The Geographic Tapestry Of Africa: Rivers, Countries, And A Continent In Flux
The Geographic Tapestry of Africa: Rivers, Countries, and a Continent in Flux
Related Articles: The Geographic Tapestry of Africa: Rivers, Countries, and a Continent in Flux
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Geographic Tapestry of Africa: Rivers, Countries, and a Continent in Flux. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Geographic Tapestry of Africa: Rivers, Countries, and a Continent in Flux

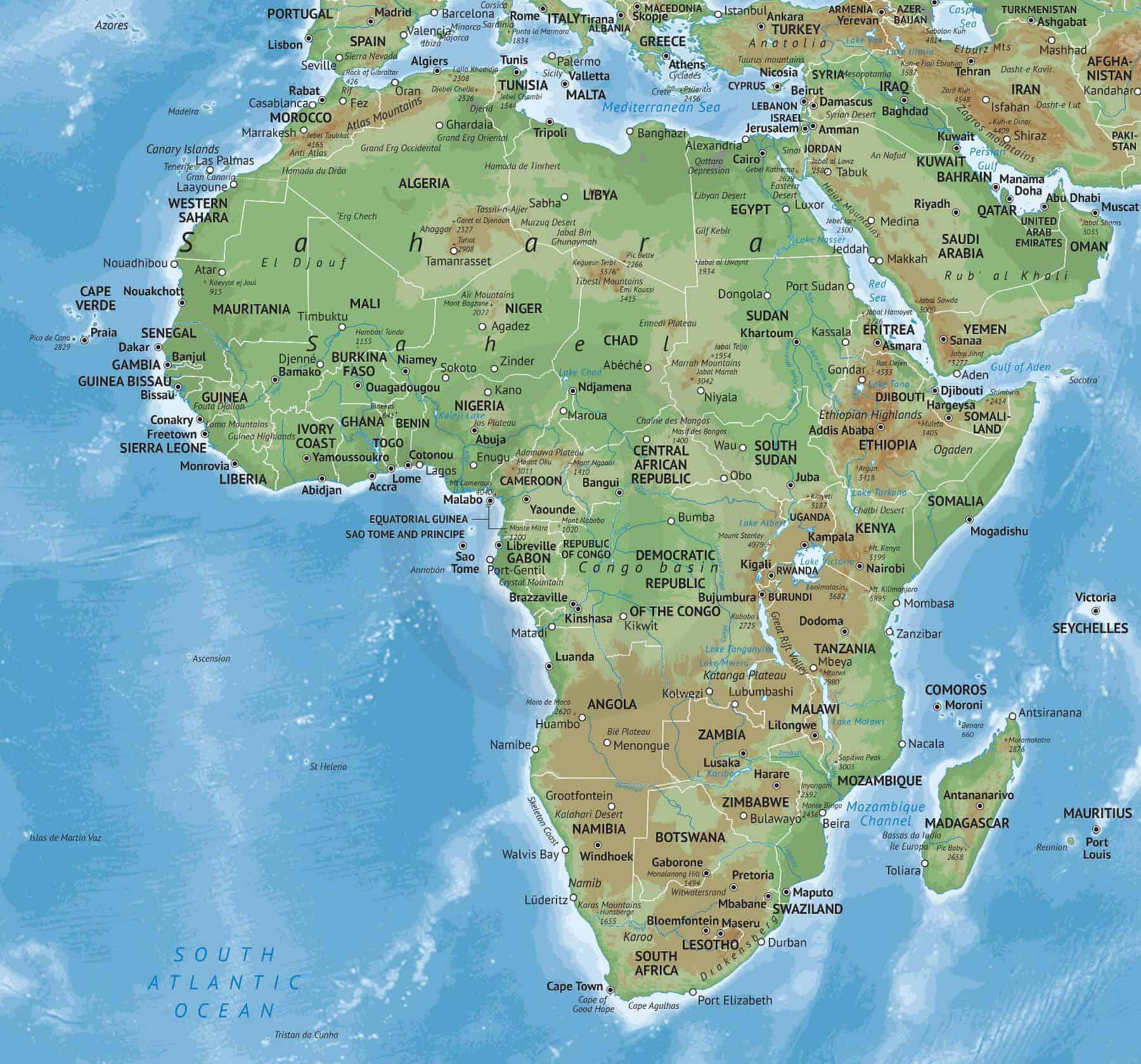
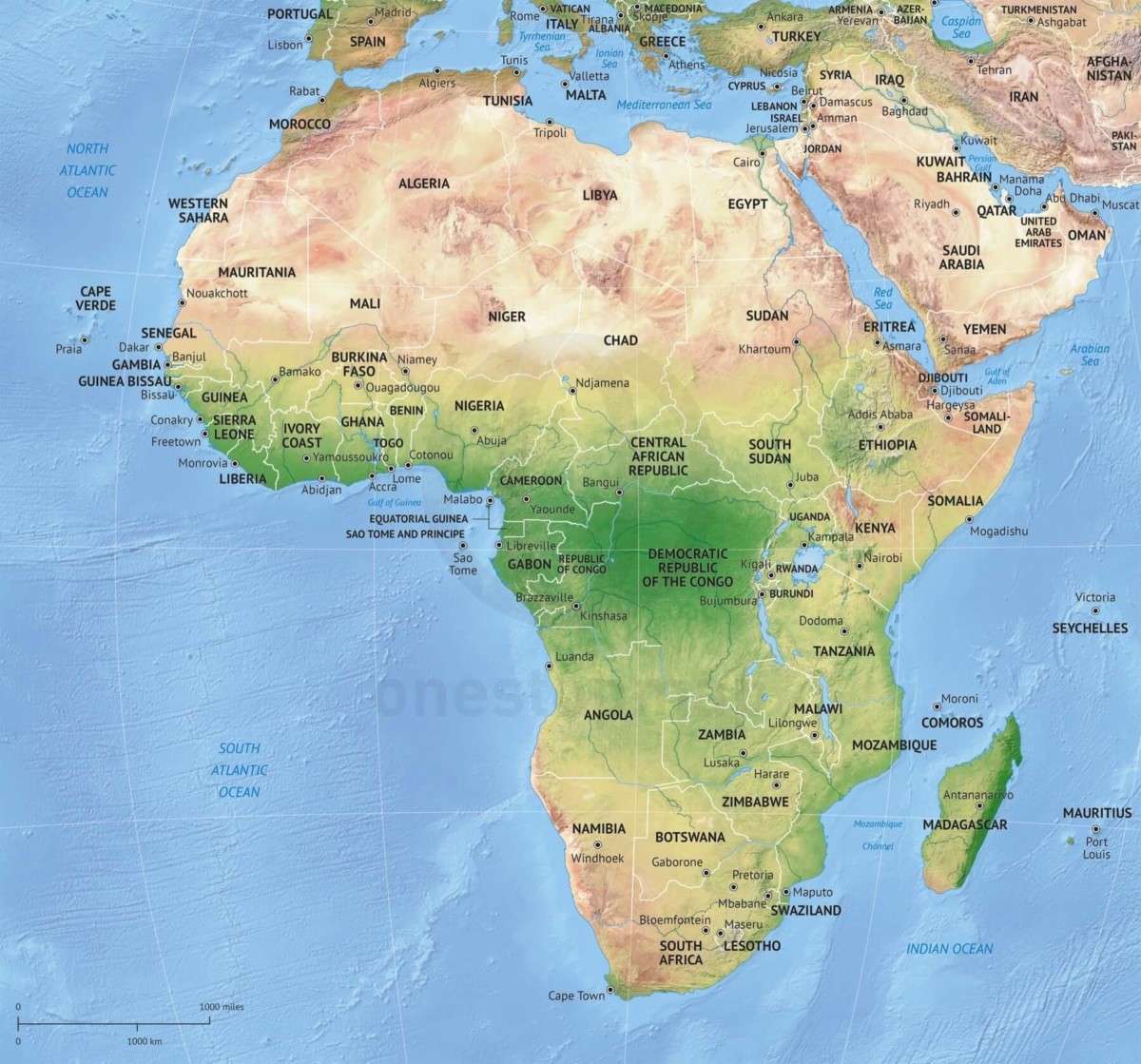
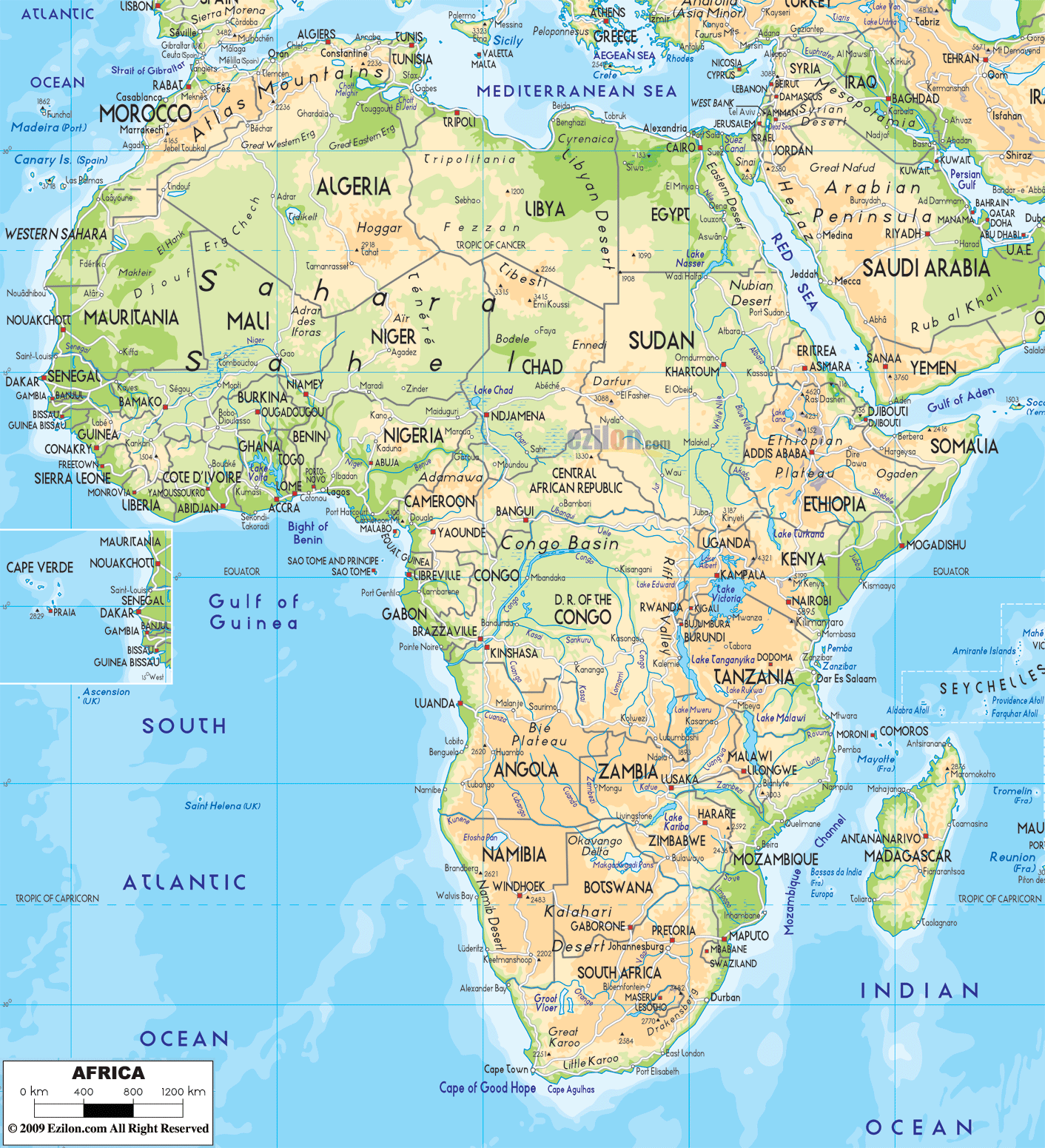
Africa, the second-largest continent on Earth, is a vast and diverse landmass characterized by its intricate network of rivers and its rich tapestry of nations. Understanding the geographical layout of Africa, its rivers, and its countries is essential for grasping the continent’s history, its present challenges, and its potential for the future.
A Continent Shaped by Rivers:
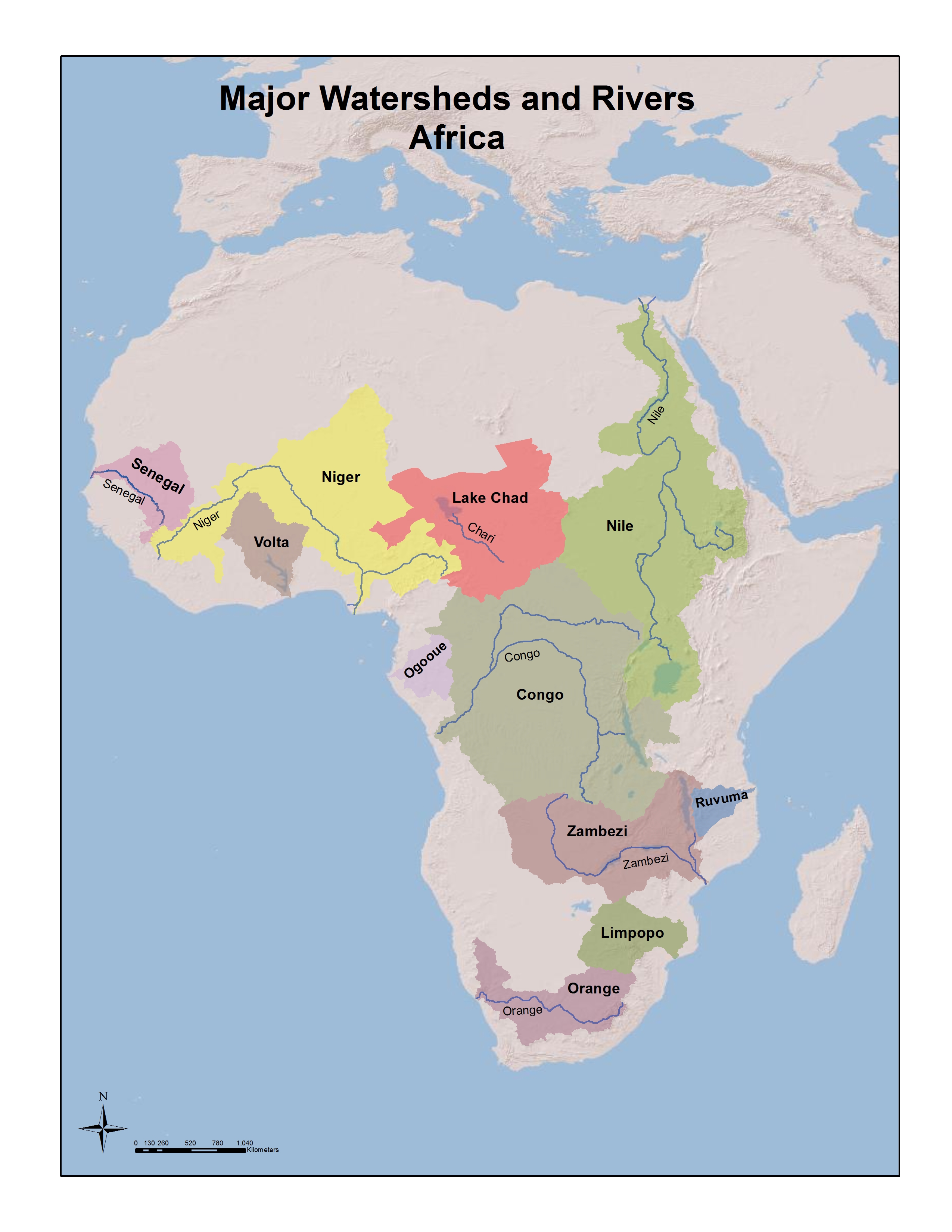
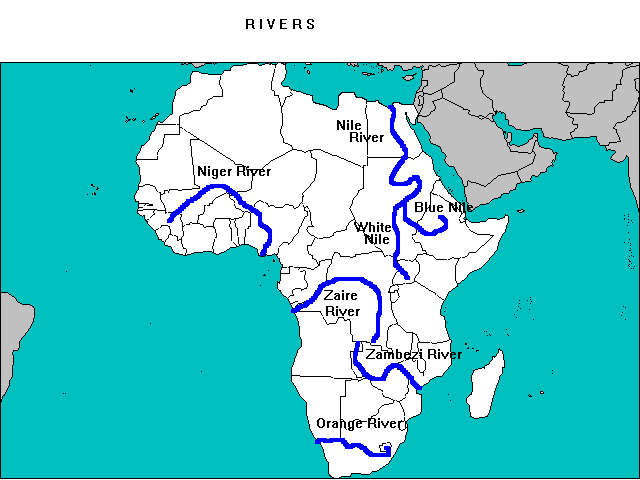
Africa’s rivers are not just geographical features; they are lifelines, arteries of trade, and sources of sustenance for millions. The continent boasts some of the world’s longest and most important rivers, each with its own unique characteristics and influence:
-
The Nile: The world’s longest river, the Nile, flows northwards from its sources in the heart of Africa, traversing eleven countries before emptying into the Mediterranean Sea. Its fertile banks have supported civilizations for millennia, and its waters are crucial for agriculture, transportation, and hydroelectric power generation in the region.
-
The Congo River: The second-largest river in Africa by volume, the Congo River is a powerful force, carving through dense rainforests and serving as a vital waterway for the Democratic Republic of Congo and surrounding nations. Its vast basin is home to a rich biodiversity and plays a crucial role in the global carbon cycle.
-
The Niger River: The Niger River, a major artery of West Africa, flows through eight countries, providing a vital source of irrigation, transportation, and fishing. Its delta is a rich ecosystem, supporting a diverse range of flora and fauna.
-
The Zambezi River: Known for its spectacular Victoria Falls, the Zambezi River flows through six countries in Southern Africa. It serves as a vital source of water for irrigation, hydroelectric power, and tourism.
-
The Orange River: The Orange River, the longest river in South Africa, flows westward through the arid landscape, providing a lifeline for agriculture and industry. Its unique ecosystems are home to diverse wildlife, including the critically endangered black rhinoceros.
The Mosaic of African Nations:
Africa’s diverse geography has shaped its political landscape, resulting in a continent of 54 sovereign nations, each with its own history, culture, and challenges. From the bustling megacities of North Africa to the vast savannas of the south, each country presents a unique story:
-
North Africa: Home to the Sahara Desert, the world’s largest hot desert, North Africa is a region of immense cultural and historical significance. Countries like Egypt, Morocco, and Algeria are known for their ancient civilizations, vibrant cultures, and bustling economies.
-
West Africa: A region characterized by its diverse landscapes, from the lush rainforests of the south to the arid Sahel in the north, West Africa is a cultural melting pot. Countries like Nigeria, Ghana, and Senegal are known for their vibrant music, art, and rich history.
-
Central Africa: Dominated by the Congo Basin, Central Africa is a region of immense biodiversity, boasting dense rainforests and vast savannas. Countries like the Democratic Republic of Congo, Gabon, and Cameroon are home to diverse ecosystems and unique cultures.
-
East Africa: Known for its iconic landscapes, including the Great Rift Valley and Mount Kilimanjaro, East Africa is a region of breathtaking beauty. Countries like Kenya, Tanzania, and Ethiopia are renowned for their wildlife, their vibrant cultures, and their growing economies.
-
Southern Africa: A region of diverse landscapes, from the arid Kalahari Desert to the lush Drakensberg Mountains, Southern Africa is home to a rich array of cultures and wildlife. Countries like South Africa, Botswana, and Namibia are known for their stunning natural beauty, their diverse wildlife, and their vibrant economies.
The Importance of Understanding the African Landscape:
Understanding the geographical layout of Africa, its rivers, and its countries is crucial for several reasons:
-
Resource Management: Africa’s rivers are vital for agriculture, transportation, and hydroelectric power generation. Understanding their flow patterns, water availability, and potential for development is crucial for managing these resources sustainably.
-
Environmental Conservation: Africa is home to a vast array of ecosystems, from rainforests to deserts. Understanding the continent’s geography and the interconnectedness of its ecosystems is essential for protecting biodiversity and mitigating the effects of climate change.
-
Economic Development: Africa’s rivers and natural resources offer significant economic potential. Understanding the continent’s geography and its resource distribution is crucial for promoting sustainable economic growth and development.
-
Political Stability: Africa’s diverse geography has played a significant role in shaping its political landscape. Understanding the continent’s history, its political structures, and its challenges is crucial for promoting peace, stability, and good governance.
-
Global Connections: Africa’s geography has a profound impact on global trade, climate patterns, and international relations. Understanding the continent’s geographical features is essential for fostering global cooperation and addressing shared challenges.
FAQs about the African Landscape:
Q: What are the main challenges facing Africa’s rivers?
A: Africa’s rivers face a range of challenges, including pollution, over-extraction, climate change, and dam construction. These challenges threaten the rivers’ ecological integrity, their ability to support human communities, and their role in the global ecosystem.
Q: What are the major environmental challenges facing Africa?
A: Africa faces a range of environmental challenges, including deforestation, desertification, climate change, and biodiversity loss. These challenges threaten the continent’s natural resources, its ability to support human populations, and its role in the global ecosystem.
Q: How is climate change affecting Africa?
A: Climate change is having a significant impact on Africa, leading to increased droughts, floods, and extreme weather events. These changes threaten the continent’s agriculture, water resources, and human health.
Q: What are the key factors driving economic growth in Africa?
A: Africa’s economic growth is driven by a range of factors, including population growth, urbanization, rising commodity prices, and increased investment in infrastructure and technology.
Q: What are the main challenges to economic development in Africa?
A: Africa faces a range of challenges to economic development, including poverty, inequality, corruption, conflict, and lack of infrastructure.
Tips for Understanding the African Landscape:
-
Use a detailed map: A detailed map of Africa, including its rivers and countries, is an invaluable tool for understanding the continent’s geography.
-
Explore online resources: Numerous online resources, including websites, databases, and interactive maps, provide detailed information about Africa’s geography, its rivers, and its countries.
-
Read books and articles: Books and articles about Africa’s geography, history, and culture provide valuable insights into the continent’s diverse landscapes and its unique challenges.
-
Engage with experts: Consult with experts on African geography, history, and development to gain a deeper understanding of the continent’s complexities.
Conclusion:
The African landscape is a complex and dynamic tapestry, shaped by its intricate network of rivers, its diverse cultures, and its unique challenges. Understanding this tapestry is crucial for addressing the continent’s challenges, harnessing its potential, and fostering a more sustainable and equitable future for all. Through continued exploration, research, and collaboration, we can deepen our understanding of Africa’s geography and its importance in shaping the global landscape.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Geographic Tapestry of Africa: Rivers, Countries, and a Continent in Flux. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!