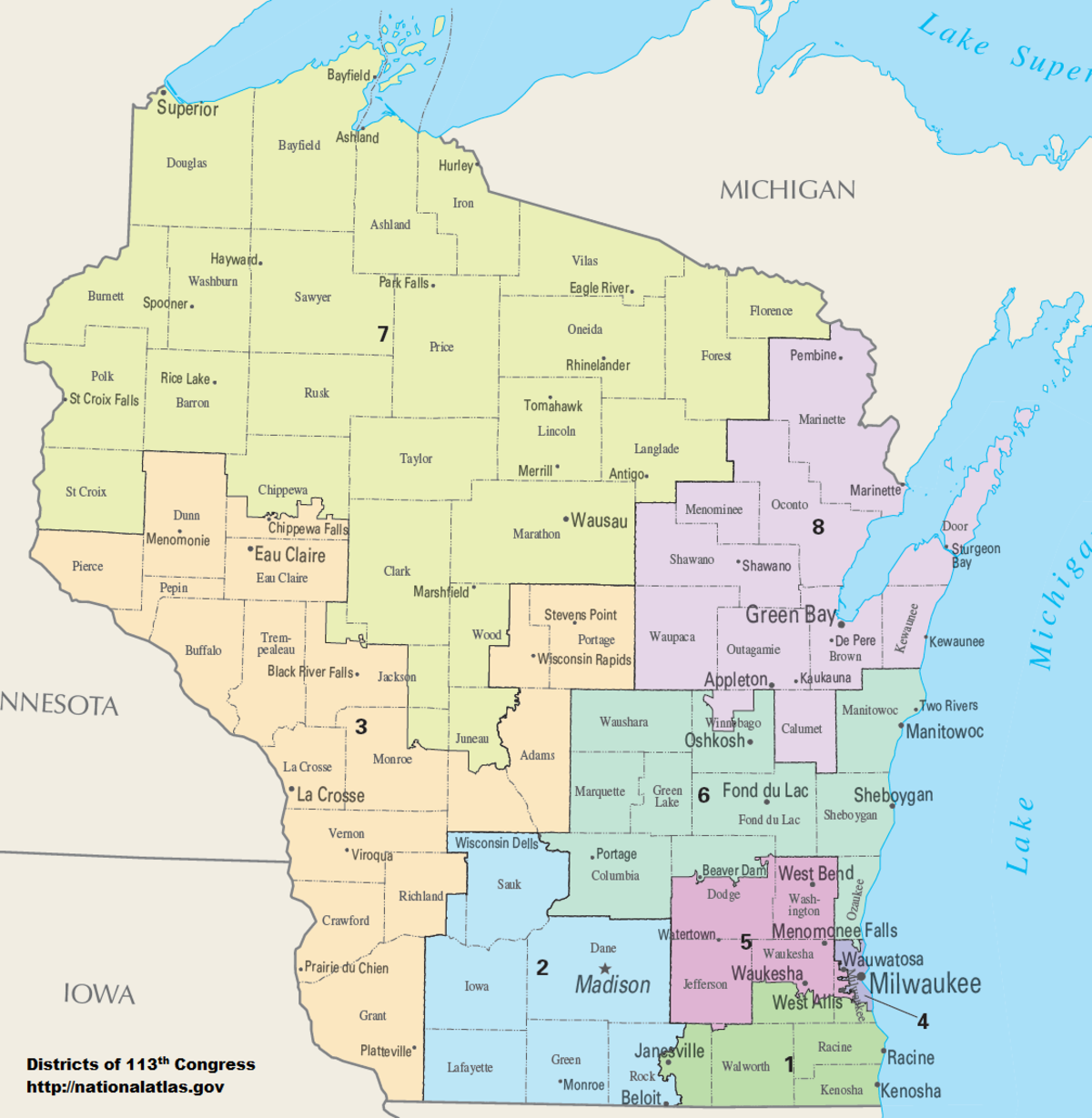
The Wisconsin Assembly District Map is a critical component of the state’s political landscape, dictating the boundaries of electoral districts for the Wisconsin Assembly, the lower house of the Wisconsin Legislature. This map, subject to periodic redrawing, directly influences the representation of citizens in the state government and, consequently, the policies that impact their lives.
Understanding the Map’s Significance
The significance of the Assembly District Map lies in its fundamental role in ensuring fair and equitable representation. It determines which geographic areas are grouped together to form a single electoral district, and thus, which constituents are represented by a single Assembly member. This process, known as redistricting, occurs every ten years following the decennial census, reflecting population shifts and changes in the state’s demographics.
The Principles of Redistricting
Redistricting in Wisconsin, as in other states, is governed by specific legal principles aimed at creating fair and balanced electoral districts. These principles include:
- Equal Population: Each Assembly district must contain, as closely as practicable, an equal number of residents. This ensures that each voter’s voice carries equal weight in the electoral process.
- Contiguity: Districts must be geographically contiguous, meaning that all parts of the district must be connected and not separated by other districts. This promotes a sense of community and ensures that representatives are accountable to a cohesive group of constituents.
- Compactness: Districts should be as compact as possible, minimizing sprawling and irregularly shaped boundaries. This enhances the efficiency of representation and facilitates communication between representatives and their constituents.
- Preservation of Communities of Interest: Redistricting should strive to preserve communities of interest, such as shared cultural, economic, or social characteristics. This ensures that representatives are sensitive to the specific needs and concerns of their constituents.
- Minimizing Division of Municipalities: Ideally, redistricting avoids splitting municipalities into multiple districts unless absolutely necessary. This fosters local representation and strengthens the relationship between municipalities and their representatives.
The Impact of Redistricting on Representation
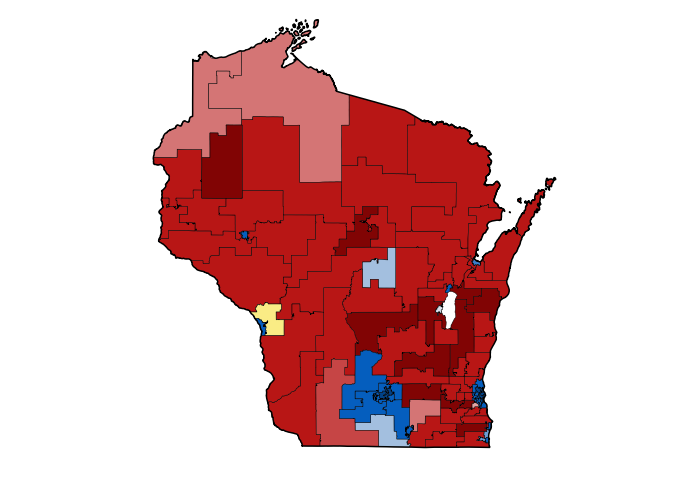
Redistricting can significantly impact the political landscape, influencing the balance of power in the Assembly and the likelihood of certain candidates being elected. When districts are drawn to favor one party or group over another, it can lead to partisan gerrymandering, where boundaries are manipulated to concentrate or dilute the voting power of specific demographics. This practice undermines the principles of fair representation and can result in uncompetitive elections, where one party has an unfair advantage.
The Process of Redistricting in Wisconsin
In Wisconsin, the responsibility for redistricting lies with the Legislative Redistricting Commission (LRC), a bipartisan body consisting of three members: one Democrat, one Republican, and one independent appointed by the chief justice of the Wisconsin Supreme Court. The LRC is tasked with creating a new Assembly District Map every ten years, adhering to the principles outlined above.
The process of redistricting is complex and involves extensive data analysis, public hearings, and negotiations between the LRC members. The proposed map is subject to public review and can be challenged in court if deemed to violate legal principles or create an unfair advantage for any party or group.
Navigating the Wisconsin Assembly District Map
Understanding the Assembly District Map is essential for citizens to engage in the political process and advocate for their interests. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Identifying Your District: The first step is to determine which Assembly district you reside in. This information is readily available online through various resources, including the Wisconsin Government website and the Wisconsin Elections Commission website.
- Knowing Your Representative: Once you know your district, you can identify your Assembly representative. This information is also available online and through the Wisconsin Legislature website.
- Engaging with Your Representative: Knowing your representative allows you to contact them directly to share your views, concerns, and ideas on issues that matter to you. You can also attend public hearings and meetings organized by your representative to engage in dialogue with them and other constituents.
- Following Redistricting: Stay informed about the redistricting process, including the proposed maps and any challenges to them. This ensures that you are aware of potential changes to your district and the impact they might have on your representation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How often is the Assembly District Map redrawn?
A: The Assembly District Map is redrawn every ten years, following the decennial census, to reflect changes in population distribution.
Q: Who is responsible for redrawing the Assembly District Map?
A: The Legislative Redistricting Commission (LRC) is responsible for redrawing the Assembly District Map.
Q: What are the criteria used for redrawing the Assembly District Map?
A: Redistricting is guided by principles such as equal population, contiguity, compactness, preservation of communities of interest, and minimizing division of municipalities.
Q: Can I challenge the Assembly District Map?
A: Yes, proposed maps can be challenged in court if they are deemed to violate legal principles or create an unfair advantage for any party or group.
Tips for Engaging with the Assembly District Map
- Stay Informed: Follow the redistricting process and stay updated on any proposed changes to the Assembly District Map.
- Contact Your Representative: Engage with your Assembly representative by sharing your views, concerns, and ideas on issues that matter to you.
- Participate in Public Hearings: Attend public hearings organized by the LRC and your representative to voice your opinions and engage in dialogue with other constituents.
- Support Fair Redistricting: Advocate for redistricting processes that prioritize fairness, transparency, and equal representation.
Conclusion
The Wisconsin Assembly District Map is a crucial element of the state’s political system, shaping the representation of citizens in the Assembly and influencing the policies that affect their lives. Understanding the map’s significance, the principles guiding redistricting, and the impact of this process on representation is essential for informed civic engagement. By staying informed, actively participating in the process, and advocating for fair representation, citizens can ensure that their voices are heard and their interests are represented effectively in the Wisconsin Legislature.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Wisconsin Assembly District Map: A Foundation for Representation. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!