Navigating The World: Understanding The Dynamics Of Moving Countries
Navigating the World: Understanding the Dynamics of Moving Countries
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding the Dynamics of Moving Countries
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding the Dynamics of Moving Countries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding the Dynamics of Moving Countries
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the World: Understanding the Dynamics of Moving Countries
- 3.1 The Global Migration Map: A Visual Representation of Movement
- 3.2 The Benefits of Moving Countries: A Multifaceted Perspective
- 3.3 The Challenges of Moving Countries: Navigating a New Landscape
- 3.4 The Impact of Moving Countries: A Ripple Effect Across Borders
- 3.5 Moving Countries on a Map: A Framework for Understanding Migration
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.7 Tips for Moving Countries
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the World: Understanding the Dynamics of Moving Countries

The act of migrating across borders is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon, driven by a confluence of factors, including economic opportunity, political instability, familial ties, and personal aspirations. In the 21st century, with globalization accelerating and communication technologies bridging geographical divides, the movement of people across national boundaries has become increasingly prevalent. This article explores the dynamics of moving countries, examining its impact on individuals, societies, and the global landscape.
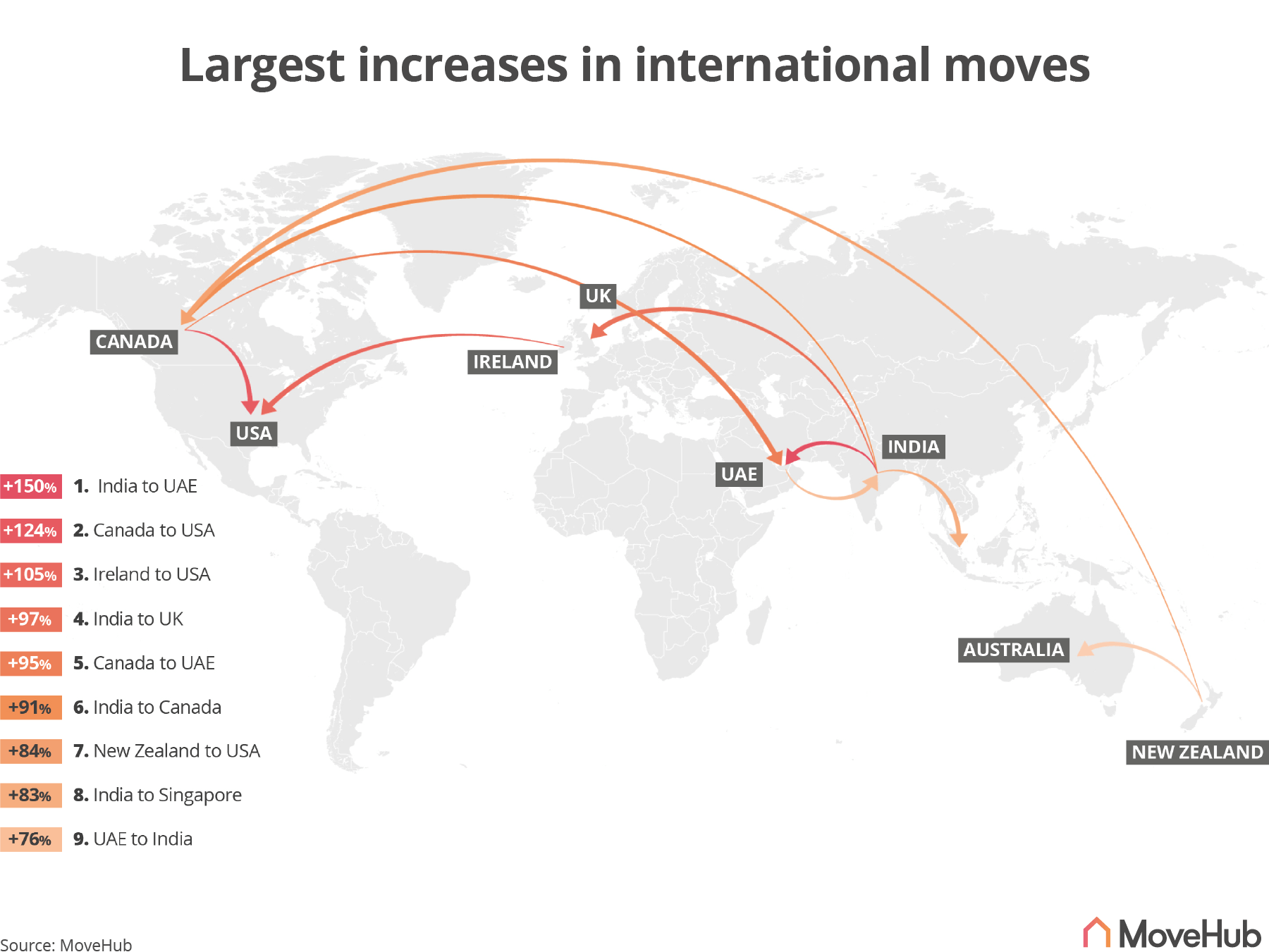
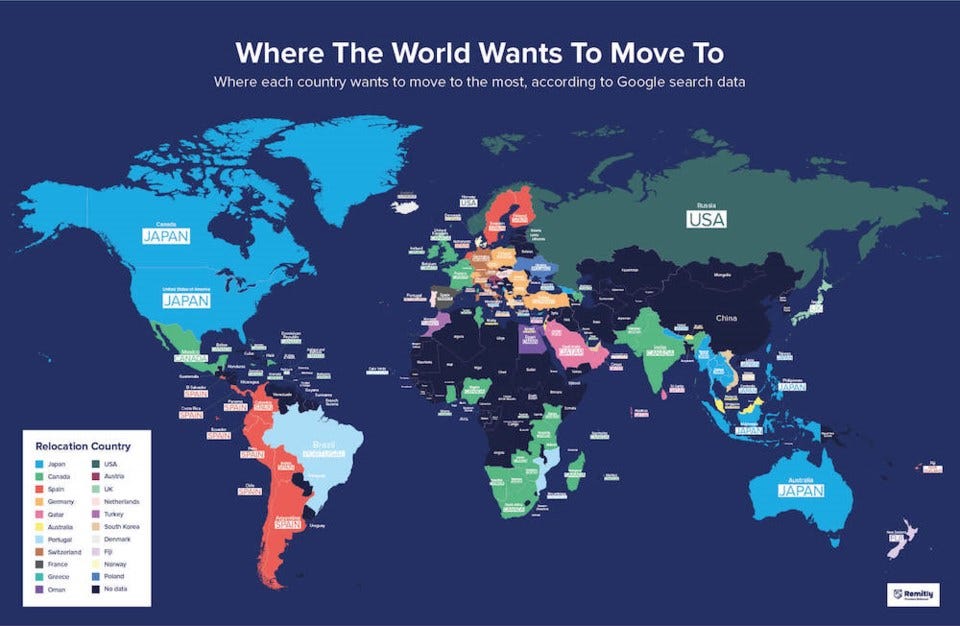
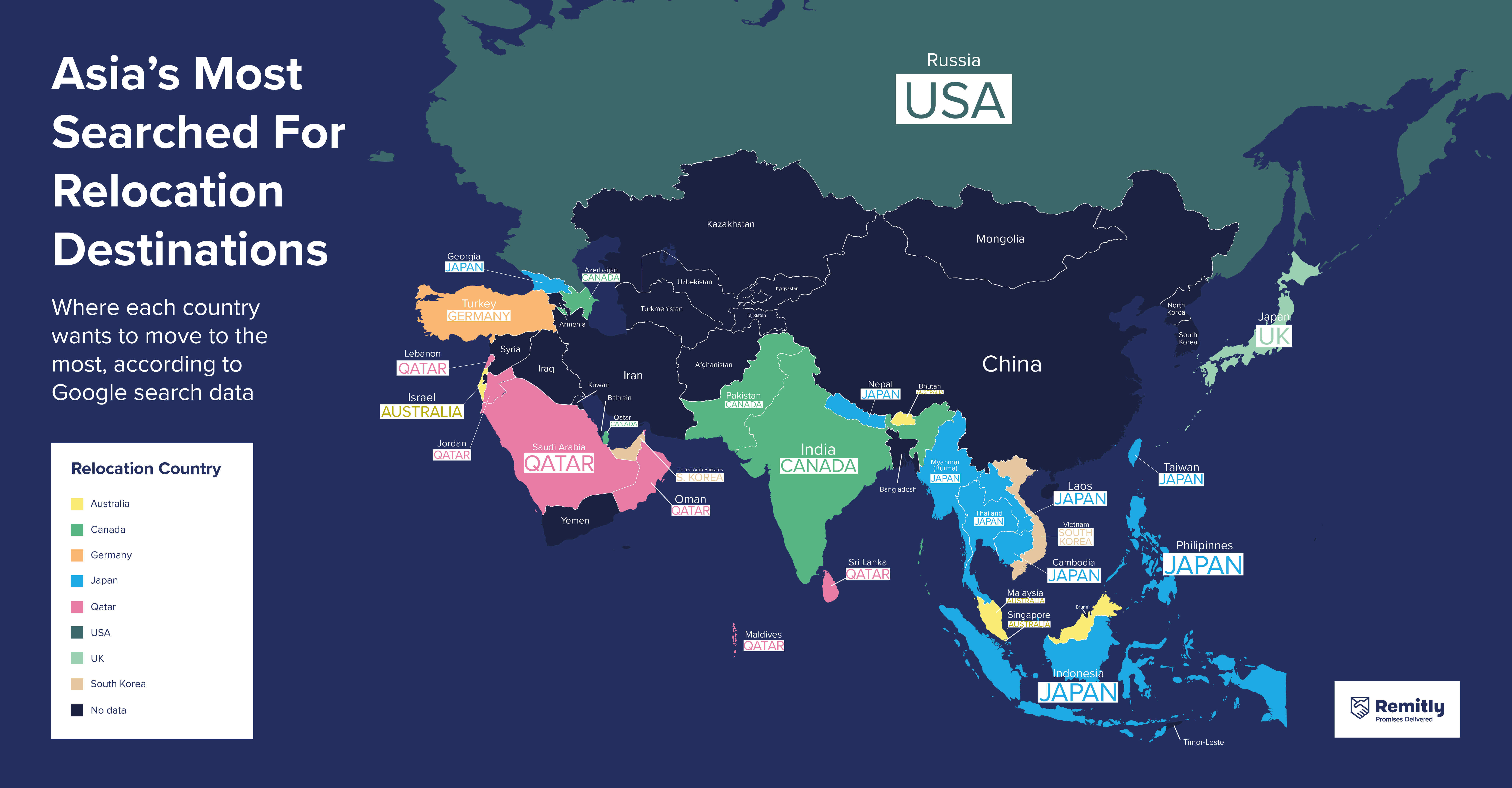
The Global Migration Map: A Visual Representation of Movement
To comprehend the scale and intricacies of international migration, visualizing it through maps becomes essential. Migration maps, whether static or dynamic, offer a powerful tool for understanding the patterns, flows, and trends of human movement across the globe.
Types of Migration Maps:
- Flow Maps: These maps depict the movement of people from one location to another using arrows of varying thickness to indicate the volume of migration. They provide a clear visual representation of the major migration corridors and their relative strength.
- Choropleth Maps: These maps use different shades or colors to represent the density of migrants in specific regions. They are particularly useful for visualizing the distribution of migrants within countries or across continents.
- Cartograms: These maps distort the size of countries or regions based on their migration volume. This allows for a visual comparison of the relative importance of different locations in the global migration landscape.
Interpreting Migration Maps:
Migration maps are not merely visual representations but offer valuable insights into the factors driving human movement. By analyzing the patterns on these maps, researchers and policymakers can identify:
- Push Factors: Economic hardship, political persecution, environmental degradation, and natural disasters are examples of factors that push people to leave their home countries.
- Pull Factors: Economic opportunities, political freedom, better living conditions, and family reunification are examples of factors that attract people to specific destinations.
- Migration Corridors: These are established routes of migration between specific countries or regions, often reflecting historical, cultural, or economic connections.
- Migration Networks: These refer to the interconnected relationships between migrants, often forming social and economic support systems in their new destinations.
The Benefits of Moving Countries: A Multifaceted Perspective
While the decision to move countries is a deeply personal one, it often stems from a desire for a better life or a pursuit of new opportunities. The benefits of moving countries can be categorized into several key areas:
Economic Opportunities:
- Higher Wages and Job Prospects: Moving to countries with stronger economies or specialized industries can lead to higher earning potential and access to a wider range of job opportunities.
- Entrepreneurial Ventures: Migration can provide a platform for individuals to start their own businesses or expand existing ones in new markets, fostering economic growth and innovation.
- Access to Education and Training: Moving to countries with advanced education systems can provide individuals with access to higher education and professional training, enhancing their skills and career prospects.
Social and Cultural Enrichment:
- Exposure to Diverse Cultures: Living in a new country offers a chance to experience different cultures, traditions, and perspectives, broadening one’s horizons and fostering intercultural understanding.
- Personal Growth and Development: Adapting to a new environment and learning a new language can be challenging but rewarding, promoting personal growth and resilience.
- Building New Relationships and Networks: Moving to a new country provides opportunities to build new relationships and networks, fostering social connections and support systems.
Political and Personal Freedom:
- Escape from Oppression or Conflict: Migration can offer a safe haven for individuals fleeing political persecution, conflict, or human rights violations.
- Access to Democracy and Freedoms: Moving to countries with democratic institutions and robust legal systems can provide individuals with greater political and personal freedoms.
- Improved Quality of Life: Moving to countries with higher standards of living can lead to improved access to healthcare, education, and other essential services, enhancing overall quality of life.
The Challenges of Moving Countries: Navigating a New Landscape
While the potential benefits of moving countries are significant, it is crucial to acknowledge the challenges that migrants often face:
Cultural Adjustment:
- Language Barriers: Communicating effectively in a new language can be a major hurdle, impacting daily interactions, employment opportunities, and social integration.
- Cultural Differences: Adapting to new social norms, customs, and values can be challenging and require a willingness to learn and adjust.
- Homesickness and Isolation: Feeling disconnected from family, friends, and familiar surroundings can lead to homesickness and social isolation, impacting mental well-being.
Legal and Administrative Hurdles:
- Immigration Procedures: Navigating complex immigration processes, including visa applications, residency permits, and citizenship requirements, can be time-consuming and stressful.
- Legal Compliance: Understanding and adhering to the laws and regulations of the new country is crucial to avoid legal complications and ensure a smooth transition.
- Discrimination and Prejudice: Migrants may face discrimination and prejudice based on their nationality, ethnicity, or religion, impacting their access to opportunities and social acceptance.
Economic Challenges:
- Job Market Competition: Finding employment in a new country can be challenging, especially in competitive job markets with limited opportunities for foreign nationals.
- Financial Constraints: Adjusting to a new currency, managing finances, and securing affordable housing can pose significant financial challenges, especially during the initial stages of migration.
- Lack of Social Safety Nets: Migrants may not have access to the same social safety nets, such as unemployment benefits or healthcare coverage, as citizens of the host country.
The Impact of Moving Countries: A Ripple Effect Across Borders
The movement of people across borders has profound implications for both sending and receiving countries, shaping economic, social, and political landscapes.
Impact on Sending Countries:
- Brain Drain: The emigration of highly skilled professionals, known as brain drain, can deplete sending countries of essential human capital, hindering economic development and progress.
- Remittances: Migrants often send money back to their families in their home countries, contributing significantly to the economies of sending nations and improving living standards.
- Social and Cultural Transformation: The departure of significant portions of the population can impact social structures, cultural traditions, and demographic trends in sending countries.
Impact on Receiving Countries:
- Economic Growth and Innovation: Migrants bring new skills, perspectives, and entrepreneurial spirit, contributing to economic growth and innovation in receiving countries.
- Demographic Change: Immigration can alter the demographic composition of receiving countries, impacting social services, cultural identities, and political landscapes.
- Social Integration Challenges: Integrating migrants into society can be challenging, requiring effective policies and programs to address language barriers, cultural differences, and potential tensions.
Moving Countries on a Map: A Framework for Understanding Migration
By analyzing migration maps and understanding the factors that drive and influence human movement, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of moving countries. This knowledge is essential for:
- Policymakers: To develop effective policies that address the challenges and opportunities presented by migration, ensuring a fair and equitable treatment of migrants and contributing to sustainable development.
- Researchers: To conduct comprehensive research on migration patterns, trends, and impacts, providing valuable insights for policymakers and the public.
- Individuals: To make informed decisions about moving countries, understanding the potential benefits and challenges, and preparing for a smooth transition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the most common reasons for moving countries?
A: The most common reasons for moving countries include economic opportunities, political stability, family reunification, and education.
Q: What are the main challenges faced by migrants?
A: Migrants often face challenges related to cultural adjustment, language barriers, legal and administrative hurdles, economic constraints, and discrimination.
Q: How can countries better manage migration?
A: Countries can better manage migration by implementing effective policies that address the needs of both migrants and host communities, fostering social inclusion, promoting economic opportunities, and ensuring the protection of human rights.
Q: What are the ethical considerations surrounding migration?
A: Ethical considerations surrounding migration include ensuring the protection of human rights, preventing exploitation and trafficking, promoting fair and equitable treatment, and fostering intercultural understanding.
Tips for Moving Countries
- Thorough Research: Conduct comprehensive research on the destination country, including its laws, culture, cost of living, and job market.
- Visa and Immigration Procedures: Understand and comply with all visa and immigration requirements, including application deadlines, documentation, and fees.
- Language Learning: Invest in language learning resources and practice your skills to facilitate communication and integration.
- Financial Planning: Secure adequate finances to cover initial expenses, including travel, accommodation, and living costs.
- Cultural Awareness: Be open to learning about the new culture and adapt your behaviors and customs accordingly.
- Build Social Networks: Connect with other migrants and local residents to build a support system and facilitate social integration.
Conclusion
Moving countries is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that impacts individuals, societies, and the global landscape. By understanding the factors that drive migration, the benefits and challenges it presents, and its broader implications, we can foster a more informed and compassionate approach to this crucial aspect of human experience. Migration maps provide a powerful visual tool for navigating the complexities of human movement, offering insights into the patterns, trends, and motivations behind the decision to move across borders. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, understanding the dynamics of moving countries is essential for building a more just, equitable, and inclusive global society.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding the Dynamics of Moving Countries. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!