Navigating The World: A Comprehensive Guide To Maps And Countries
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps and Countries
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps and Countries
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps and Countries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps and Countries
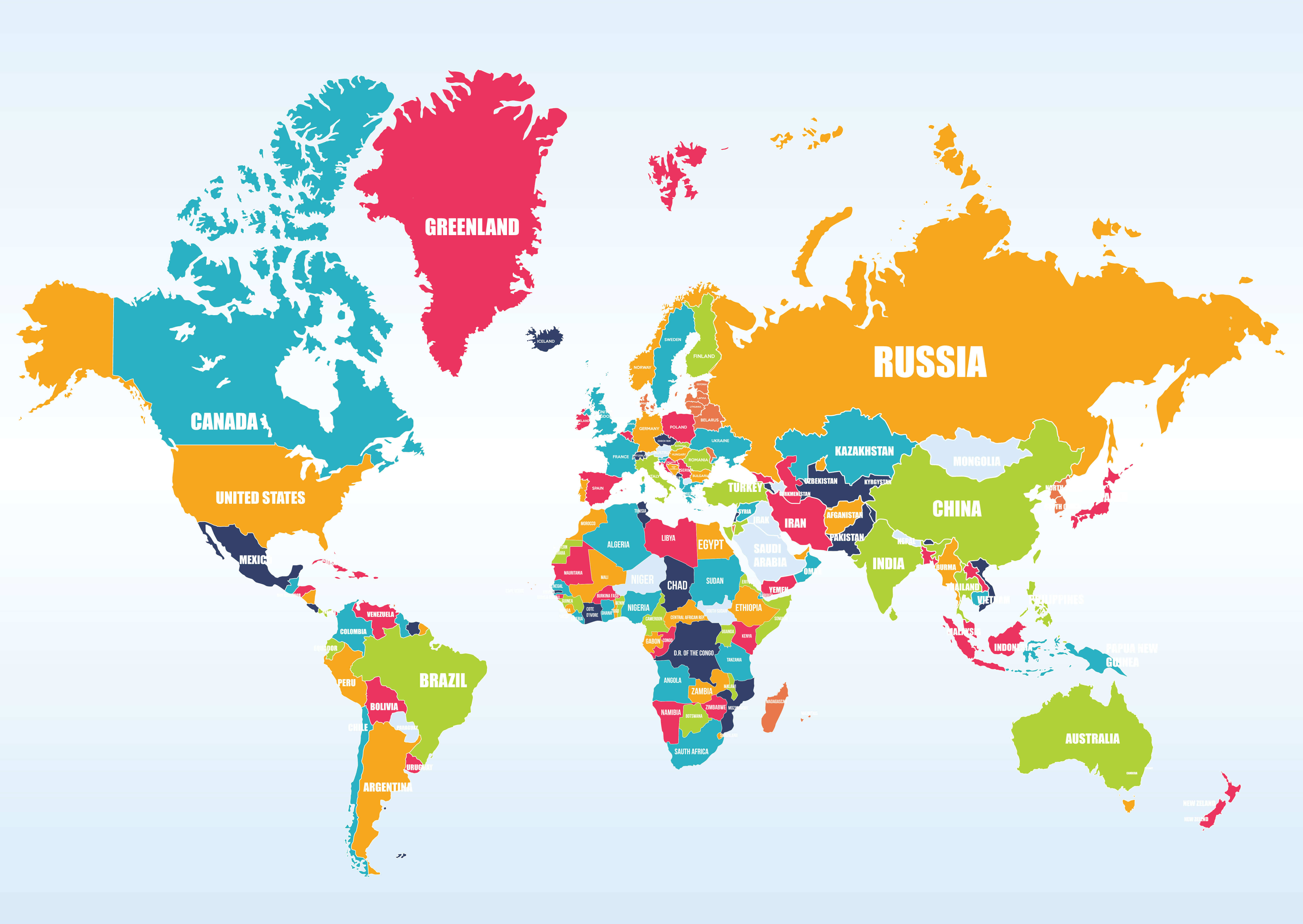
The world map, a seemingly simple representation of our planet, is a powerful tool that underpins countless aspects of human life. From navigating our daily commutes to understanding global events, maps offer a visual framework for comprehending the intricate tapestry of nations, cultures, and landscapes that comprise our world. This article delves into the world of maps and countries, exploring their history, types, uses, and the profound impact they have on our understanding of the globe.
The Evolution of Mapping: From Ancient Origins to Digital Representations
The earliest known maps, dating back thousands of years, were rudimentary sketches etched onto clay tablets, cave walls, or papyrus. These primitive representations, often depicting local terrain or celestial bodies, laid the foundation for the sophisticated cartographic techniques we employ today.
The development of mapmaking was intertwined with advancements in navigation, astronomy, and surveying. The ancient Greeks, renowned for their contributions to mathematics and geometry, developed a system of latitude and longitude, paving the way for more accurate representations of the earth’s surface. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century revolutionized map production, enabling mass dissemination of geographical knowledge.
The 18th and 19th centuries witnessed a surge in exploration and scientific discovery, leading to the creation of increasingly detailed and accurate maps. The advent of photography and satellite imagery in the 20th century further transformed mapmaking, allowing for the creation of highly precise and comprehensive representations of the Earth.
Types of Maps: Unveiling Diverse Perspectives on the World
Maps are not simply static representations of geographical features; they are powerful tools that convey information in various ways, serving diverse purposes. The multitude of map types reflects the multifaceted nature of cartographic information.
-
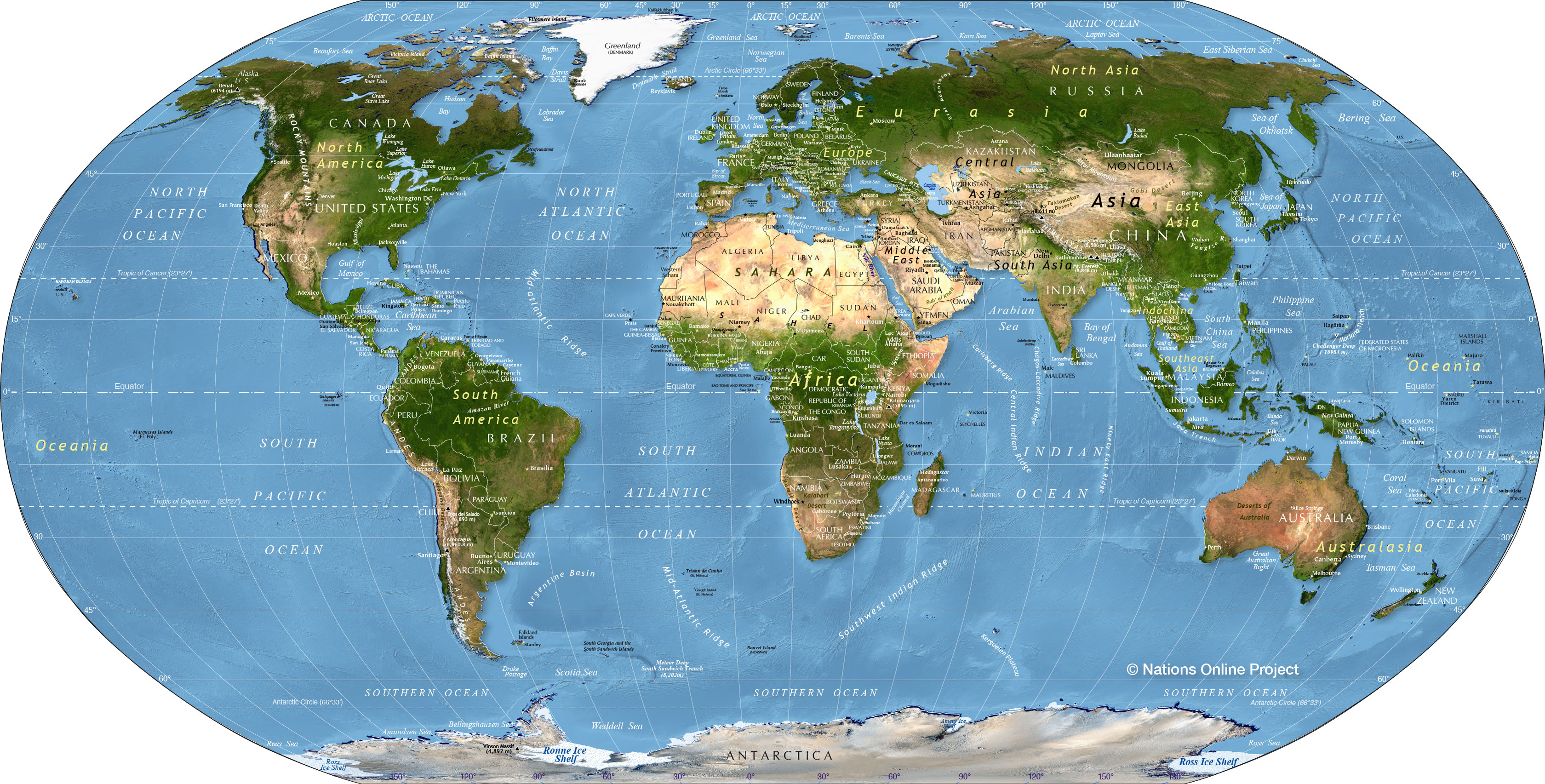
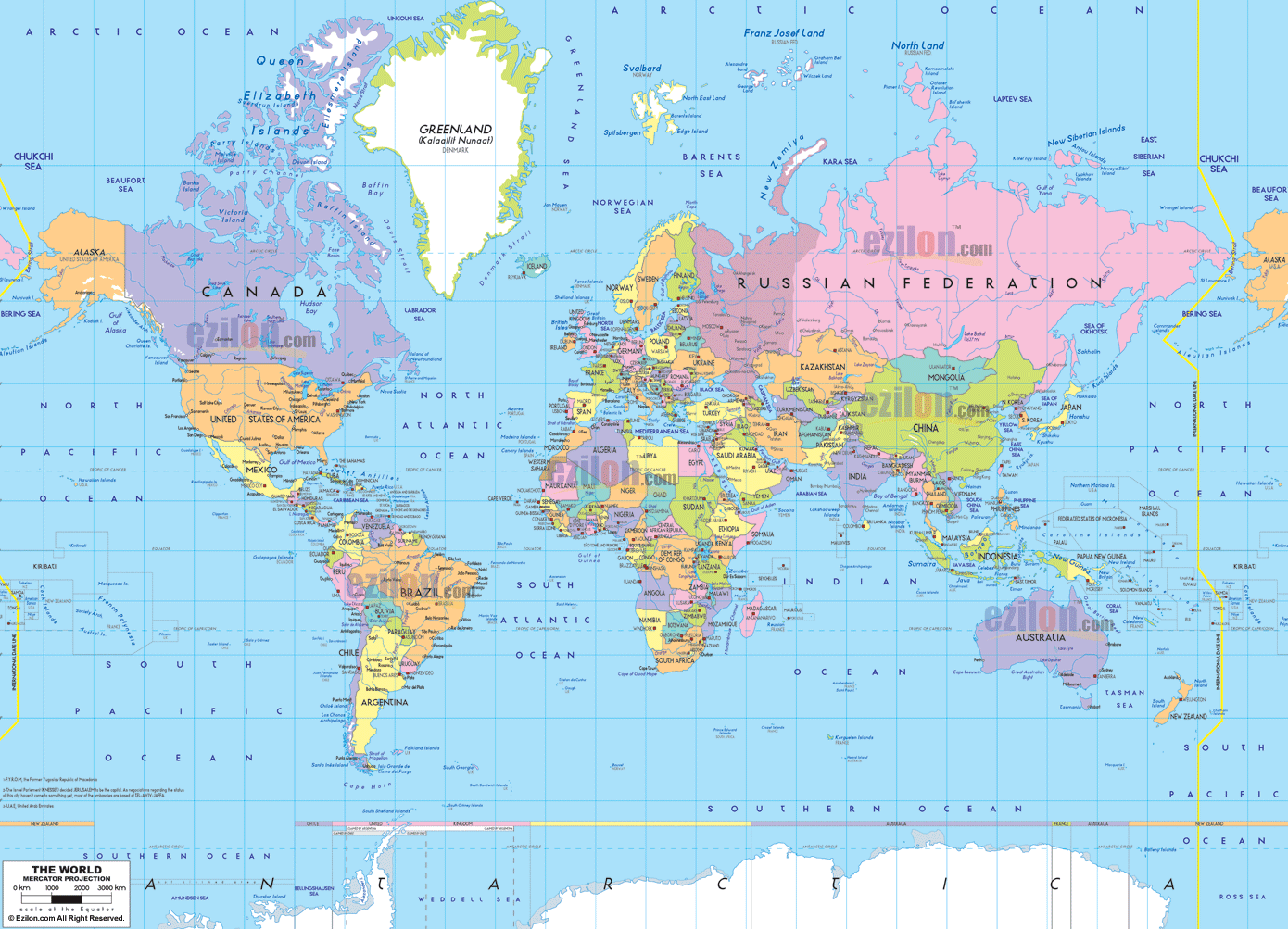
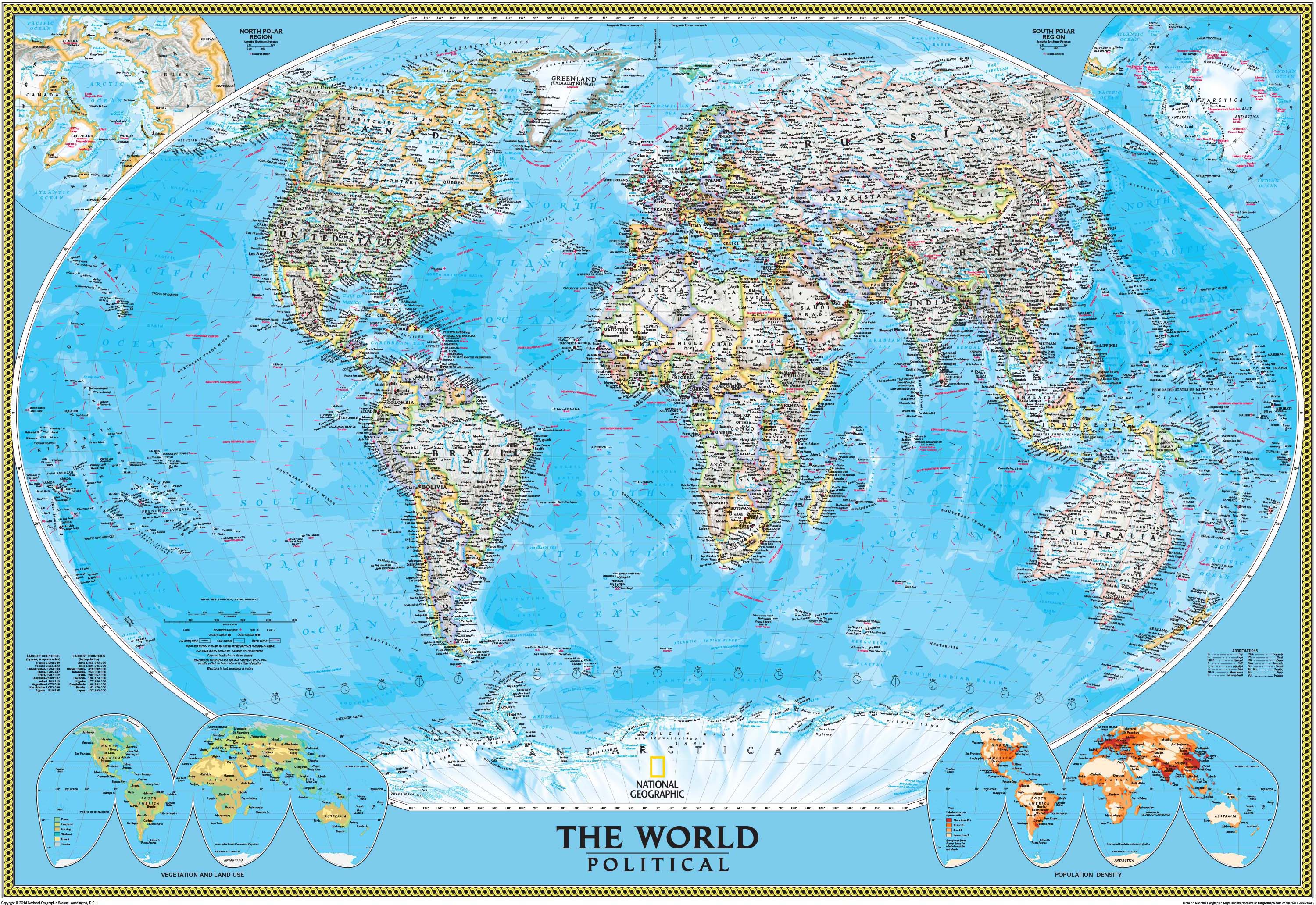
Political Maps: These maps depict the boundaries of countries, states, and other administrative divisions. They are essential for understanding the political landscape of the world and the distribution of power.
-
Physical Maps: These maps focus on the Earth’s physical features, such as mountains, rivers, lakes, and oceans. They provide insights into the geological formations, topography, and natural resources of different regions.
-
Thematic Maps: These maps showcase specific data or themes, such as population density, climate patterns, or economic indicators. They enable visualization of complex information and facilitate analysis of geographical trends.
-
Road Maps: These maps, designed for navigation, depict highways, roads, and major landmarks. They are essential for travelers and commuters, providing a clear visual guide for reaching their destinations.
-
Topographic Maps: These maps provide detailed representations of elevation, contour lines, and terrain features. They are crucial for hikers, climbers, and engineers, offering a comprehensive understanding of the landscape’s three-dimensional structure.
The Importance of Maps: Navigating a Complex World
Maps are integral to our understanding and interaction with the world. Their significance extends far beyond simply providing directions; they serve as vital tools in various fields, including:
-
Navigation and Transportation: Maps are essential for navigating roads, oceans, and airspaces. They guide travelers, pilots, and sailors, ensuring safe and efficient journeys.
-
Urban Planning and Development: Maps are crucial for urban planners in designing sustainable and efficient cities. They facilitate the analysis of land use, transportation infrastructure, and population density, informing decisions on infrastructure development and resource allocation.
-
Environmental Management: Maps play a critical role in environmental monitoring and management. They help track deforestation, pollution levels, and climate change impacts, enabling informed decisions on conservation and resource protection.
-
Military Strategy and Operations: Maps are indispensable tools for military commanders, providing a visual representation of battlefields, terrain features, and enemy positions. They facilitate strategic planning and tactical decision-making.
-
Education and Research: Maps are essential learning tools in geography, history, and other disciplines. They provide a visual framework for understanding historical events, cultural patterns, and geographical processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between a map and a globe?
A: A map is a flat representation of the Earth’s surface, while a globe is a three-dimensional model. Globes provide a more accurate representation of the Earth’s shape and proportions, but maps are more practical for everyday use due to their portability and ease of use.
Q: How are maps made?
A: Maps are created through a combination of surveying, aerial photography, satellite imagery, and computer processing. Surveyors measure distances and elevations, while aerial and satellite imagery capture detailed visual information. This data is then processed and integrated using specialized software to create accurate and detailed maps.
Q: What are some of the challenges in mapmaking?
A: Mapmaking faces challenges related to accuracy, scale, and projection. Representing the Earth’s curved surface on a flat map inevitably involves distortion, requiring cartographers to choose appropriate projections that minimize inaccuracies. Additionally, balancing the level of detail with the scale of the map is crucial for ensuring clarity and readability.
Tips for Using Maps Effectively
-
Understand the map’s scale and projection: The scale indicates the relationship between distances on the map and corresponding distances on the Earth’s surface. The projection determines how the Earth’s curved surface is flattened onto a plane.
-
Identify key features: Pay attention to major landmarks, cities, rivers, and other prominent features. Use these reference points to orient yourself and navigate effectively.
-
Utilize the map’s legend: The legend explains the symbols and colors used on the map, enabling you to interpret the information accurately.
-
Consider the map’s purpose: Different maps are designed for different purposes. Choose a map that is appropriate for your specific needs.
Conclusion
Maps, from their humble beginnings as crude sketches to their sophisticated digital representations, have played a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of the world. They provide a visual framework for navigating our planet, understanding its diverse cultures and landscapes, and making informed decisions about our future. As technology continues to evolve, maps will continue to adapt, offering increasingly powerful tools for exploring, analyzing, and managing our world.
![Printable Detailed Interactive World Map With Countries [PDF]](https://worldmapswithcountries.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/Interactive-World-Map-Printable.jpg)
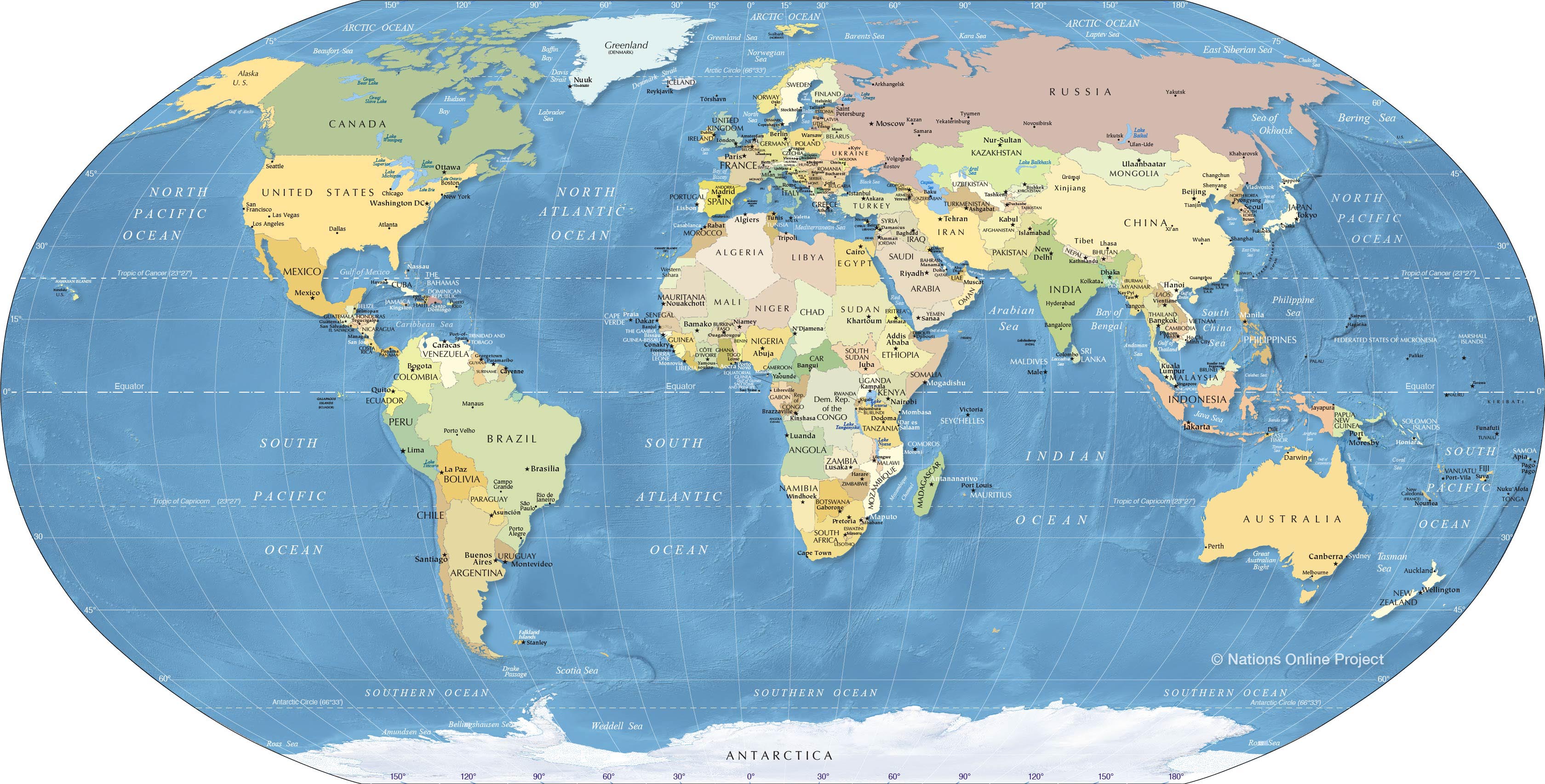
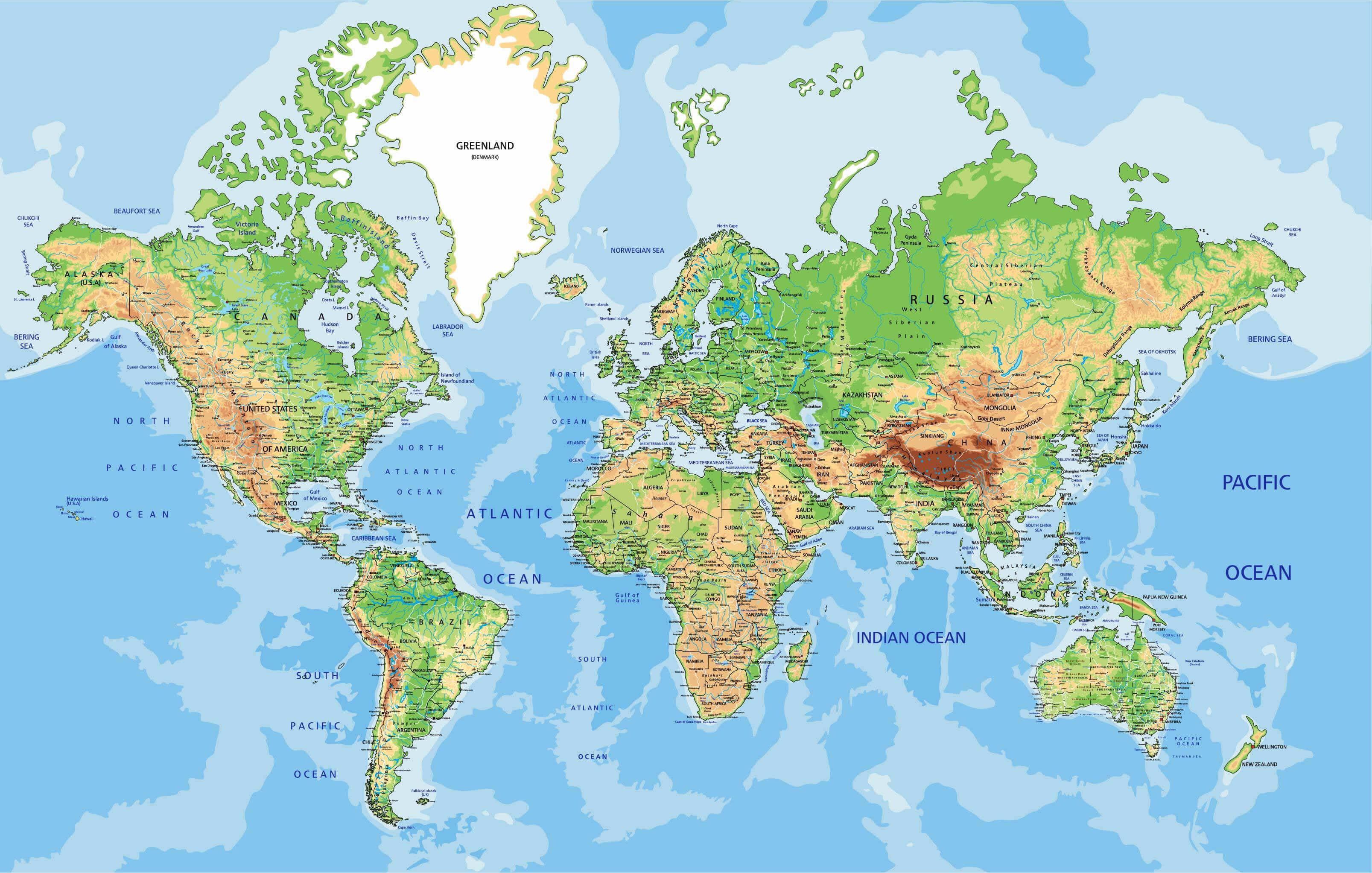

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps and Countries. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!