Navigating The Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide To Topographical Maps And Compasses
Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographical Maps and Compasses
Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographical Maps and Compasses
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographical Maps and Compasses. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographical Maps and Compasses

In an age dominated by digital navigation systems, the traditional art of map and compass navigation might seem antiquated. However, the ability to navigate using a topographical map and compass remains a valuable skill, offering a level of independence and resilience unmatched by technology alone. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of using these tools, equipping readers with the knowledge to confidently navigate any terrain.
Understanding Topographical Maps
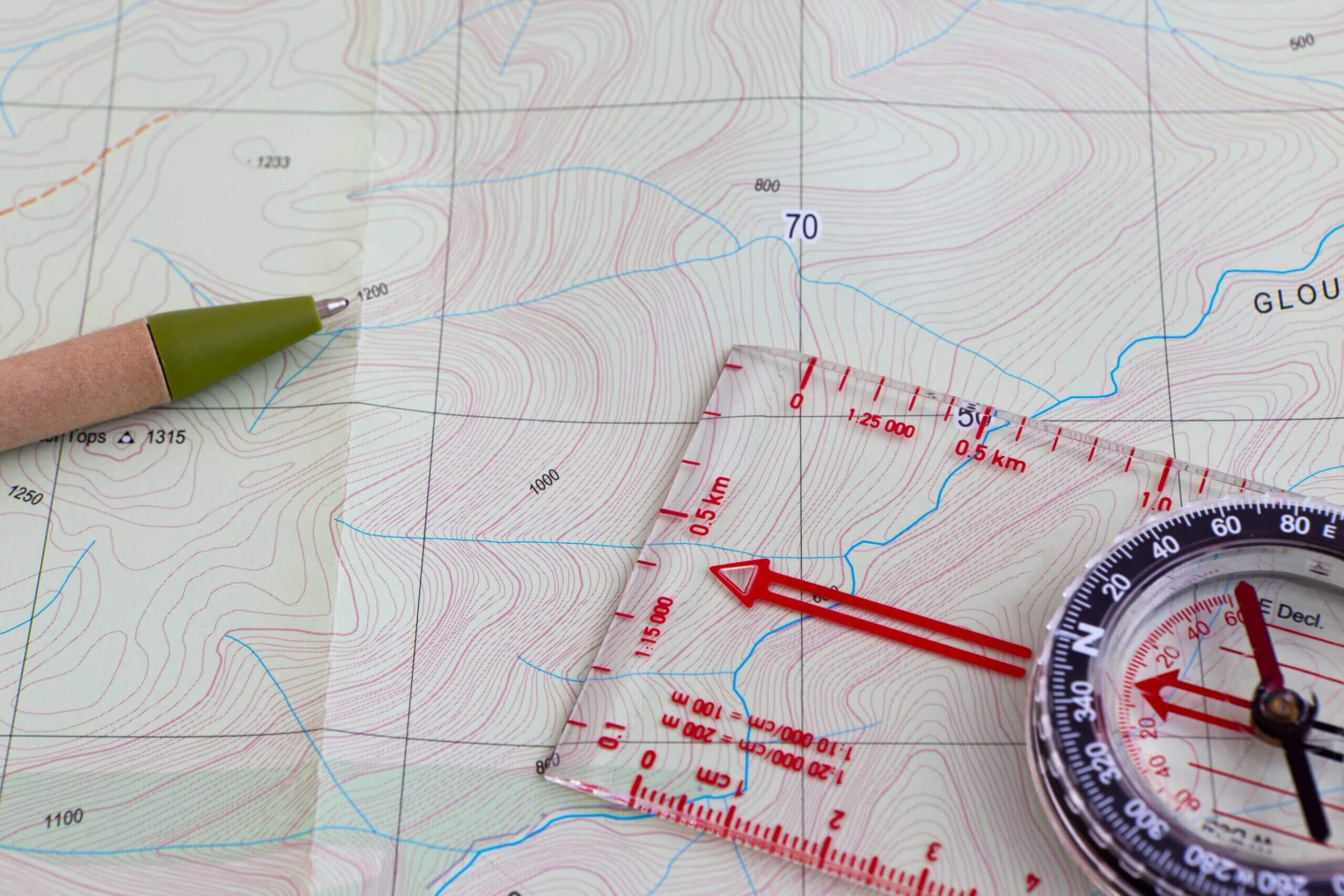
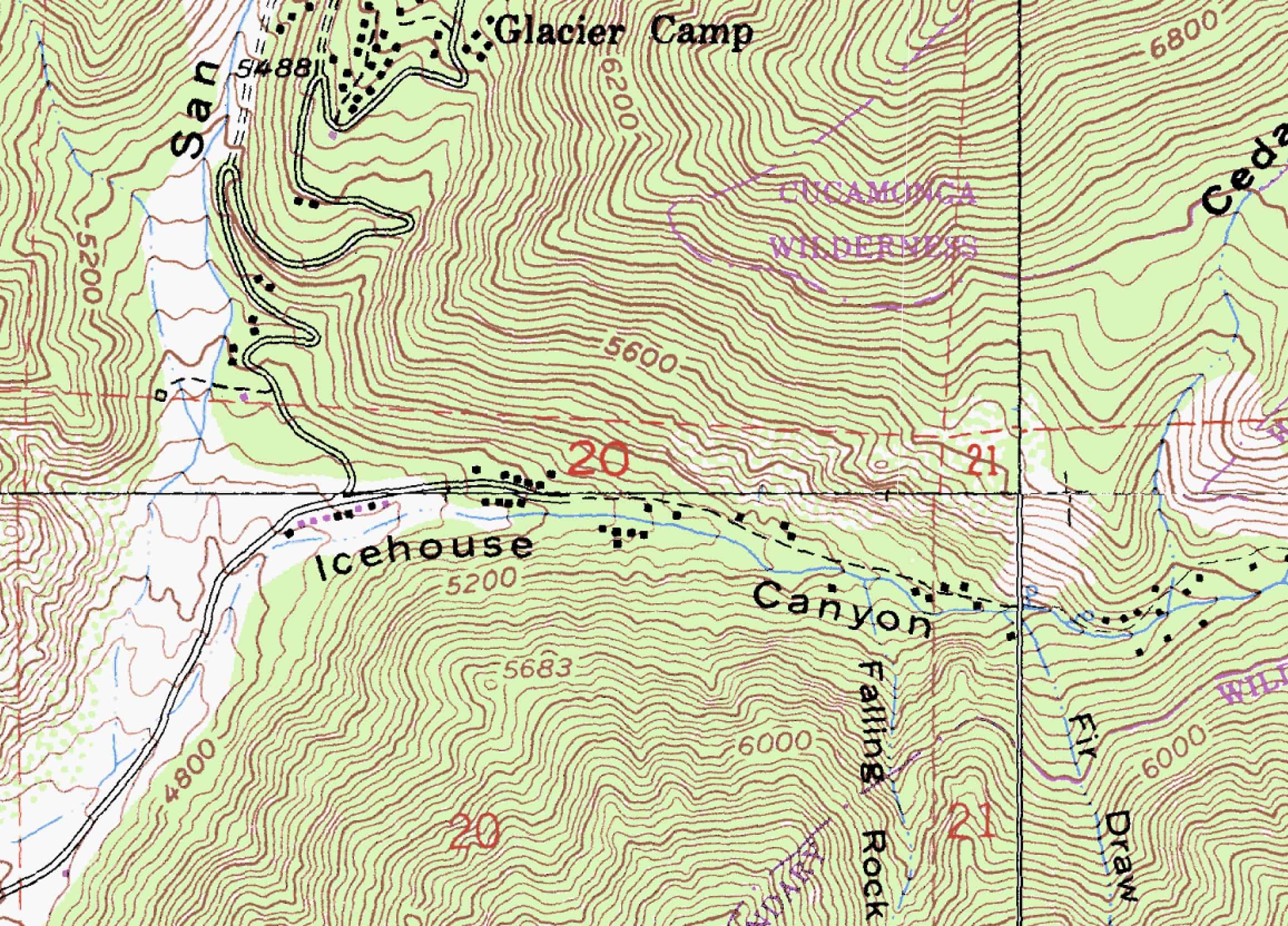
Topographical maps are specialized maps that depict the three-dimensional features of the earth’s surface. They are essential tools for navigating through diverse landscapes, providing a wealth of information beyond simple location markers.
Key Elements of a Topographical Map:
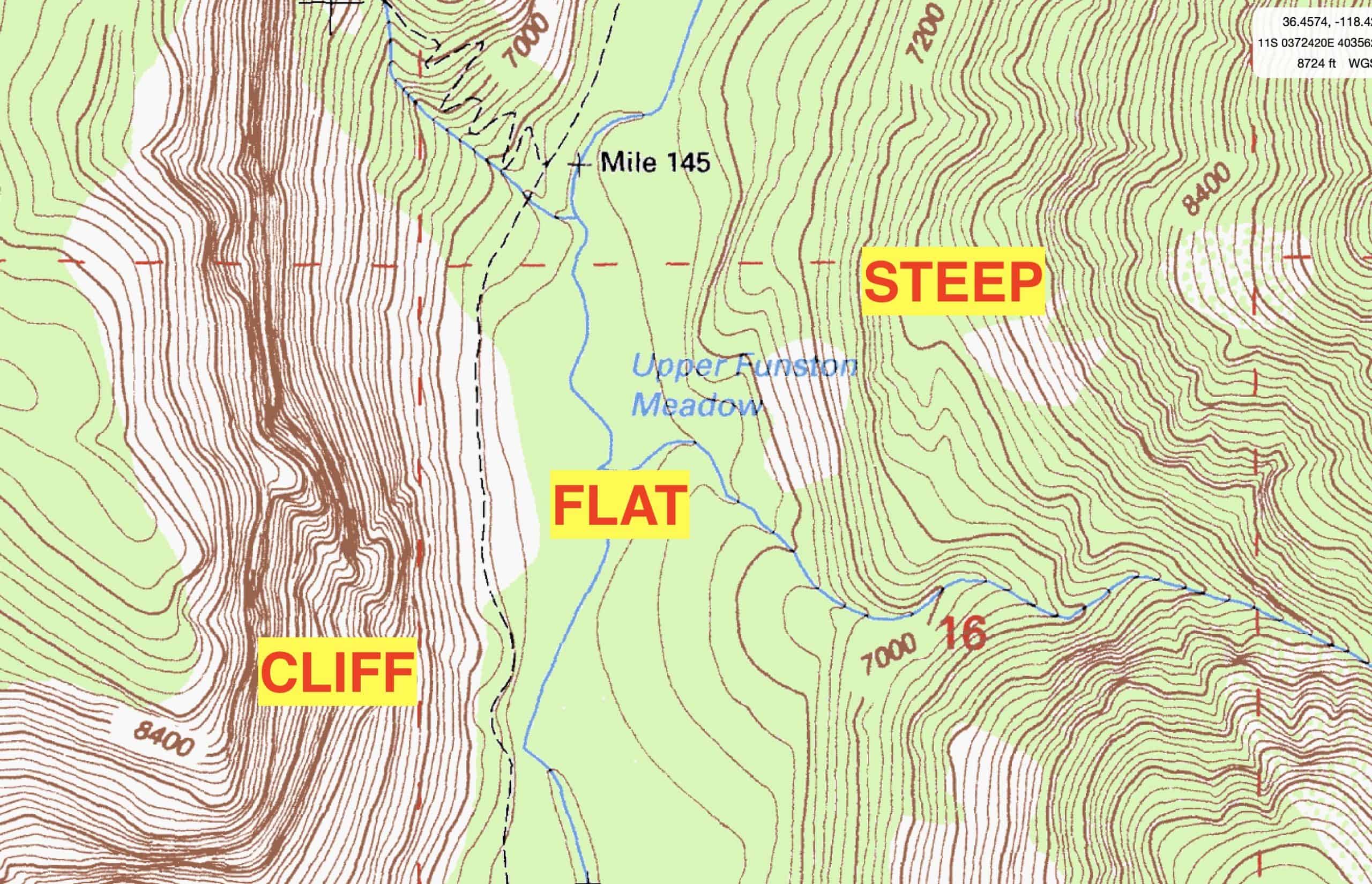
- Contour Lines: These lines represent points of equal elevation, forming a visual representation of the terrain’s shape. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope.
- Elevation: Numbers on the map indicate specific elevations, often marked along contour lines or at prominent features.
- Scale: The map scale defines the ratio between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground. Understanding the scale is crucial for accurate distance estimations.
- Symbols: A variety of symbols represent features such as roads, trails, water bodies, buildings, and vegetation. Familiarity with these symbols is essential for interpreting the map’s information.
- Grid System: A grid system, often using a combination of letters and numbers, allows for precise location referencing.
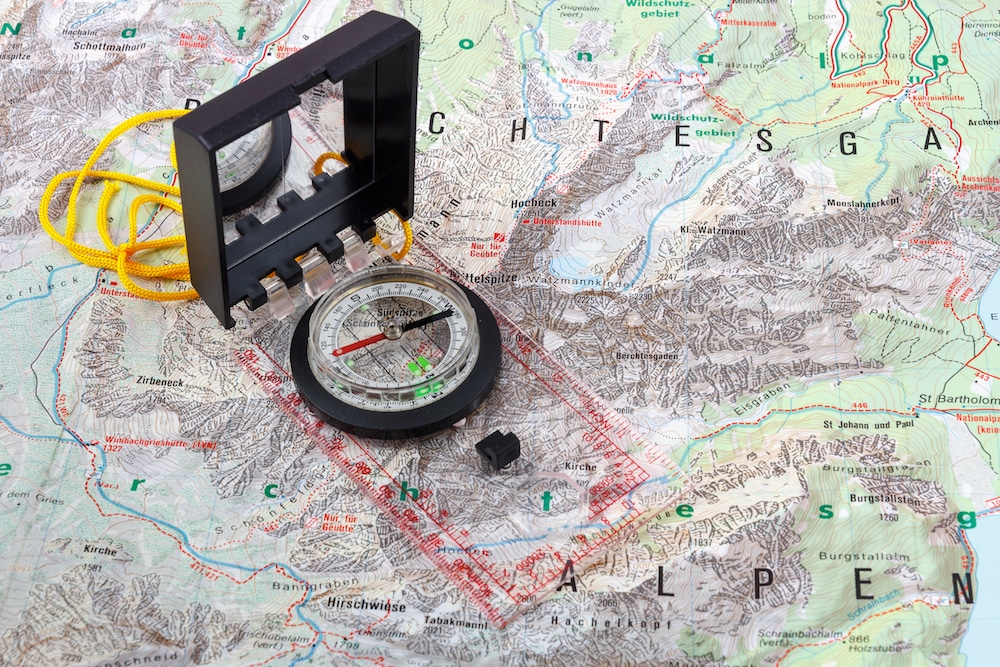
The Compass: Your Directional Guide
A compass is a simple yet powerful tool that utilizes the earth’s magnetic field to determine direction. It consists of a magnetic needle that aligns itself with the magnetic north pole, providing a reliable reference for orienting oneself.
Understanding Compass Components:
- Compass Needle: The magnetic needle, typically painted red at one end, points towards magnetic north.
- Compass Housing: The housing encloses the needle and provides a platform for reading bearings.
- Bezel Ring: This rotating ring allows for setting and reading bearings.
- Direction of Travel Arrow: A fixed arrow on the housing indicates the direction of travel.
Navigating with Map and Compass: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Orient the Map: Align the map with the terrain by matching prominent features like roads, rivers, or ridges. Use a compass to determine the direction of north on the map and align it with the direction of north indicated by the compass needle.
- Determine Your Location: Identify a prominent feature on the map and locate its corresponding position on the ground. This can be a road intersection, a stream crossing, or a distinctive hilltop.
- Plan Your Route: Use the map to identify your desired destination and plan a suitable route. Consider terrain features, elevation changes, and potential obstacles.
- Take Bearings: Use the compass to determine the bearing (angle relative to north) to your destination. Align the compass needle with the direction of north, then rotate the bezel ring until the direction of travel arrow points towards your destination. Read the bearing from the bezel ring.
- Navigate Using Bearings: Follow the bearing you’ve established using the compass. Maintain a constant bearing, making adjustments as needed to stay on course.
- Regularly Check Your Position: Periodically re-orient the map and confirm your location using prominent features. This ensures you haven’t deviated significantly from your planned route.
Benefits of Map and Compass Navigation
- Independence: Provides the ability to navigate without relying on electronic devices or cellular service.
- Resilience: Offers a backup navigation system in case of technology failure.
- Enhanced Understanding of Terrain: Promotes a deeper understanding of the landscape and its features.
- Improved Spatial Awareness: Develops a strong sense of direction and spatial reasoning.
- Outdoor Safety: Provides essential tools for navigating challenging terrain and ensuring personal safety.
FAQs: Navigating with Map and Compass
Q: What are the differences between magnetic north and true north?
A: Magnetic north is the direction indicated by a compass needle, while true north is the geographic North Pole. There is a difference between the two, known as magnetic declination, which varies depending on location. Most topographical maps include a declination diagram to adjust compass bearings for accurate navigation.
Q: How do I adjust for magnetic declination?
A: Consult the declination diagram on the map to determine the declination value for your location. If the declination is east, add the value to your compass bearing. If the declination is west, subtract the value from your compass bearing.
Q: What are some common navigational errors?
A: Common errors include misinterpreting the map, misreading compass bearings, failing to adjust for declination, and neglecting to regularly check your position.
Q: How can I improve my map and compass skills?
A: Practice using a map and compass in familiar environments. Join a local hiking club or outdoor group for guided navigation sessions. Attend workshops or courses to enhance your skills.
Tips for Effective Map and Compass Navigation
- Practice Regularly: Familiarize yourself with the tools and techniques through regular practice.
- Invest in Quality Equipment: Use a reliable compass and a durable, waterproof map.
- Study the Terrain: Thoroughly analyze the map and understand the terrain before embarking on your journey.
- Take Detailed Notes: Record important bearings, landmarks, and observations.
- Stay Aware of Your Surroundings: Be mindful of your environment and potential hazards.
Conclusion
Navigating with a topographical map and compass is a skill that transcends technological advancements. It empowers individuals with a profound understanding of the terrain, a sense of independence, and the ability to navigate with confidence and resilience. By mastering the art of map and compass navigation, individuals can unlock a world of exploration and adventure, venturing into the wilderness with a sense of preparedness and self-reliance.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographical Maps and Compasses. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!