Navigating The Waters Of History And Commerce: The Strait Of Juan De Fuca
Navigating the Waters of History and Commerce: The Strait of Juan de Fuca
Related Articles: Navigating the Waters of History and Commerce: The Strait of Juan de Fuca
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Waters of History and Commerce: The Strait of Juan de Fuca. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Waters of History and Commerce: The Strait of Juan de Fuca
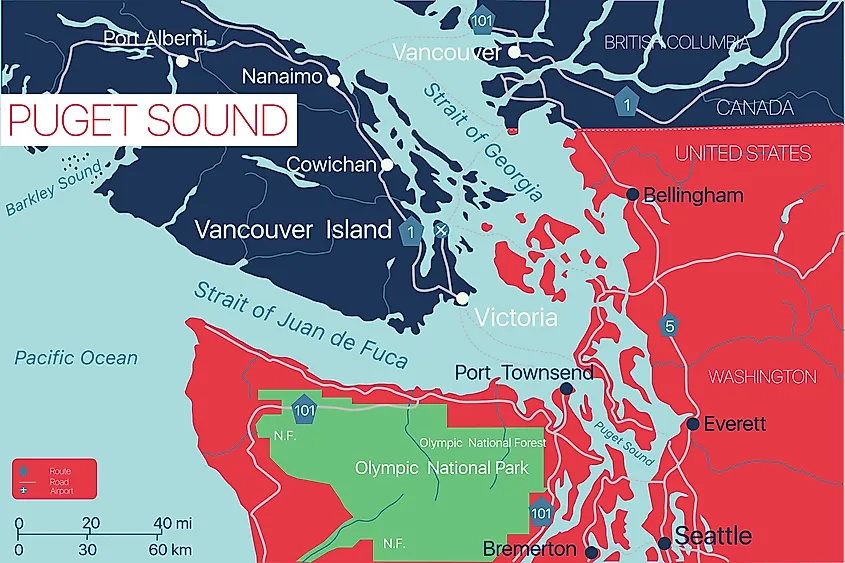
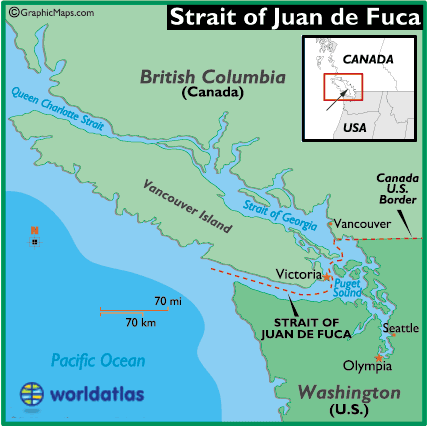
The Strait of Juan de Fuca, a narrow body of water separating the Olympic Peninsula of Washington State from Vancouver Island in British Columbia, is a geographical feature of immense historical, ecological, and economic significance. Its strategic location at the entrance to the Salish Sea, a vast network of inland waterways, has shaped the region’s development and continues to influence its present and future.
A Gateway to the Pacific:
The Strait of Juan de Fuca is named after the Greek explorer Juan de Fuca, who, according to historical accounts, sailed through the passage in 1592, searching for the mythical Strait of Anian, a rumored waterway connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. While his claim of discovery remains debated, the name he bestowed on the strait endures, marking a pivotal moment in the exploration of the Pacific Northwest.
The strait’s significance transcends its historical significance. It serves as a crucial waterway for maritime trade, connecting the Pacific Ocean with the inland ports of Puget Sound and the Salish Sea. The Strait of Juan de Fuca is a vital artery for shipping, facilitating the transport of goods, resources, and people between the United States and Canada.
Ecological Significance:
Beyond its commercial value, the Strait of Juan de Fuca is a critical habitat for a diverse array of marine life. Its waters teem with salmon, herring, whales, and various other species, making it a hotspot for fishing and whale watching. The strait’s rich ecosystem is supported by a delicate balance of currents, tides, and nutrients, making it a crucial component of the broader Salish Sea ecosystem.
The Strait of Juan de Fuca also serves as a conduit for the exchange of marine life between the Pacific Ocean and the inland waters of the Salish Sea. This ecological connection is crucial for maintaining the health and biodiversity of both ecosystems.
Navigational Challenges and Opportunities:
Navigating the Strait of Juan de Fuca presents unique challenges due to its narrow width, strong currents, and unpredictable weather patterns. However, the strait also offers opportunities for maritime trade and transportation. The development of modern navigation technology, including GPS and radar systems, has significantly enhanced safety and efficiency for vessels transiting the strait.
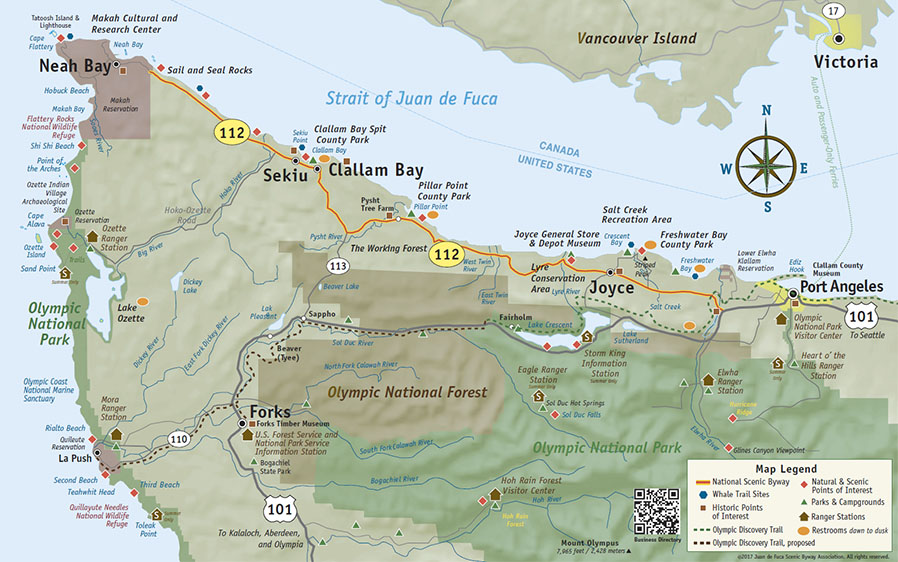
The presence of numerous islands, shoals, and reefs within the strait necessitates careful navigation and adherence to maritime regulations. The U.S. Coast Guard maintains a strong presence in the region, ensuring the safety of vessels and protecting the environment.
The Strait’s Future:
The Strait of Juan de Fuca faces a number of challenges in the 21st century, including climate change, increasing maritime traffic, and the need for sustainable resource management. Rising sea levels and changes in ocean currents could impact the strait’s ecosystem, potentially affecting marine life and coastal communities.
The increasing volume of maritime traffic through the strait necessitates ongoing efforts to ensure safe and efficient navigation. This includes the development of new technologies, improved communication systems, and the implementation of stricter regulations.
Sustainable resource management is another crucial aspect of the strait’s future. Balancing the needs of the fishing industry with the preservation of marine life requires careful planning and collaboration between governments, industry stakeholders, and conservation organizations.
Understanding the Strait of Juan de Fuca:
The Strait of Juan de Fuca is a vital waterway that plays a significant role in the history, ecology, and economy of the Pacific Northwest. Understanding its importance and the challenges it faces is crucial for ensuring its continued health and prosperity.
FAQs:
Q: What are the major ports located on the Strait of Juan de Fuca?
A: The major ports located on the Strait of Juan de Fuca include Port Angeles, Washington, and Victoria, British Columbia. These ports serve as hubs for maritime trade, transportation, and tourism.
Q: What are the main industries that rely on the Strait of Juan de Fuca?
A: The main industries that rely on the Strait of Juan de Fuca include shipping, fishing, tourism, and energy production. The strait’s strategic location and rich resources make it a valuable asset for these industries.
Q: What are the environmental concerns associated with the Strait of Juan de Fuca?
A: Environmental concerns associated with the Strait of Juan de Fuca include pollution from shipping, overfishing, habitat loss, and the impact of climate change.
Q: What measures are being taken to protect the Strait of Juan de Fuca?
A: Measures being taken to protect the Strait of Juan de Fuca include the establishment of marine reserves, pollution control regulations, sustainable fishing practices, and research efforts to monitor and understand the impact of climate change.
Tips for Navigating the Strait of Juan de Fuca:
- Consult nautical charts and navigational aids: Ensure you have the latest charts and information on currents, tides, and hazards.
- Plan your route carefully: Consider weather conditions, vessel traffic, and potential hazards before embarking on a journey.
- Be aware of the strong currents: The strait’s currents can be unpredictable and powerful, potentially affecting vessel speed and maneuverability.
- Maintain a safe distance from other vessels: Be mindful of the traffic density and maintain a safe distance from other vessels to avoid collisions.
- Monitor weather conditions: Stay informed about weather forecasts and be prepared for changes in conditions.
- Respect marine life: Be aware of the presence of marine mammals and other wildlife and take steps to minimize disturbance.
- Follow maritime regulations: Adhere to all applicable maritime regulations, including speed limits and navigation rules.
Conclusion:
The Strait of Juan de Fuca is a vital waterway that plays a crucial role in the Pacific Northwest. Its historical significance, ecological importance, and economic value make it a valuable asset for the region. As we move forward, it is essential to address the challenges facing the strait, including climate change, maritime traffic, and resource management, to ensure its continued health and prosperity. By embracing sustainable practices, promoting responsible stewardship, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders, we can protect this vital waterway for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Waters of History and Commerce: The Strait of Juan de Fuca. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!