The Evolution Of Representation: A Look At Washington State’s Congressional Districts
The Evolution of Representation: A Look at Washington State’s Congressional Districts
Related Articles: The Evolution of Representation: A Look at Washington State’s Congressional Districts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Evolution of Representation: A Look at Washington State’s Congressional Districts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Evolution of Representation: A Look at Washington State’s Congressional Districts
The United States Constitution mandates a decennial census, a process that not only counts the population but also shapes the political landscape. Following the census, states are tasked with redrawing their congressional districts, ensuring each district represents a roughly equal population. This process, known as redistricting, is crucial for maintaining fair and equitable representation in the House of Representatives.
Washington State, with its diverse geography and dynamic population, provides a compelling case study of the redistricting process. Examining the evolution of Washington’s congressional districts reveals the complex interplay of political, demographic, and legal factors that shape the way its citizens are represented at the federal level.
A Historical Perspective:
In the early 20th century, Washington State’s congressional districts were largely defined by geographic boundaries, with districts often encompassing vast and sparsely populated areas. As the state’s population grew, particularly in urban centers like Seattle and Spokane, the need for more equitable representation became apparent.
The 1960s brought significant changes to the redistricting process with the landmark Supreme Court case, Reynolds v. Sims (1964). This ruling established the principle of "one person, one vote," requiring districts to be drawn with roughly equal populations to ensure fair representation. This principle significantly impacted Washington’s redistricting efforts, leading to the creation of districts that more accurately reflected the state’s population distribution.
The 1990s and the Rise of Partisan Gerrymandering:
The 1990s saw the emergence of partisan gerrymandering, a practice where political parties manipulate district boundaries to favor their candidates and consolidate their power. This practice, while not explicitly illegal, has been the subject of intense scrutiny and legal challenges.
Washington State, like many other states, experienced the effects of partisan gerrymandering. In the 1990s, the Republican-controlled legislature drew districts that favored their party, leading to accusations of unfair representation. This led to a series of legal challenges and ultimately to the establishment of the Washington State Redistricting Commission in 2000.
The Washington State Redistricting Commission: A Model for Independent Redistricting:
The Washington State Redistricting Commission is a non-partisan body composed of four members, two from each major political party, and a fifth member selected by the four commissioners. This commission is responsible for drawing the state’s congressional and legislative districts, ensuring the process is transparent and fair.
The commission’s creation marked a significant shift in Washington’s redistricting process, moving away from partisan control and towards a more independent and objective system. The commission’s work has been praised for its commitment to transparency, public engagement, and adherence to legal and ethical standards.
The 2020 Redistricting Cycle:
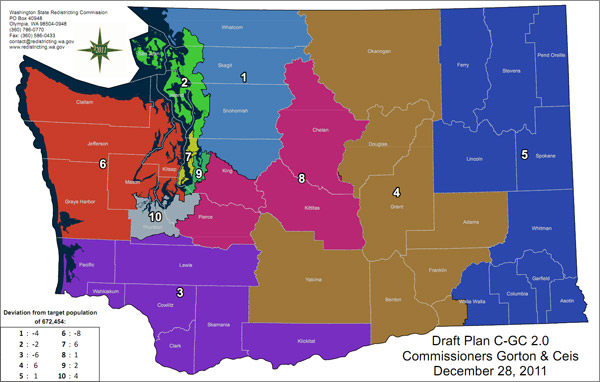
The 2020 census data triggered another round of redistricting in Washington State. The commission, guided by the "one person, one vote" principle and other legal requirements, engaged in a rigorous process of data analysis, public hearings, and community outreach to draw new district boundaries.
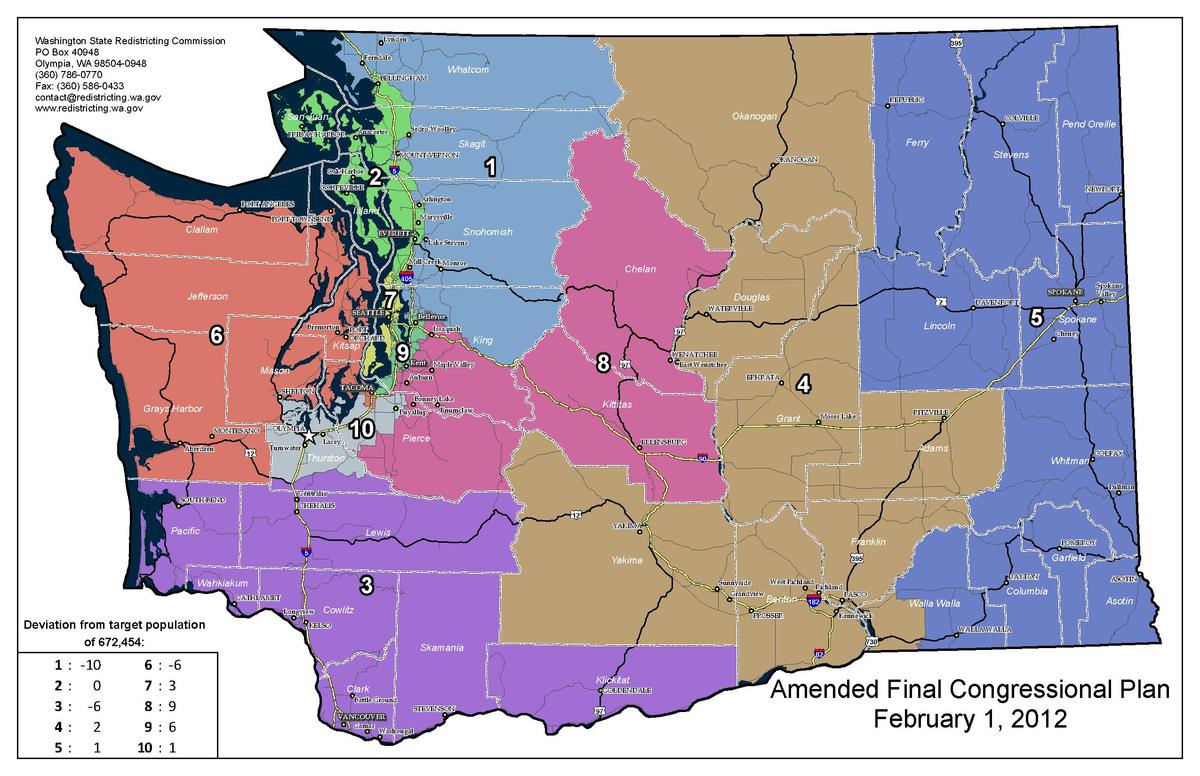
The 2020 redistricting cycle saw the creation of ten congressional districts, reflecting the state’s growing population. The commission’s work resulted in districts that were largely considered fair and representative, with minimal partisan bias.
The Importance of Redistricting:
The redistricting process is crucial for maintaining a democratic society. Fair and equitable districts ensure that all citizens have an equal voice in government and that their interests are adequately represented. Redistricting also plays a critical role in:
- Promoting Equal Representation: By ensuring that each district represents a roughly equal population, redistricting promotes fair representation and prevents one group from having an undue advantage over others.
- Maintaining Democratic Accountability: Redistricting helps hold elected officials accountable to their constituents by ensuring that they are representing a diverse range of interests and perspectives.
- Encouraging Political Competition: Fair districts can foster political competition, as candidates from different parties have a more equal chance of winning elections.
- Preserving Community Interests: Redistricting can be used to preserve communities of interest by drawing district boundaries that reflect shared values and concerns.
FAQs about Washington State’s Congressional Districts:
Q: How many congressional districts are there in Washington State?
A: Washington State currently has ten congressional districts.
Q: What are the criteria used to draw congressional districts?
A: The Washington State Redistricting Commission uses various criteria to draw congressional districts, including:
- Equal population: Each district must have approximately the same population.
- Contiguity: All parts of a district must be connected.
- Compactness: Districts should be drawn in a way that minimizes their overall area.
- Respect for communities of interest: Districts should avoid dividing communities with shared interests.
- Minority representation: Districts should be drawn in a way that allows for adequate representation of minority groups.
Q: How can I get involved in the redistricting process?
A: The Washington State Redistricting Commission actively encourages public participation in the redistricting process. You can engage in the following ways:
- Attend public hearings: The commission holds public hearings throughout the state to gather input from residents.
- Submit written comments: You can submit written comments to the commission on the proposed district maps.
- Use online mapping tools: The commission provides online mapping tools that allow you to explore proposed district boundaries and provide feedback.
Tips for Understanding Washington State’s Congressional Districts:
- Familiarize yourself with the Redistricting Commission: The commission’s website provides comprehensive information on the redistricting process, including maps, data, and public hearings schedules.
- Pay attention to the news: Stay informed about the redistricting process by following news coverage and engaging in public discourse.
- Get involved in your community: Join local organizations and engage in discussions about the importance of fair representation and redistricting.
Conclusion:
Washington State’s congressional districts have evolved significantly over time, reflecting the state’s changing demographics and political landscape. The establishment of the Redistricting Commission has been a major step forward in ensuring a more transparent and independent redistricting process. While challenges remain, the commission’s commitment to fairness and representation provides a model for other states seeking to improve their redistricting processes. By understanding the importance of redistricting and engaging in the process, citizens can play a vital role in ensuring that their voices are heard and their interests are represented at the federal level.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Evolution of Representation: A Look at Washington State’s Congressional Districts. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
_Congressional_Districts%2C_113th_Congress.tif)