Navigating The World: Understanding Maps And Compass Points
Navigating the World: Understanding Maps and Compass Points
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Maps and Compass Points
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding Maps and Compass Points. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Maps and Compass Points
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the World: Understanding Maps and Compass Points
- 3.1 The Compass Rose: A Guide to Direction
- 3.2 The Importance of Compass Points
- 3.3 Using a Compass with a Map
- 3.4 The Difference Between True North and Magnetic North
- 3.5 FAQs About Maps and Compass Points
- 3.6 Tips for Using Maps and Compass Points
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the World: Understanding Maps and Compass Points
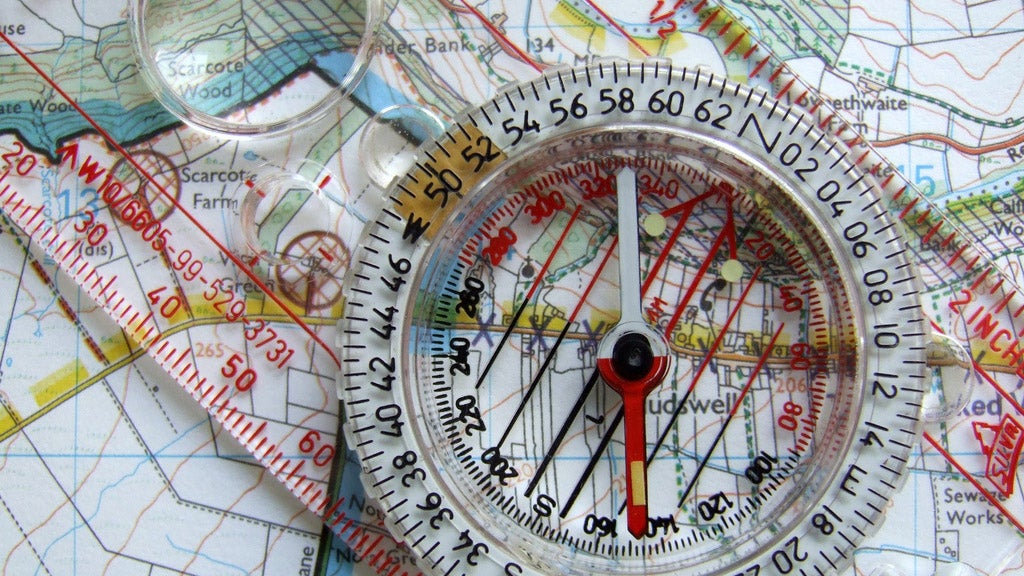

Maps are fundamental tools for understanding and navigating our world. They provide a visual representation of geographic features, distances, and directions, enabling us to explore, travel, and plan effectively. A crucial component of map interpretation is the understanding of compass points, which serve as the foundation for determining direction and orientation.
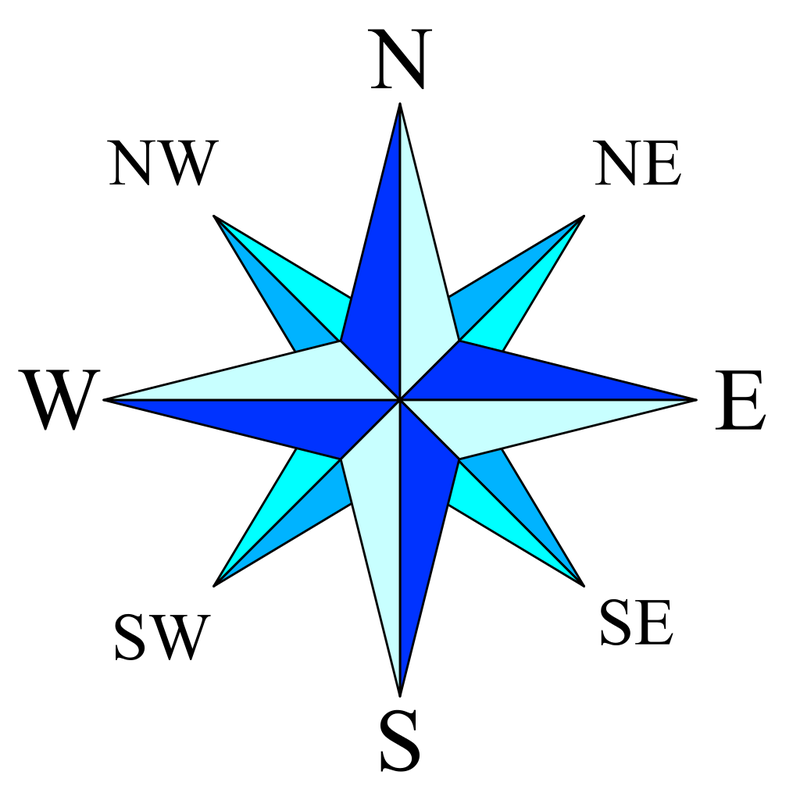
The Compass Rose: A Guide to Direction
The compass rose, a circular diagram found on most maps, is the visual representation of the cardinal directions: North, South, East, and West. These four points are the primary directions, forming the basis for all other compass points.
- North (N) points towards the geographic North Pole, the northernmost point on Earth.
- South (S) points towards the geographic South Pole, the southernmost point on Earth.
- East (E) points towards the direction where the sun rises.
- West (W) points towards the direction where the sun sets.
Beyond the cardinal directions, the compass rose also includes intercardinal directions, which are points located halfway between the cardinal directions:
- Northeast (NE) is halfway between North and East.
- Southeast (SE) is halfway between South and East.
- Northwest (NW) is halfway between North and West.
- Southwest (SW) is halfway between South and West.
The Importance of Compass Points
Compass points are essential for various reasons:
- Orientation: They allow us to determine our position relative to the cardinal directions. This is crucial for understanding the layout of a map and finding our way around.
- Navigation: Compass points guide us in determining the direction we need to travel to reach a specific destination.
- Understanding Geographic Features: Compass points help us understand the relationship between different geographic features, such as the location of mountains, rivers, or cities.
- Mapping and Surveying: Compass points are fundamental in mapping and surveying, as they provide a standard system for recording location and direction.
- Military and Emergency Services: Compass points are vital for military operations, search and rescue efforts, and emergency response, ensuring accurate navigation and communication.
Using a Compass with a Map
While maps themselves provide a visual representation of compass points, using a compass alongside a map allows for precise navigation.
- A compass is a tool that uses the Earth’s magnetic field to determine the direction of magnetic north.
- A compass bearing is the angle measured clockwise from north to a specific direction, expressed in degrees.
To use a compass with a map:
- Orient the map: Align the map with the compass by matching the north arrow on the map with the compass needle pointing to magnetic north.
- Determine the compass bearing: Locate the desired destination on the map and use the compass to measure the angle between the north arrow and the destination point.
- Navigate: Use the compass bearing to guide your travel direction.
The Difference Between True North and Magnetic North
It’s crucial to understand that the compass needle points to magnetic north, which is not the same as true north, the geographic North Pole. The difference between these two points is known as magnetic declination.
- True north is the direction towards the geographic North Pole.
- Magnetic north is the direction towards the Earth’s magnetic north pole, which is located in northern Canada.
Magnetic declination varies depending on location and over time. Maps typically include a declination diagram indicating the difference between true north and magnetic north for the specific area.
FAQs About Maps and Compass Points
1. What is a map legend?
A map legend, also called a map key, is a table or box that explains the symbols, colors, and patterns used on a map. It helps users understand the meaning of various elements on the map, such as roads, rivers, buildings, and elevation.
2. What is a map scale?
A map scale indicates the ratio between distances on the map and corresponding distances in the real world. It allows users to estimate actual distances between points on the map.
3. How do I read a topographic map?
Topographic maps depict the shape and elevation of the Earth’s surface using contour lines. Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, allowing users to visualize the terrain’s features, such as hills, valleys, and slopes.
4. What is a UTM grid?
The Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) grid is a system for mapping the Earth’s surface using a grid of coordinates. It divides the Earth into zones, each with its own set of coordinates, allowing for precise location determination.
5. What is a GPS device?
A Global Positioning System (GPS) device uses satellites to determine the user’s precise location on Earth. It provides latitude, longitude, and altitude coordinates, aiding navigation and location tracking.
Tips for Using Maps and Compass Points
- Always carry a compass and a map: They are essential for safe and effective navigation, especially in unfamiliar areas.
- Orient your map before using it: Align the map with the compass to ensure accurate direction determination.
- Learn to read a compass: Understand the difference between true north and magnetic north, and use the declination diagram on your map to adjust your readings.
- Practice using a compass and map: Familiarize yourself with the tools and techniques before venturing into unfamiliar territory.
- Use landmarks and other features to confirm your location: This helps ensure you are on the right track and prevents getting lost.
Conclusion
Maps and compass points are invaluable tools for understanding and navigating our world. By understanding the fundamental concepts of compass points, map features, and navigation techniques, individuals can explore, travel, and plan with confidence and efficiency. Whether for personal adventures, professional endeavors, or emergency response, the knowledge of maps and compass points empowers individuals to navigate the world effectively and safely.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding Maps and Compass Points. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!