Navigating The World: Understanding Compass Directions On Maps
Navigating the World: Understanding Compass Directions on Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Compass Directions on Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding Compass Directions on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Compass Directions on Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the World: Understanding Compass Directions on Maps
- 3.1 The Compass Rose: A Foundation for Orientation
- 3.2 North: The Guiding Star
- 3.3 South: Opposite North
- 3.4 East: The Rising Sun
- 3.5 West: The Setting Sun
- 3.6 Intermediate Directions: Filling the Gaps
- 3.7 Understanding Map Scales and Bearings
- 3.8 Practical Applications of Compass Directions on Maps
- 3.9 FAQs by Compass Directions on Map
- 3.10 Tips by Compass Directions on Map
- 3.11 Conclusion by Compass Directions on Map
- 4 Closure
Navigating the World: Understanding Compass Directions on Maps

Maps are essential tools for understanding and navigating our world. They provide a visual representation of geographical features, distances, and locations, enabling us to plan journeys, explore new places, and gain a deeper understanding of our surroundings. Central to the utility of maps is the concept of compass directions, a system that allows for precise orientation and location identification.
The Compass Rose: A Foundation for Orientation
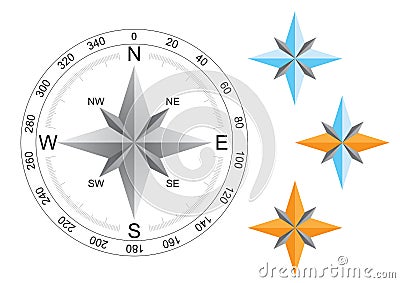
At the heart of map navigation lies the compass rose, a circular diagram typically found at the edge of a map. This rose depicts the four cardinal directions – North, South, East, and West – along with their intermediate directions: Northeast, Northwest, Southeast, and Southwest. The compass rose serves as a visual reference point, allowing map users to determine their orientation relative to these cardinal directions.
North: The Guiding Star
North is the fundamental direction on a map, serving as the primary reference point for all other directions. It is typically denoted by an arrow pointing upwards on the compass rose. Understanding North is crucial, as it forms the basis for determining the locations of all other points on the map.
South: Opposite North
South is the direction directly opposite North. On a compass rose, it is usually depicted by an arrow pointing downwards. South is essential for navigating in relation to North, providing a clear understanding of the direction away from the North Pole.
East: The Rising Sun
East is the direction to the right of North, indicated by an arrow pointing to the right on a compass rose. It is traditionally associated with the rising sun, a visual cue that helps in remembering its position. East is crucial for navigating in relation to North and West, aiding in determining the direction of sunrise and the location of points east of a given reference.
West: The Setting Sun
West is the direction to the left of North, represented by an arrow pointing to the left on a compass rose. It is associated with the setting sun, providing a visual reminder of its position. West is essential for navigating in relation to North and East, assisting in determining the direction of sunset and the location of points west of a given reference.
Intermediate Directions: Filling the Gaps
The intermediate directions – Northeast, Northwest, Southeast, and Southwest – provide more precise orientation than the cardinal directions. They represent the directions located between the cardinal directions.
- Northeast: Located between North and East, represented by an arrow pointing upwards and slightly to the right.
- Northwest: Located between North and West, represented by an arrow pointing upwards and slightly to the left.
- Southeast: Located between South and East, represented by an arrow pointing downwards and slightly to the right.
- Southwest: Located between South and West, represented by an arrow pointing downwards and slightly to the left.
These intermediate directions are essential for more accurate navigation, enabling users to pinpoint locations with greater precision.
Understanding Map Scales and Bearings
The compass rose provides the framework for navigating on a map. However, to accurately determine directions and distances, it is essential to understand map scales and bearings.
- Map Scale: This indicates the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. A large-scale map represents a smaller area with greater detail, while a small-scale map represents a larger area with less detail.
- Bearings: These are angles measured clockwise from North, used to express the direction of a line or path on a map. They are typically measured in degrees, with 0° representing North, 90° representing East, 180° representing South, and 270° representing West.
By understanding map scales and bearings, users can accurately measure distances and determine directions on a map, enabling them to navigate effectively.
Practical Applications of Compass Directions on Maps
Compass directions on maps have numerous practical applications, ranging from everyday activities to specialized fields:
- Navigation: Compass directions are essential for navigating on foot, by car, or by boat. They allow users to follow specific routes, find their way around unfamiliar areas, and reach their destinations safely.
- Outdoor Activities: Hikers, campers, and other outdoor enthusiasts rely on compass directions to navigate trails, find campsites, and explore wilderness areas.
- Emergency Services: First responders, such as firefighters and paramedics, use compass directions to locate emergencies, navigate to accident sites, and provide assistance effectively.
- Military Operations: Compass directions are critical for military operations, enabling troops to navigate battlefields, coordinate attacks, and maintain situational awareness.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS professionals use compass directions to analyze spatial data, map geographic features, and create visualizations that support decision-making in various fields, including urban planning, environmental management, and resource allocation.
FAQs by Compass Directions on Map
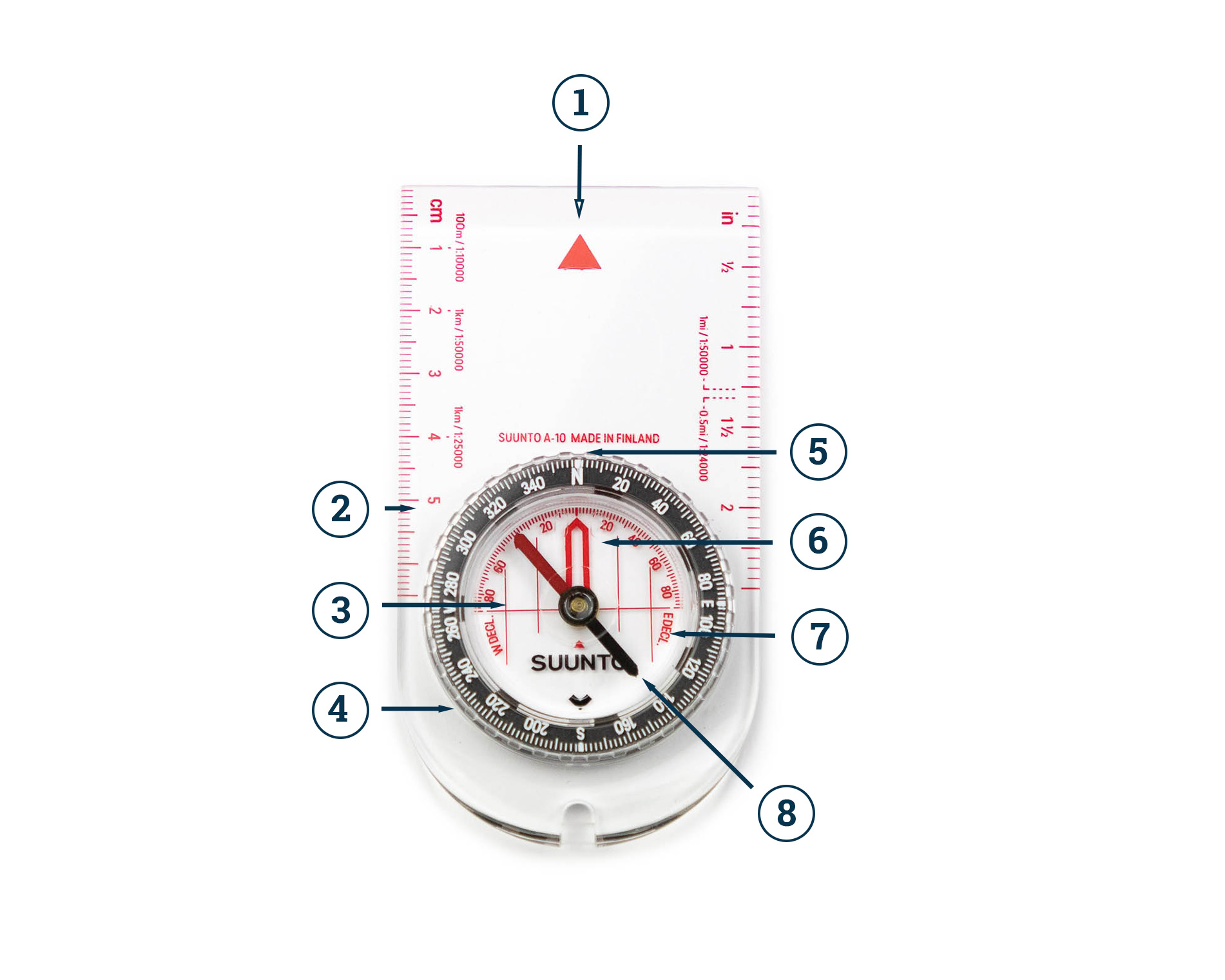
1. How do I use a compass to determine my current location on a map?
To determine your current location using a compass and a map, follow these steps:
- Orient the map: Align the map with North by rotating it until the compass rose’s North arrow points towards the actual North.
- Find a landmark: Identify a recognizable landmark on the map that you can also see in your surroundings.
- Locate yourself: Place the compass on the map, aligning the landmark on the map with the corresponding landmark in your view. Your current location will be where the compass needle points on the map.
2. What are the different types of compass roses found on maps?
There are several types of compass roses found on maps, each with its own specific design and orientation. Common types include:
- Standard Compass Rose: This features the four cardinal directions and their intermediate directions, with North usually pointing upwards.
- Circular Compass Rose: This is a circular design that includes all 360 degrees of a compass, with North at the top.
- Magnetic Compass Rose: This rose displays the magnetic declination, which is the angle between true North and magnetic North.
3. How do I account for magnetic declination when navigating with a compass?
Magnetic declination is the angle between true North and magnetic North, which varies depending on location. To account for magnetic declination, you need to adjust your compass readings. This can be done by consulting a declination chart or using a compass that automatically corrects for declination.
4. What are some common mistakes to avoid when navigating with a compass and a map?
Some common mistakes to avoid when navigating with a compass and a map include:
- Not orienting the map correctly: Ensure the map is aligned with North before using it for navigation.
- Misinterpreting map symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used on the map to avoid misinterpreting information.
- Not accounting for magnetic declination: Make sure to adjust your compass readings for magnetic declination to ensure accurate navigation.
- Ignoring terrain features: Pay attention to terrain features, such as hills and valleys, as they can affect your compass readings and navigation.
Tips by Compass Directions on Map
- Always carry a compass and a map: These are essential tools for safe and efficient navigation.
- Learn to read a map effectively: Familiarize yourself with map symbols, scales, and bearings.
- Practice using a compass: Get familiar with how to orient a compass, take bearings, and adjust for magnetic declination.
- Plan your route in advance: Study the map and plan your route before embarking on any journey.
- Check for updates and changes: Maps can become outdated, so check for recent updates and changes before using them for navigation.
Conclusion by Compass Directions on Map
Understanding compass directions on maps is fundamental for navigating our world effectively. The compass rose, with its cardinal and intermediate directions, provides a framework for orientation and location identification. By understanding map scales, bearings, and the practical applications of compass directions, individuals can navigate safely, explore new places, and gain a deeper understanding of their surroundings. Whether for everyday travel, outdoor adventures, or specialized fields, compass directions on maps remain an indispensable tool for navigating our world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding Compass Directions on Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!