The Shifting Sands Of Europe: A Visual History Of World War II German Occupation
The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Visual History of World War II German Occupation
Related Articles: The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Visual History of World War II German Occupation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Visual History of World War II German Occupation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Visual History of World War II German Occupation

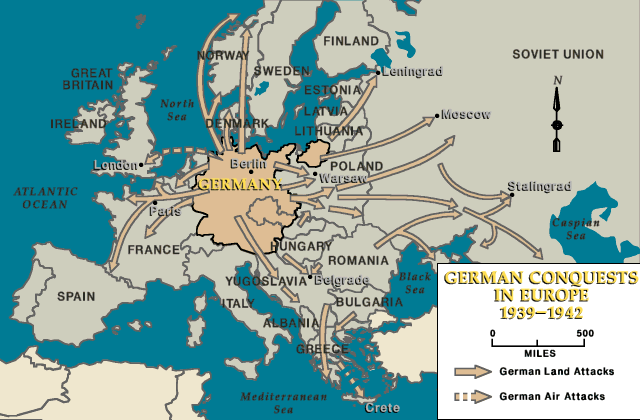
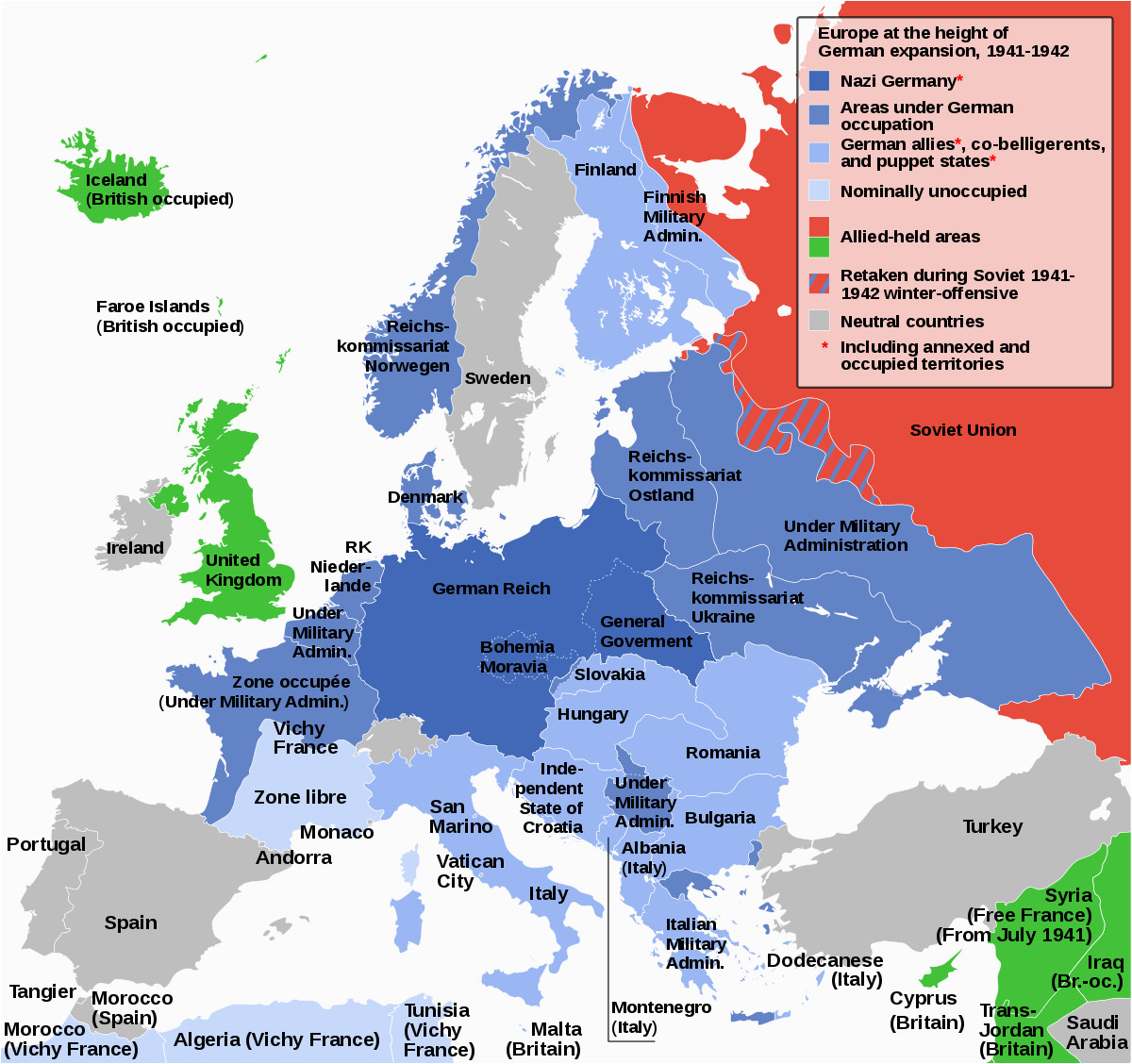
The map of Europe during World War II is a testament to the sheer scale of Nazi Germany’s ambitions and the brutal reality of their conquests. It depicts not just a geographical expansion but a systematic subjugation of nations, cultures, and populations. Understanding this map, with its ever-shifting borders and territories, offers invaluable insight into the complexities of the war, its impact on the occupied countries, and the long-lasting consequences that reverberate even today.
The Blitzkrieg and the Rapid Expansion of the Reich:
The German invasion of Poland in September 1939 marked the beginning of World War II and set in motion a rapid expansion of German control. The swiftness of the Blitzkrieg, a lightning-fast military strategy, overwhelmed Poland’s defenses and established the foundation for future conquests.
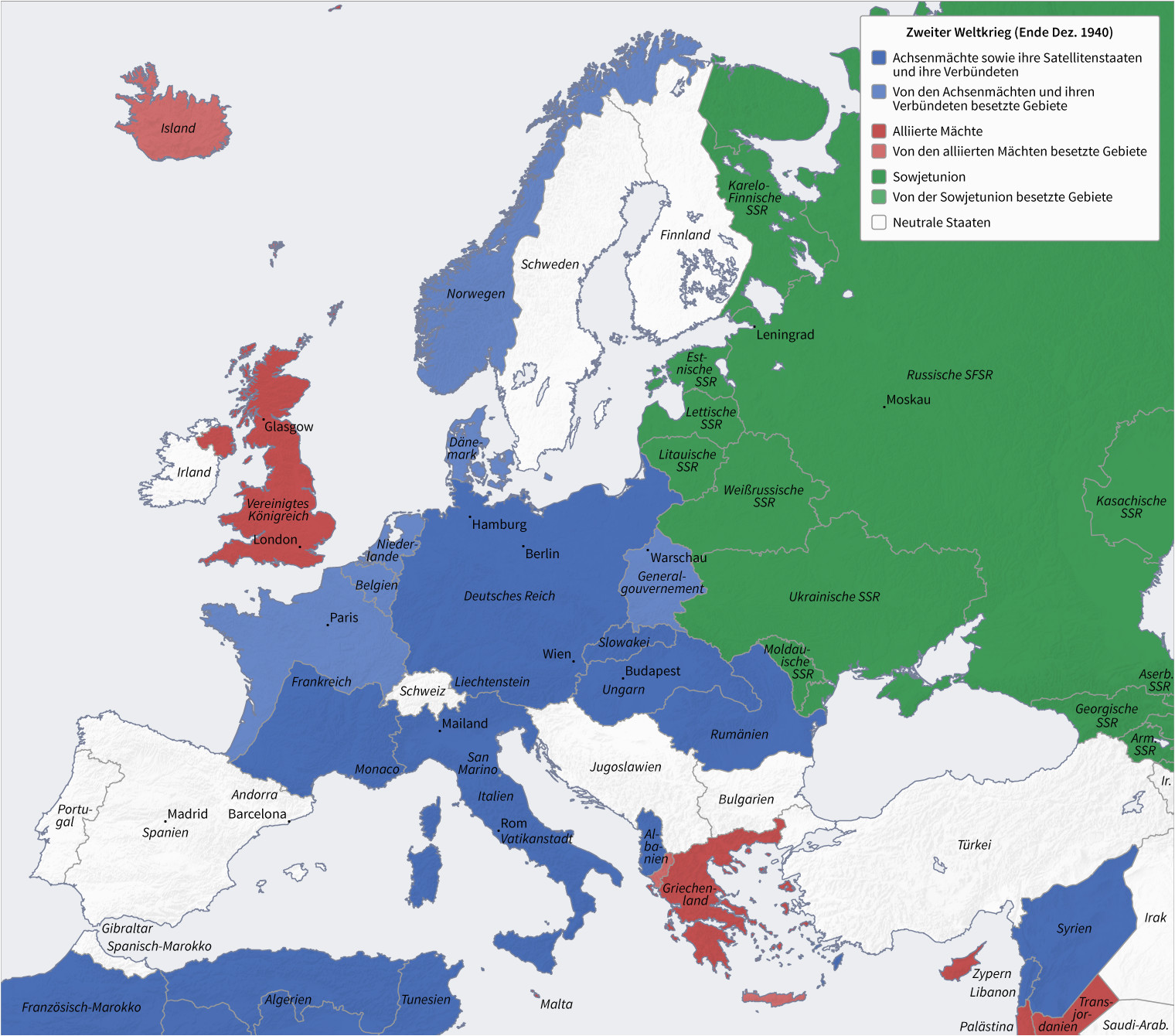
Within a year, Germany had annexed Austria and Czechoslovakia, adding these territories to the growing Reich. The map of Europe began to transform, with the swastika flag replacing national banners in conquered cities.
The Western Front and the Fall of France:
In 1940, Germany turned its attention to Western Europe. The invasion of France, a seemingly impregnable fortress, demonstrated the devastating power of the Wehrmacht. The French surrender in June 1940 marked a turning point, as Germany now controlled a vast swathe of Western Europe, including Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg.
The map of Europe now reflected a stark reality: Nazi Germany dominated the continent, with its borders stretching from the Atlantic coast to the Soviet Union.
The Eastern Front and the Brutal Occupation of the Soviet Union:
The invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941 marked a pivotal moment in the war. This campaign, known as "Operation Barbarossa," aimed to conquer the vast Soviet territories and secure resources for the German war machine.
The map of Europe became a battleground for brutal fighting, with Germany’s advance pushing deep into Soviet territory. The occupation of the Soviet Union was marked by unparalleled brutality, with the systematic implementation of the "Holocaust by Bullets," the Einsatzgruppen, and the mass starvation of civilians.
The Occupation Regimes: A System of Control and Exploitation:
The German occupation of Europe was not merely a military conquest but a systematic attempt to subjugate the conquered populations. The Nazi regime implemented a multi-layered system of control, designed to exploit resources, suppress resistance, and impose its ideology.
- Political Control: Puppet governments were established in occupied countries, often staffed by collaborators who served the interests of the Nazi regime. These governments were used to enforce German policies, suppress dissent, and facilitate the exploitation of resources.
- Economic Exploitation: The occupied countries were treated as economic colonies, their resources plundered to fuel the German war machine. Factories were retooled for war production, food was requisitioned for the German army, and labor was forcibly conscripted for German industries.
- Cultural and Ideological Control: The Nazi regime sought to eradicate local cultures and impose its own ideology. Schools were forced to teach Nazi propaganda, cultural institutions were purged of "undesirable" elements, and languages and traditions were suppressed.
- Persecution and Genocide: The Nazi regime implemented a systematic policy of persecution against Jews, Roma, and other "undesirable" groups. Ghettos were established, mass deportations were carried out, and genocide was perpetrated on a scale never before seen in human history.
The Resistance: A Beacon of Hope and Courage:
Despite the overwhelming power of the Nazi regime, resistance movements emerged throughout occupied Europe. These underground networks, often operating in the shadows, engaged in acts of sabotage, espionage, and armed combat.
The resistance movements, fueled by a desire for freedom and a deep sense of patriotism, played a crucial role in undermining German control and providing hope for liberation.
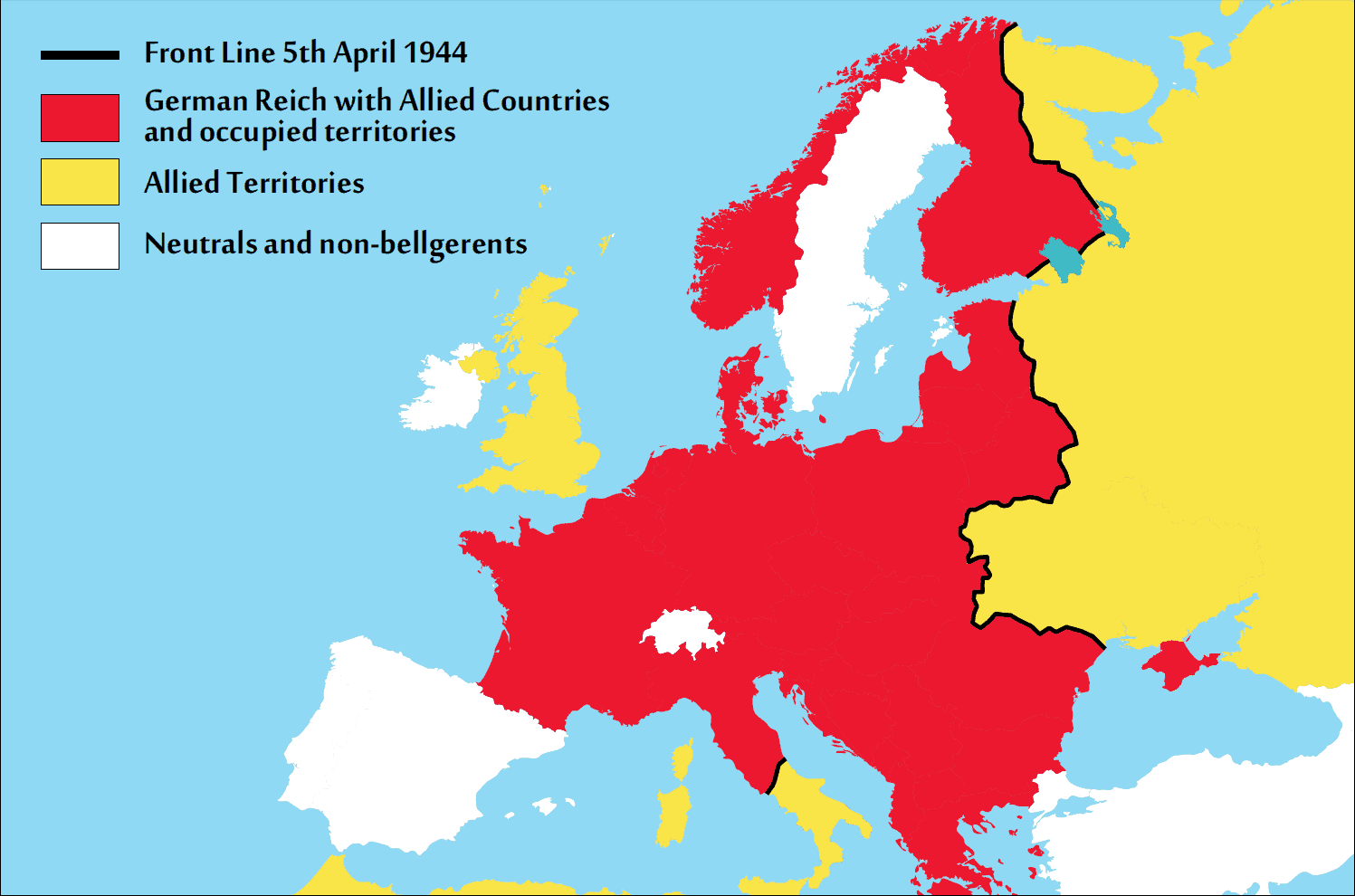
The Liberation of Europe: A Gradual Process of Reclaiming Freedom:
The tide of war began to turn in 1944, with the Allied invasion of Normandy and the subsequent liberation of France. The map of Europe gradually shifted, as Allied forces pushed back German troops and reclaimed occupied territories.
The liberation of Europe was a long and arduous process, marked by fierce battles and countless casualties. It was a testament to the collective determination of the Allied forces and the unwavering spirit of resistance movements.
The Legacy of Occupation: A Scarred Continent and Lasting Consequences:
The map of Europe during World War II serves as a powerful reminder of the horrors of war and the devastating impact of occupation. The war left a scarred continent, with its infrastructure destroyed, its economies shattered, and its societies deeply divided.
The legacy of occupation continues to shape Europe today. The trauma of war, the loss of life, and the enduring impact of Nazi ideology continue to be felt in the lives of individuals, communities, and nations.
FAQs:
1. What countries were occupied by Germany during World War II?
Germany occupied a vast swathe of Europe during World War II, including:
- Western Europe: France, Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg, Denmark, Norway
- Central Europe: Austria, Czechoslovakia, Poland, parts of Yugoslavia and Greece
- Eastern Europe: The Soviet Union (including Ukraine, Belarus, Baltic states), parts of Romania, Hungary, and Bulgaria
2. How did the German occupation affect the occupied countries?
The German occupation had a devastating impact on the occupied countries, resulting in:
- Economic devastation: Resources were plundered, industries were retooled for war production, and economies were crippled.
- Social disruption: Families were separated, communities were fractured, and traditional ways of life were disrupted.
- Cultural suppression: Local cultures were suppressed, languages were banned, and traditional values were undermined.
- Political oppression: Puppet governments were established, dissent was ruthlessly suppressed, and political freedom was extinguished.
- Genocide and persecution: Jews, Roma, and other "undesirable" groups were subjected to systematic persecution, deportation, and genocide.
3. What role did resistance movements play in the occupied countries?
Resistance movements played a crucial role in undermining German control and providing hope for liberation. They engaged in:
- Sabotage: Disrupting German infrastructure, supply lines, and military operations.
- Espionage: Gathering intelligence and providing information to Allied forces.
- Armed combat: Engaging in direct confrontations with German troops.
- Psychological warfare: Spreading propaganda, undermining morale, and fostering resistance among the population.
4. What were the long-term consequences of the German occupation?
The German occupation left a lasting legacy on the occupied countries, including:
- Physical and economic destruction: Infrastructure was destroyed, economies were crippled, and rebuilding efforts were extensive.
- Social and cultural divisions: Communities were fractured, traditions were disrupted, and trust between groups was eroded.
- Political instability: The war and occupation contributed to political instability and the rise of extremism.
- Psychological trauma: The experience of war, occupation, and persecution left a lasting psychological impact on individuals and societies.
- The Holocaust: The systematic extermination of Jews, Roma, and other groups during the war left an indelible mark on the conscience of humanity.
Tips:
- Use maps as visual tools: Studying maps of Europe during World War II can provide a powerful visual understanding of the scope of German occupation and the shifting borders of the conflict.
- Research individual countries: Each occupied country had a unique experience under German rule. Researching specific countries can provide deeper insights into the diverse impacts of occupation.
- Explore the role of resistance: Learn about the different resistance movements that emerged in occupied Europe, their strategies, and their impact on the war effort.
- Connect the past to the present: Reflect on the long-term consequences of the war and occupation, and their impact on the political, social, and cultural landscape of Europe today.
Conclusion:
The map of Europe during World War II is a stark reminder of the destructive power of war and the consequences of unchecked ambition. It reflects a period of immense suffering, loss, and resilience, and it serves as a powerful reminder of the need for peace, understanding, and international cooperation. Studying this map, with its shifting borders and territories, offers invaluable insight into the complexities of the war, its impact on the occupied countries, and the long-lasting consequences that reverberate even today. It is a reminder that history must be remembered, not only to honor those who suffered but also to ensure that such atrocities are never repeated.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Visual History of World War II German Occupation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!