Navigating Washington: A Comprehensive Look At The State’s Freeway Network
Navigating Washington: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Freeway Network
Related Articles: Navigating Washington: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Freeway Network
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Washington: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Freeway Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Washington: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Freeway Network
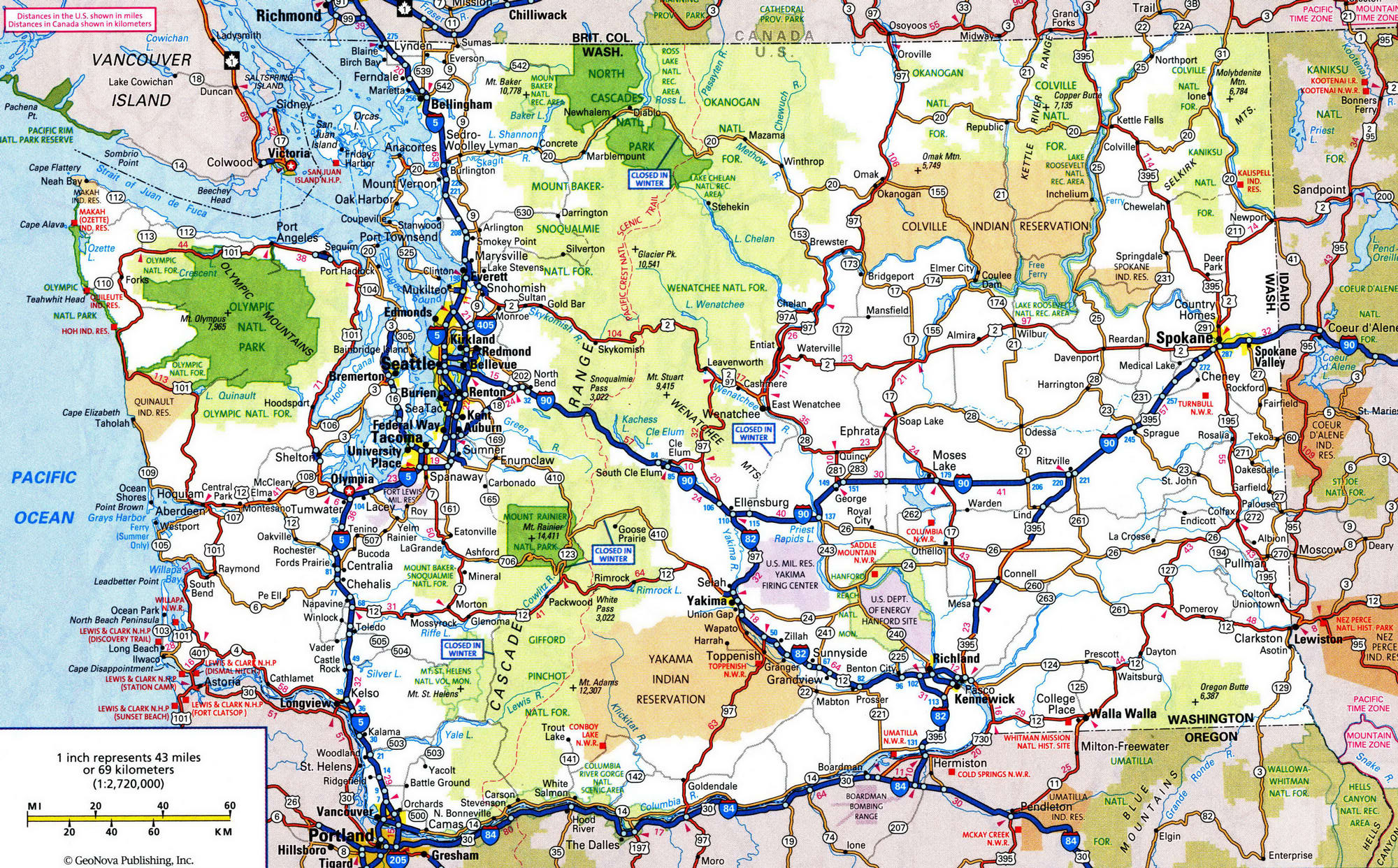
Washington state’s intricate network of freeways, stretching across diverse landscapes from the rugged Cascade Mountains to the sprawling Puget Sound, plays a vital role in the state’s economic and social fabric. Understanding this complex system is crucial for navigating the state efficiently and appreciating its impact on daily life.
A Detailed Look at the Freeway System:
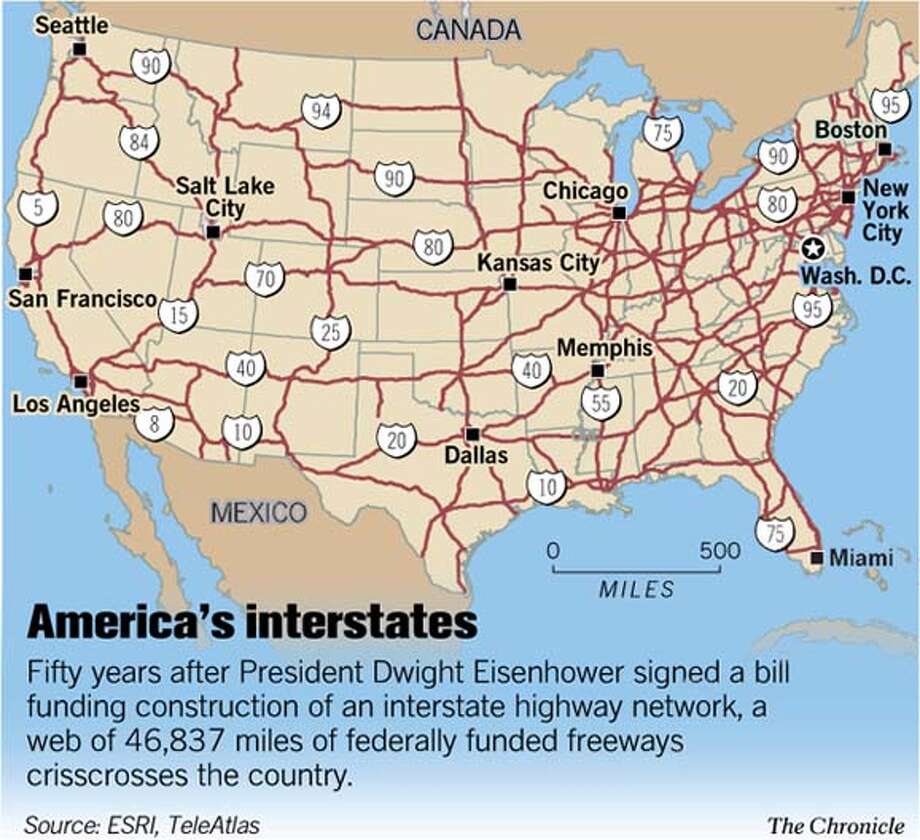
The state’s freeway network is a tapestry woven from Interstate Highways, State Routes, and locally-maintained roads. This interconnected system facilitates the movement of people, goods, and services across the state, connecting urban centers, rural communities, and key economic hubs.
Interstate Highways:
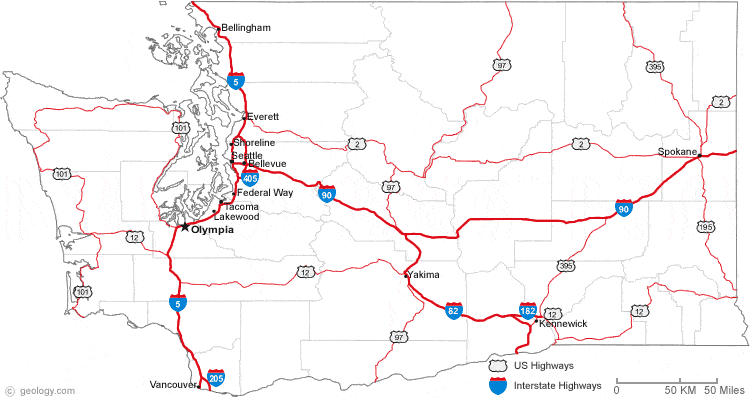
- Interstate 5 (I-5): The backbone of the state, I-5 traverses Washington from north to south, connecting the Canadian border with the Oregon border. It serves as the primary north-south artery, linking major cities like Seattle, Tacoma, Olympia, and Vancouver, Washington.
- Interstate 90 (I-90): This east-west corridor connects Seattle to the eastern part of the state, crossing the Cascade Mountains via Snoqualmie Pass. It links Seattle to Spokane, the state’s second-largest city, and provides access to the Columbia River Gorge and the Eastern Washington wheat fields.
- Interstate 82 (I-82): This highway runs east-west across central Washington, connecting the Tri-Cities region to the Yakima Valley and ultimately linking to I-90 in the eastern part of the state.
- Interstate 405 (I-405): A major loop around Seattle, I-405 provides a vital connection between the city’s northern and southern suburbs, easing congestion on I-5.
- Interstate 905 (I-905): This short spur connects I-5 to the Port of Tacoma, facilitating the movement of goods and cargo within the region.
State Routes:
- State Route 16 (SR 16): This highway connects Seattle to the Olympic Peninsula, offering scenic views and access to the Olympic National Park.
- State Route 520 (SR 520): This floating bridge crosses Lake Washington, connecting Seattle to the eastern suburbs and providing a crucial link for commuters.
- State Route 509 (SR 509): This highway runs north-south through the Puget Sound region, connecting Tacoma to Seattle and providing an alternative to I-5.
- State Route 167 (SR 167): This highway runs south from Seattle, connecting to I-5 near Tacoma and providing a critical link for commuters and freight traffic.
- State Route 18 (SR 18): This highway connects I-90 to the Snoqualmie Pass, offering a scenic route to the eastern part of the state.
Local Freeways:
- State Route 500 (SR 500): Known as the "Tacoma Freeway," SR 500 connects the Port of Tacoma to the city’s downtown area.
- State Route 522 (SR 522): This scenic highway runs through the foothills of the Cascade Mountains, connecting I-405 to the city of Snohomish.
- State Route 163 (SR 163): This highway connects I-5 to the University of Washington campus and the Seattle Center.
Benefits of the Freeway Network:
- Economic Development: Freeways facilitate the efficient movement of goods and services, supporting industries like manufacturing, agriculture, and tourism. They connect businesses to markets and resources, fostering economic growth and job creation.
- Improved Connectivity: Freeways connect urban centers, rural communities, and key economic hubs, fostering social and cultural exchange. They facilitate access to education, healthcare, and other essential services.
- Tourism and Recreation: Freeways provide access to scenic landscapes, national parks, and recreational areas, attracting tourists and supporting the state’s tourism industry.
- Emergency Response: Freeways play a crucial role in emergency response, facilitating the rapid movement of emergency vehicles and supplies during disasters.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Traffic Congestion: The growing population and increasing reliance on personal vehicles lead to traffic congestion, particularly in urban areas.
- Environmental Impact: Freeway construction and maintenance can impact natural habitats, water quality, and air quality.
- Infrastructure Maintenance: Maintaining a vast network of freeways requires significant investment, posing challenges for state and local governments.
Navigating the Freeway System:
- Traffic Information: Utilize real-time traffic information provided by sources like the Washington State Department of Transportation (WSDOT) website and mobile apps.
- Route Planning: Use online mapping services like Google Maps or Waze to plan your route and avoid congestion.
- Road Conditions: Be aware of road conditions, especially during inclement weather. Check WSDOT’s website or mobile apps for updates.
- Safety First: Follow traffic laws, drive defensively, and be aware of your surroundings.
Conclusion:
Washington’s freeway network is a complex and vital system that plays a critical role in the state’s economy, social fabric, and overall quality of life. Understanding the network’s intricacies and navigating it safely and efficiently is essential for residents, businesses, and visitors alike. By recognizing its importance, embracing its benefits, and addressing its challenges, Washington can continue to develop and maintain a robust and reliable freeway system for the future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Washington: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Freeway Network. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!