Navigating The World: Understanding The Compass On A Map
Navigating the World: Understanding the Compass on a Map
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding the Compass on a Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding the Compass on a Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Understanding the Compass on a Map

Maps are essential tools for understanding and exploring our world. They provide a visual representation of landscapes, cities, and geographical features, allowing us to plan journeys and comprehend spatial relationships. However, to truly utilize a map effectively, one must understand the role of the compass, a crucial element that bridges the gap between the two-dimensional map and the three-dimensional world.
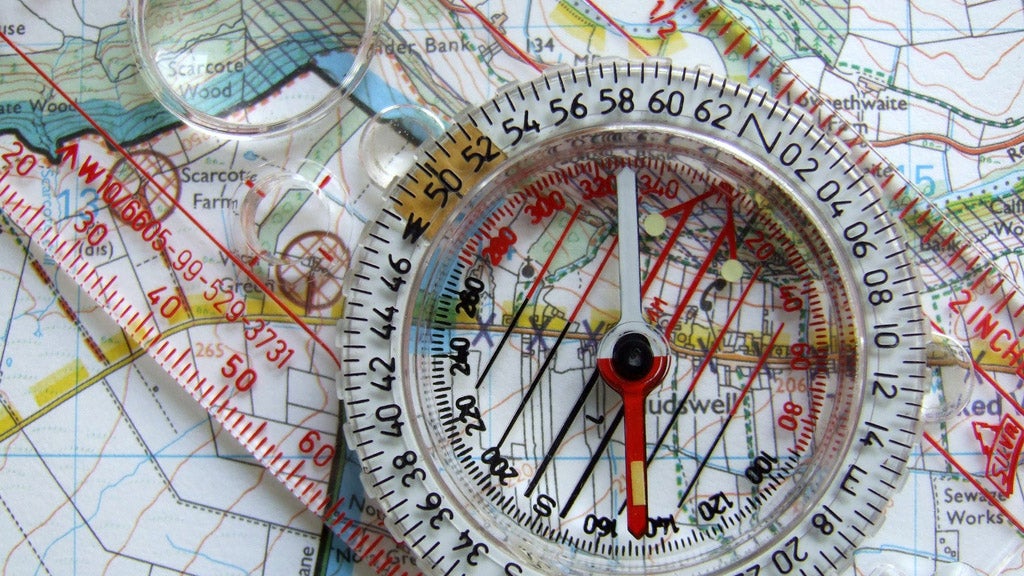
The compass, with its magnetic needle pointing towards north, serves as a vital reference point on a map. It establishes a fixed direction, enabling users to orient themselves and determine the location of various points relative to their current position.
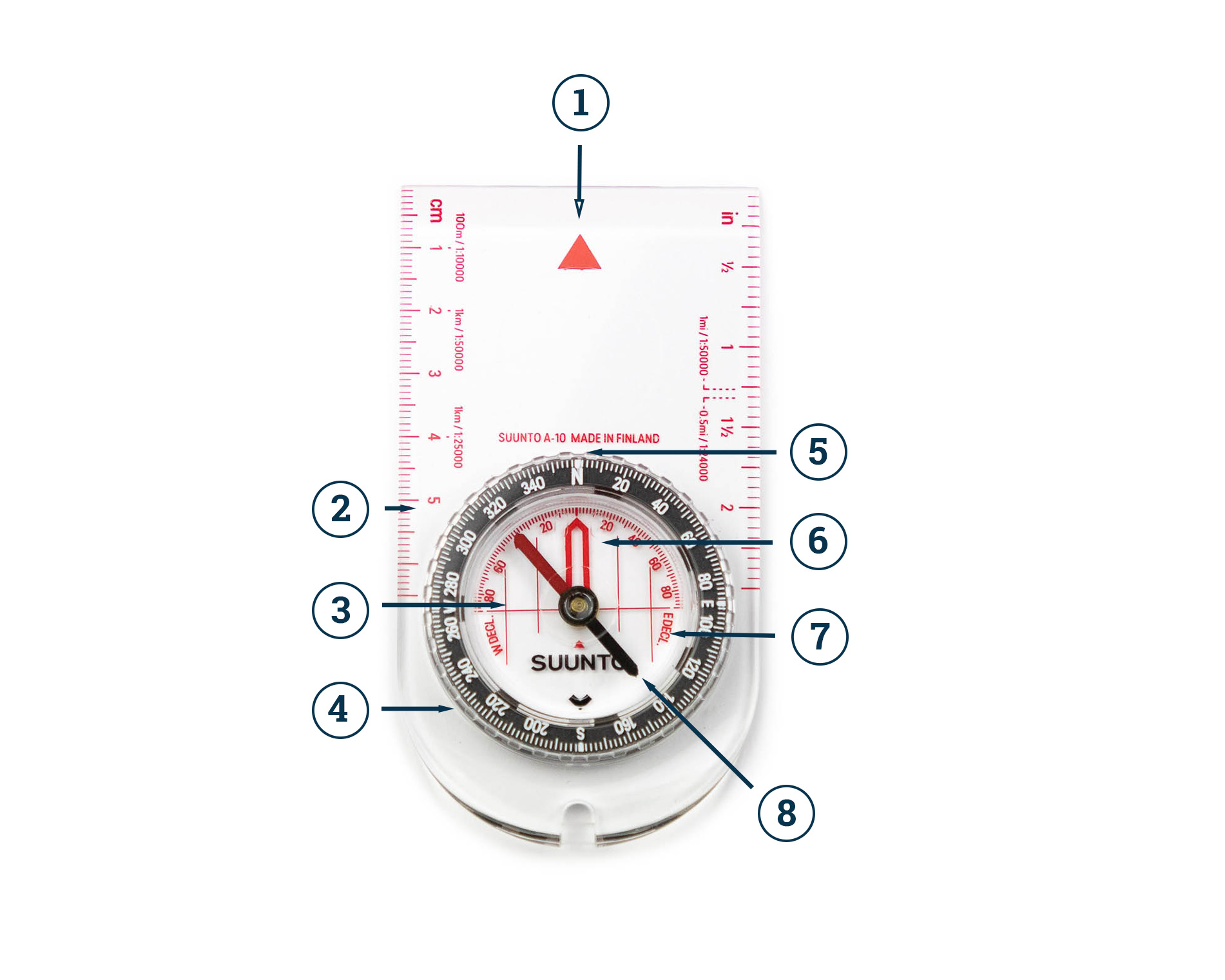
The Compass and Its Components:
A compass typically consists of a magnetized needle that freely rotates within a casing. The needle aligns itself with the Earth’s magnetic field, indicating magnetic north. The casing often features a circular dial marked with cardinal directions (North, South, East, and West) and sometimes intermediate directions (Northeast, Southeast, Southwest, and Northwest).
Using the Compass with a Map:
- Orientation: Begin by aligning the compass with the map. Ensure the compass needle is pointing towards magnetic north, which is often indicated on the map’s margin.
- Determining Direction: Identify the desired location on the map and draw a line from your current position to that point. This line represents the direction you need to travel.
- Following the Bearing: Align the compass with the line you drew. The compass needle will now point towards your desired location, providing the bearing (the angle between north and your destination).
- Navigation: Use the compass to maintain this bearing as you move. Regularly check your position on the map and adjust your course as needed.
Types of Compasses:
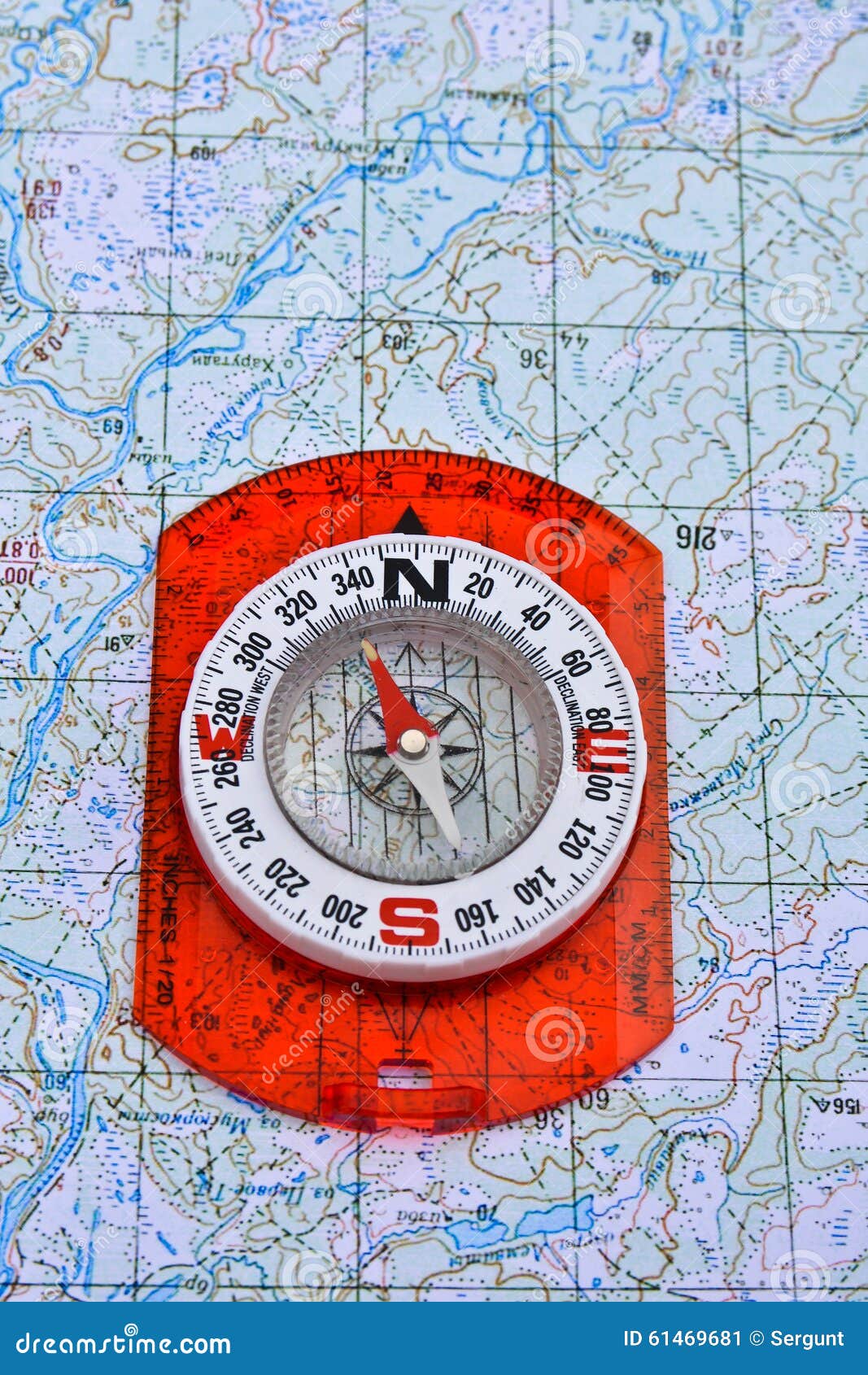
- Traditional Compass: This type features a liquid-filled casing and a needle that rotates freely, offering accurate readings.
- Baseplate Compass: This compass is mounted on a baseplate, often with a ruler and protractor, facilitating precise measurement and bearing determination.
- Lensatic Compass: This compact compass utilizes a lens to magnify the needle, improving visibility in low-light conditions.
Benefits of Using a Compass:
- Accurate Direction: The compass provides a reliable and precise method for determining direction, ensuring you stay on course.
- Independence from External Factors: Unlike GPS, which relies on satellite signals, a compass operates independently, making it a valuable tool in areas with limited or no signal reception.
- Enhanced Safety: By accurately determining direction and maintaining a bearing, a compass helps prevent getting lost and enhances safety in unfamiliar environments.
- Increased Exploration: Using a compass allows you to explore beyond familiar paths, venturing into unknown territories with confidence.
Understanding Magnetic Declination:
Magnetic north, the direction indicated by a compass, is not the same as true north, which is the geographical north pole. The difference between these two points is known as magnetic declination. This variation is influenced by the Earth’s magnetic field and changes geographically.
Maps often include a declination diagram or value, allowing users to adjust their compass readings to account for this difference and obtain accurate bearings.
FAQs about Using a Compass with a Map:
Q: What is magnetic declination, and why is it important?
A: Magnetic declination is the difference between magnetic north (the direction indicated by a compass) and true north (the geographical north pole). It is crucial to consider declination when using a compass with a map because it ensures accurate bearing determination. Maps often include declination information to enable users to adjust their compass readings accordingly.
Q: How do I find the magnetic declination for my location?
A: Magnetic declination varies geographically and over time. You can find declination information for your location using online resources like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) website or by consulting a map that includes a declination diagram or value.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when using a compass?
A: Common mistakes include:
- Not properly orienting the compass with the map.
- Ignoring magnetic declination.
- Misreading the compass needle or bearing.
- Failing to check the compass regularly during navigation.
Tips for Using a Compass with a Map:
- Practice using the compass in familiar areas before venturing into unfamiliar terrain.
- Always double-check your bearings and map readings.
- Carry a spare compass in case of malfunction.
- Consider using a compass with a built-in clinometer to determine elevation changes.
- Consult experienced navigators or take a compass navigation course to enhance your skills.
Conclusion:
The compass, when used effectively with a map, is an indispensable tool for navigating the world. Its ability to provide accurate direction and orientation empowers individuals to explore new places, plan journeys, and enhance their understanding of spatial relationships. By understanding the principles of compass navigation and utilizing it responsibly, individuals can unlock a world of possibilities and navigate with confidence.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding the Compass on a Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!