Navigating The World: An Exploration Of Maps And Their Significance
Navigating the World: An Exploration of Maps and Their Significance
Related Articles: Navigating the World: An Exploration of Maps and Their Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: An Exploration of Maps and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: An Exploration of Maps and Their Significance
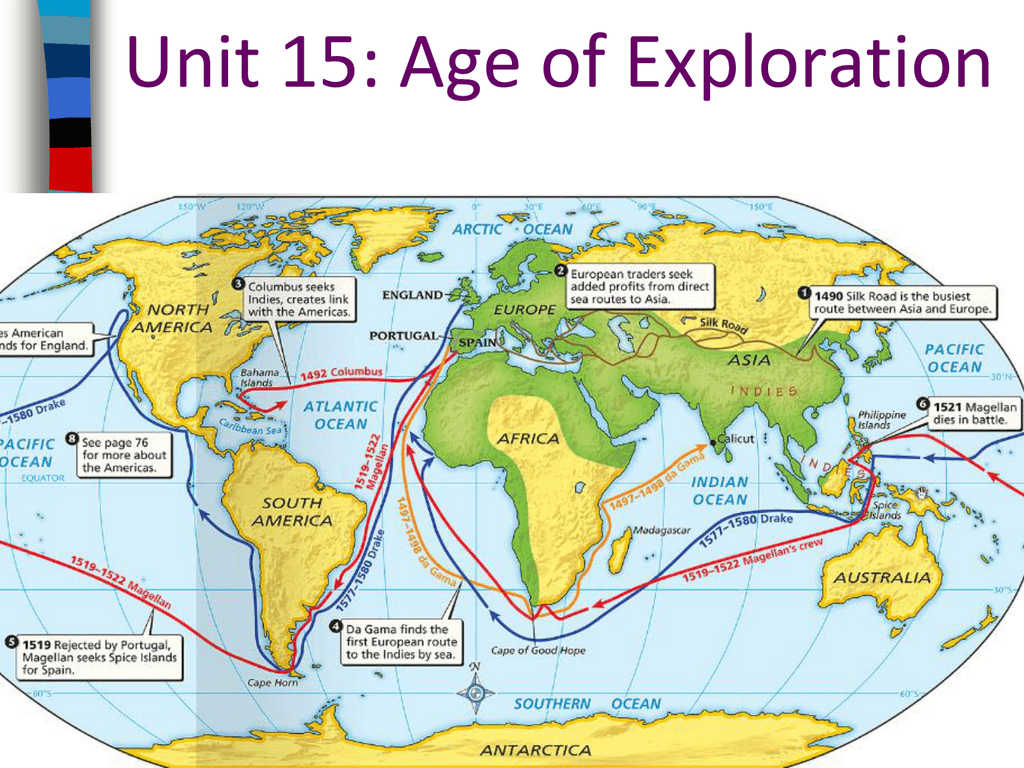
Maps, in their myriad forms, serve as essential tools for understanding and navigating the world. They provide a visual representation of the Earth’s surface, capturing the intricate network of countries, continents, oceans, and physical features. This ability to depict spatial relationships, distances, and geographic information makes maps invaluable for diverse purposes, ranging from everyday navigation to complex scientific research.
The Evolution of Maps: From Ancient Origins to Modern Technology
The earliest maps, dating back to ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Babylonians, were primarily rudimentary depictions of local areas or celestial charts. These early maps were drawn on papyrus, clay tablets, or cave walls, often relying on observation and rudimentary surveying techniques.
As civilizations progressed, so did the sophistication of mapmaking. The Greeks, known for their contributions to geometry and astronomy, produced more accurate maps based on mathematical principles and the concept of latitude and longitude. The Roman Empire, with its extensive network of roads, developed detailed road maps for military and administrative purposes.
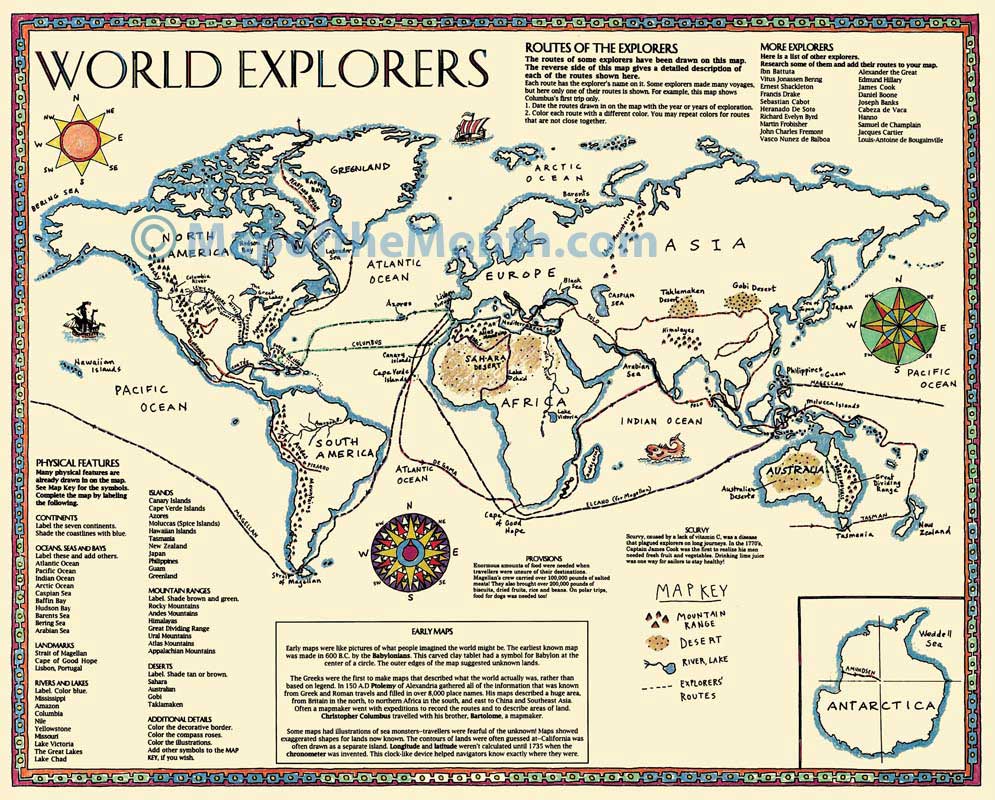
The invention of the printing press in the 15th century revolutionized map production, enabling mass distribution and widespread accessibility. The Age of Exploration, fueled by European voyages of discovery, led to a surge in mapmaking, with cartographers meticulously charting new lands and sea routes.
The 19th century saw further advancements in mapmaking with the development of accurate geodetic surveys and the use of aerial photography. The 20th century witnessed the emergence of digital mapping, fueled by advancements in computer technology and satellite imagery. Today, maps are readily available in various digital formats, offering interactive and dynamic representations of the world.
Types of Maps: A Diverse Spectrum of Representations
Maps can be broadly categorized based on their purpose, scale, and the information they convey. Some common types include:
- Political Maps: Depicting national boundaries, capital cities, and major cities. These maps are essential for understanding geopolitical relationships and administrative divisions.
- Physical Maps: Focusing on landforms, such as mountains, valleys, rivers, and oceans. They provide insights into the Earth’s topography and natural features.
- Thematic Maps: Presenting specific data or themes, such as population density, climate zones, or economic activity. These maps offer visual representations of complex information and patterns.
- Road Maps: Designed for navigation, showing roads, highways, and major landmarks. They are indispensable for travelers and commuters.
- Topographic Maps: Showing elevation contours and terrain features, providing detailed information for hiking, camping, and other outdoor activities.
The Importance of Maps: A Multifaceted Significance
Maps play a crucial role in various aspects of human life, contributing to:
- Navigation and Travel: Maps are essential for finding our way around, whether traveling by car, foot, or public transportation. They provide directions, distances, and landmarks, facilitating efficient and safe journeys.
- Education and Research: Maps are invaluable educational tools, helping students visualize geographic concepts, understand spatial relationships, and explore diverse cultures and environments. Researchers rely on maps for data analysis, environmental studies, and resource management.
- Planning and Development: Maps are used for urban planning, infrastructure development, and resource allocation. They help decision-makers visualize potential impacts and optimize resource utilization.
- Disaster Response: Maps are essential for coordinating emergency response efforts, providing information on affected areas, evacuation routes, and resource availability.
- Environmental Management: Maps are used to monitor and assess environmental conditions, track deforestation, analyze climate change impacts, and develop conservation strategies.
FAQs about Maps:
-
What is the difference between a globe and a map?
- A globe is a three-dimensional representation of the Earth, while a map is a two-dimensional representation. Globes are more accurate in depicting distances and shapes, but maps are more practical for everyday use due to their portability and ease of use.
-
What are the main elements of a map?
- A map typically includes a title, legend, scale, compass rose, and grid system. These elements provide context, explain symbols, indicate distances, show directions, and facilitate location identification.
-
What are the limitations of maps?
- Maps are inherently simplifications of reality, with limitations in terms of scale, projection, and data accuracy. They cannot capture all the complexities of the Earth’s surface and may distort shapes and distances.
-
What are some examples of innovative map technologies?
- Interactive maps, satellite imagery, GPS navigation systems, and augmented reality maps are examples of innovative technologies that enhance map functionality and provide richer experiences.
Tips for Using Maps Effectively:
- Understand the map’s scale and projection: The scale indicates the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground, while the projection method affects the accuracy of shapes and distances.
- Pay attention to the legend: The legend explains the symbols and colors used on the map, enabling you to interpret the information correctly.
- Use a compass rose to orient yourself: The compass rose indicates north, south, east, and west, helping you understand the map’s orientation and navigate effectively.
- Consider the map’s purpose and intended audience: Different maps serve different purposes and cater to specific audiences. Choose a map that best suits your needs and level of understanding.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Maps
Maps, throughout history, have played a vital role in shaping our understanding of the world and facilitating human endeavors. From ancient explorers charting new lands to modern-day scientists analyzing complex data, maps continue to be indispensable tools for navigation, education, planning, and research. With the advent of digital mapping technologies, maps are evolving into dynamic and interactive platforms, providing unprecedented levels of detail and accessibility. As we navigate the complexities of the 21st century, maps remain essential for understanding our planet and shaping our future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: An Exploration of Maps and Their Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!