Navigating The World: A Comprehensive Guide To Compass Points On Maps
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Compass Points on Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Compass Points on Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Compass Points on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Compass Points on Maps
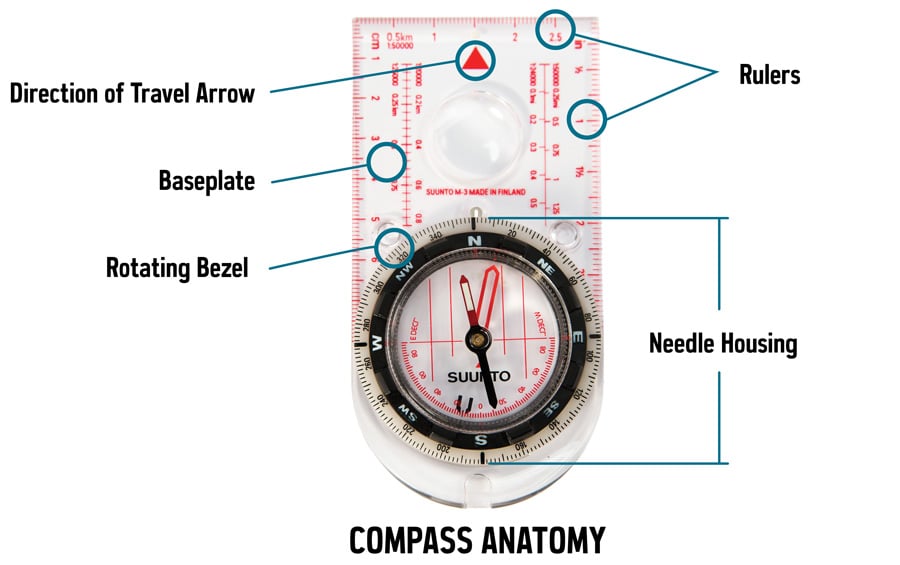
Maps are essential tools for understanding the world around us. They provide a visual representation of geographic features, distances, and locations, enabling us to navigate, explore, and gain insights into our planet. A fundamental element of map comprehension lies in understanding the compass points, which serve as directional references and guide our understanding of spatial relationships. This article delves into the significance of compass points on maps, their historical evolution, and their practical applications in various fields.
Understanding the Compass Points
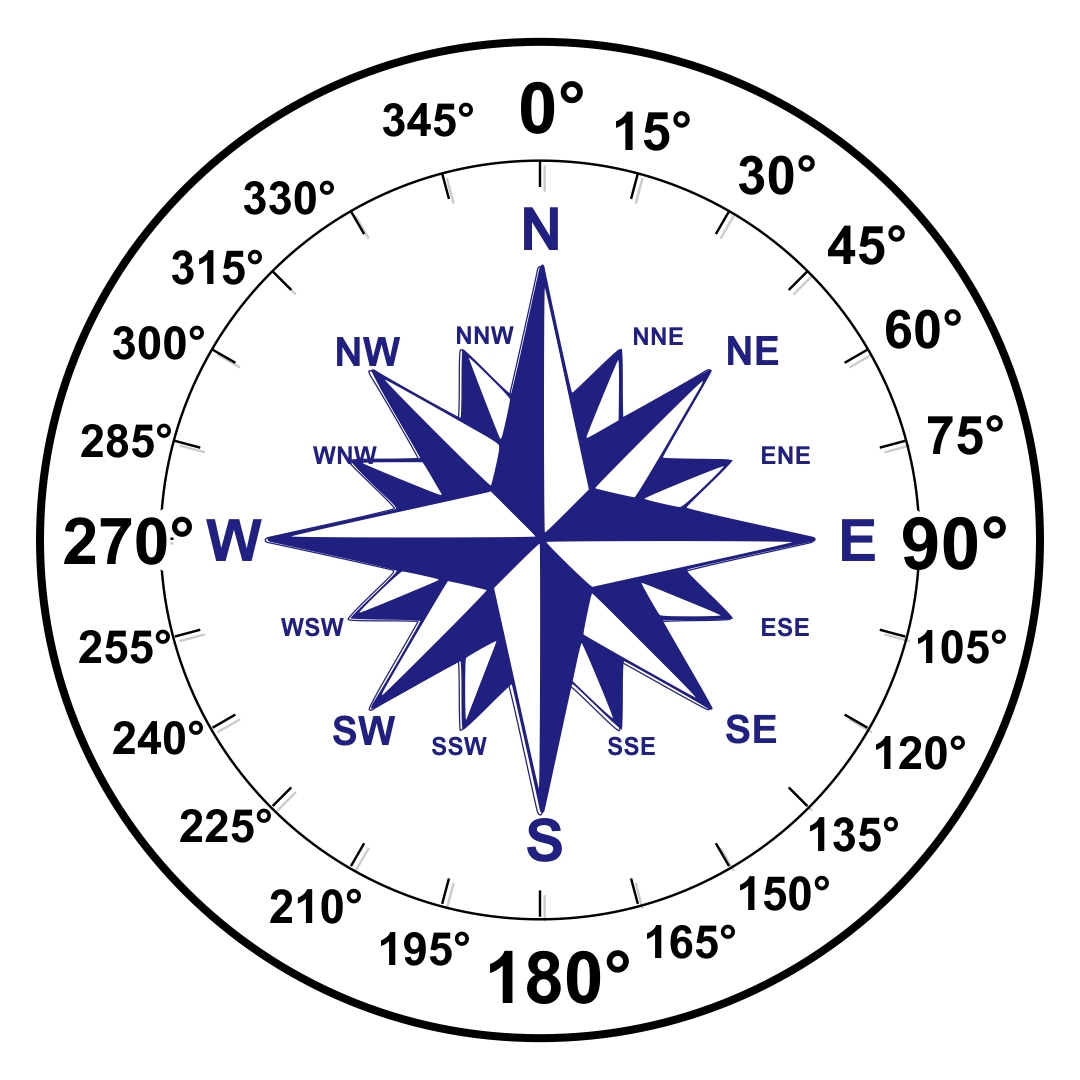
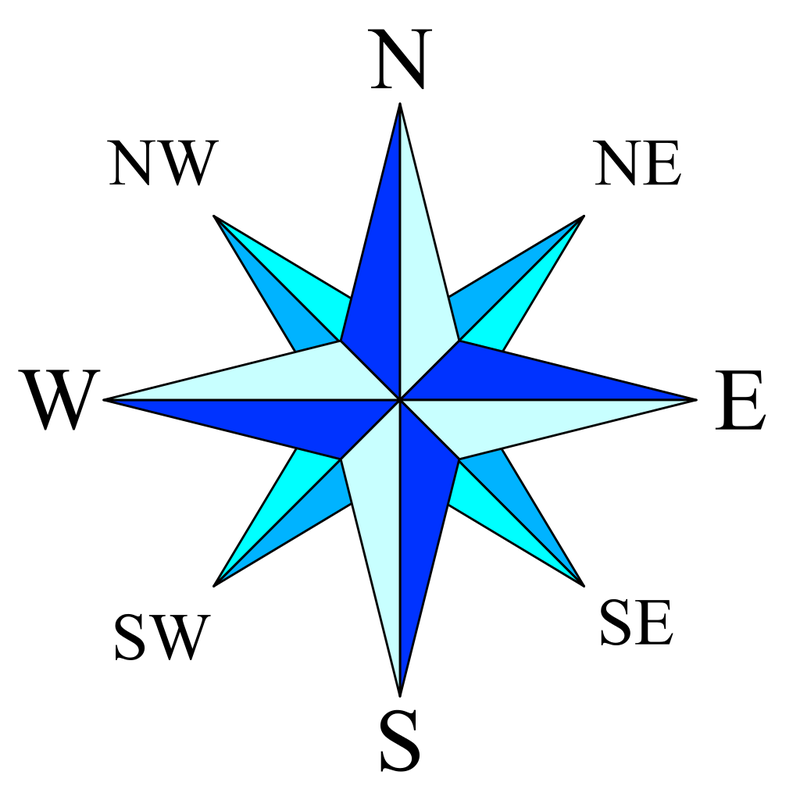
The compass points, also known as cardinal directions, are fundamental to map interpretation. They represent the four main directions: North, South, East, and West. These directions are based on the Earth’s rotation and its relationship to the sun.
- North: The direction towards the North Pole, typically represented by the top of the map.
- South: The direction towards the South Pole, typically represented by the bottom of the map.
- East: The direction towards the rising sun, typically represented by the right side of the map.
- West: The direction towards the setting sun, typically represented by the left side of the map.
The Evolution of Compass Points
The concept of compass points has roots in ancient civilizations. Early societies relied on celestial bodies, primarily the sun and stars, for navigation. They observed the sun’s trajectory throughout the day, noting its rising in the east and setting in the west. This led to the development of the first rudimentary compass points, guiding their movement and understanding of direction.
The invention of the magnetic compass in ancient China revolutionized navigation. This device, utilizing the Earth’s magnetic field, provided a more accurate and reliable means of determining true north. This innovation enabled sailors to navigate vast oceans, leading to increased exploration and trade.
The Importance of Compass Points on Maps
Compass points on maps are crucial for various reasons:
- Orientation: They provide a fundamental framework for understanding the spatial relationships between different locations on the map. By using compass points, individuals can determine the relative position of one point in relation to another.
- Navigation: Compass points are indispensable for navigation, allowing individuals to follow a specific route or locate a desired destination. They are used in conjunction with other map features, such as landmarks and grid references, to guide movement.
- Spatial Awareness: Understanding compass points fosters spatial awareness, enhancing our ability to visualize and comprehend the world around us. It enables us to understand the relative position of places and navigate effectively.
- Data Interpretation: Maps often use compass points to indicate the direction of flow, such as rivers, currents, or winds. This information is essential for understanding geographic phenomena and their impact on the environment.
Compass Points in Different Map Types
Compass points are universally used across different map types, each employing them in specific ways:
- Topographic Maps: These maps depict the physical features of a region, using contour lines, elevation data, and compass points to provide detailed spatial information.
- Road Maps: Road maps primarily focus on transportation routes, using compass points to indicate the direction of roads and highways.
- Nautical Charts: These maps are designed for maritime navigation, incorporating compass points to guide ships and vessels.
- Aerial Maps: Aerial maps provide a bird’s-eye view of a region, utilizing compass points to orient the viewer and understand the spatial arrangement of features.
Applications of Compass Points
The understanding of compass points extends beyond map reading, impacting various fields:
- Architecture: Architects use compass points to design buildings that optimize natural light and ventilation, considering the sun’s path throughout the day.
- Surveying: Surveyors rely on compass points to determine the precise location of points on the Earth’s surface, enabling accurate land measurement and mapping.
- Geology: Geologists use compass points to map geological formations and understand the direction of rock strata, aiding in the exploration and extraction of natural resources.
- Meteorology: Meteorologists utilize compass points to track the movement of weather systems and predict their impact on different regions.
FAQs on Compass Points
Q: Why is north typically at the top of a map?
A: While north is often at the top of a map, it is not a universal rule. This convention stems from the historical use of maps for navigation, where north was considered the primary direction of travel for explorers. However, maps can be oriented in any direction, depending on the specific purpose and context.
Q: How can I determine the cardinal directions without a compass?
A: You can use the sun’s position to approximate cardinal directions. At noon, the sun is typically in the south (in the Northern Hemisphere). Observing the sun’s rising in the east and setting in the west can also provide directional cues.
Q: What are the intermediate compass points?
A: In addition to the four cardinal directions, there are four intermediate compass points: Northeast, Northwest, Southeast, and Southwest. These points represent directions halfway between the cardinal directions.
Q: How are compass points used in conjunction with grid references?
A: Grid references, often found on maps, provide a precise location using a system of coordinates. Compass points are used in conjunction with grid references to understand the direction of movement between two points.
Tips for Understanding Compass Points
- Practice: Practice identifying compass points on maps and in real-world settings.
- Use a compass: A compass is an invaluable tool for determining true north and understanding directions.
- Learn the intermediate points: Familiarize yourself with the four intermediate compass points to enhance your directional understanding.
- Observe the sun’s path: Pay attention to the sun’s position throughout the day to gain a sense of direction.
- Utilize maps and navigation apps: These tools often incorporate compass points and provide directional guidance.
Conclusion
Compass points are fundamental elements of map comprehension, providing a framework for understanding spatial relationships, navigating effectively, and interpreting geographic data. From ancient navigation to modern-day applications, the concept of compass points has remained a cornerstone of our understanding of the world around us. By understanding and utilizing compass points, individuals can enhance their spatial awareness, navigate confidently, and gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of our planet.
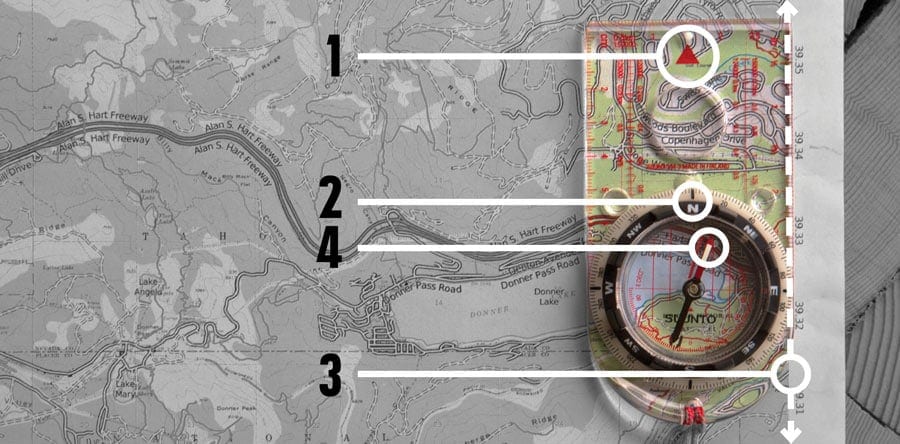





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Compass Points on Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!