Navigating The Landscape: Understanding Washington State’s Voting Districts
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Washington State’s Voting Districts
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Washington State’s Voting Districts
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Washington State’s Voting Districts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Washington State’s Voting Districts

The intricate web of political representation in Washington State is woven through a system of voting districts, each designed to ensure fair and equitable representation for its residents. This article delves into the complex world of Washington State’s voting district maps, exploring their historical development, current configuration, and the crucial role they play in shaping the state’s political landscape.
A History of Division and Representation:
The concept of voting districts is rooted in the fundamental principle of democratic representation. In the United States, the principle of "one person, one vote" mandates that each district should contain approximately the same number of people, ensuring that every citizen’s vote carries equal weight.
Washington State’s journey toward its current voting district map has been marked by a series of redrawings, driven by population shifts, evolving political realities, and the pursuit of fair representation. The state’s first legislative districts were established in 1889, following its admission to the Union. Over the decades, these districts have undergone numerous revisions, often marked by controversy and legal challenges.
The Importance of Redistricting:
Redistricting, the process of redrawing voting districts, is a critical component of maintaining a fair and democratic system. It ensures that representation reflects the changing demographics of a state and prevents gerrymandering, a practice where district lines are manipulated to favor a particular political party or group.
In Washington State, redistricting occurs every ten years following the decennial census. This process is overseen by a nonpartisan commission, the Washington State Redistricting Commission, tasked with creating fair and impartial district maps. The commission’s work is guided by specific criteria, including:
- Population Equality: Each district should contain roughly the same number of people.
- Contiguity: Districts must be geographically connected, preventing fragmented or scattered representation.
- Communities of Interest: Districts should preserve communities with shared interests and concerns.
- Political Fairness: Districts should not be drawn to unfairly favor one political party over another.
The Current Landscape: A Mosaic of Districts
Washington State’s current voting district map is a complex mosaic of lines and boundaries, dividing the state into a network of electoral units for both state and federal elections. These districts are classified into several categories:
- Congressional Districts: These districts determine representation in the United States House of Representatives. Washington State has ten congressional districts, each electing a representative to serve in the national legislature.
- State Legislative Districts: These districts define representation in the Washington State Legislature, which consists of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The state is divided into 49 Senate districts and 98 House districts.
- County Council Districts: These districts determine representation on county councils, the governing bodies of individual counties within the state.
- School Board Districts: These districts determine representation on school boards, responsible for overseeing local public education.
Understanding the Impact: A Closer Look
The voting district map has a profound impact on the political landscape of Washington State. It determines:
- Electoral Outcomes: The configuration of districts can influence the outcome of elections by creating advantages for certain candidates or parties.
- Representation: The districts define who represents the people in various levels of government, shaping the policies and decisions that affect their lives.
- Political Power: The distribution of districts can influence the balance of power between different political groups and ideologies.
Navigating the Complexities: FAQs
Q: How are voting districts drawn in Washington State?
A: Voting districts in Washington State are drawn by the Washington State Redistricting Commission, a nonpartisan body responsible for ensuring fair and impartial district maps. The commission uses specific criteria to guide its work, including population equality, contiguity, communities of interest, and political fairness.
Q: How often are voting districts redrawn?
A: Voting districts in Washington State are redrawn every ten years following the decennial census. This process ensures that representation reflects the changing demographics of the state and prevents gerrymandering.
Q: How can I find out what voting district I live in?
A: You can find out your voting district by visiting the Washington State Secretary of State’s website or contacting your local election official.
Q: What are the benefits of having voting districts?
A: Voting districts are essential for ensuring fair and equitable representation in government. They ensure that each citizen’s vote carries equal weight and prevent gerrymandering, which can distort electoral outcomes and undermine democratic principles.
Q: What are some of the challenges associated with voting districts?
A: One of the main challenges associated with voting districts is the potential for gerrymandering, where district lines are manipulated to favor a particular party or group. Another challenge is ensuring that districts accurately reflect the diversity and interests of the communities they represent.
Tips for Navigating the Political Landscape
- Stay Informed: Regularly consult reliable news sources and participate in civic engagement activities to stay informed about the political landscape and the issues that affect your community.
- Engage in Dialogue: Engage in respectful and informed discussions with people who hold different viewpoints to foster understanding and promote constructive dialogue.
- Vote: Exercise your right to vote and participate in the democratic process by casting your ballot in every election.
- Advocate for Fair Representation: Advocate for fair and equitable redistricting processes that prioritize community interests and prevent gerrymandering.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Democracy
Washington State’s voting district map is a crucial element of the state’s democratic system. It serves as a framework for ensuring fair representation, reflecting the diversity of the state’s population, and facilitating a robust political process. By understanding the intricacies of the voting district map, citizens can better engage in the political process, advocate for their interests, and contribute to the ongoing evolution of democratic governance in Washington State.

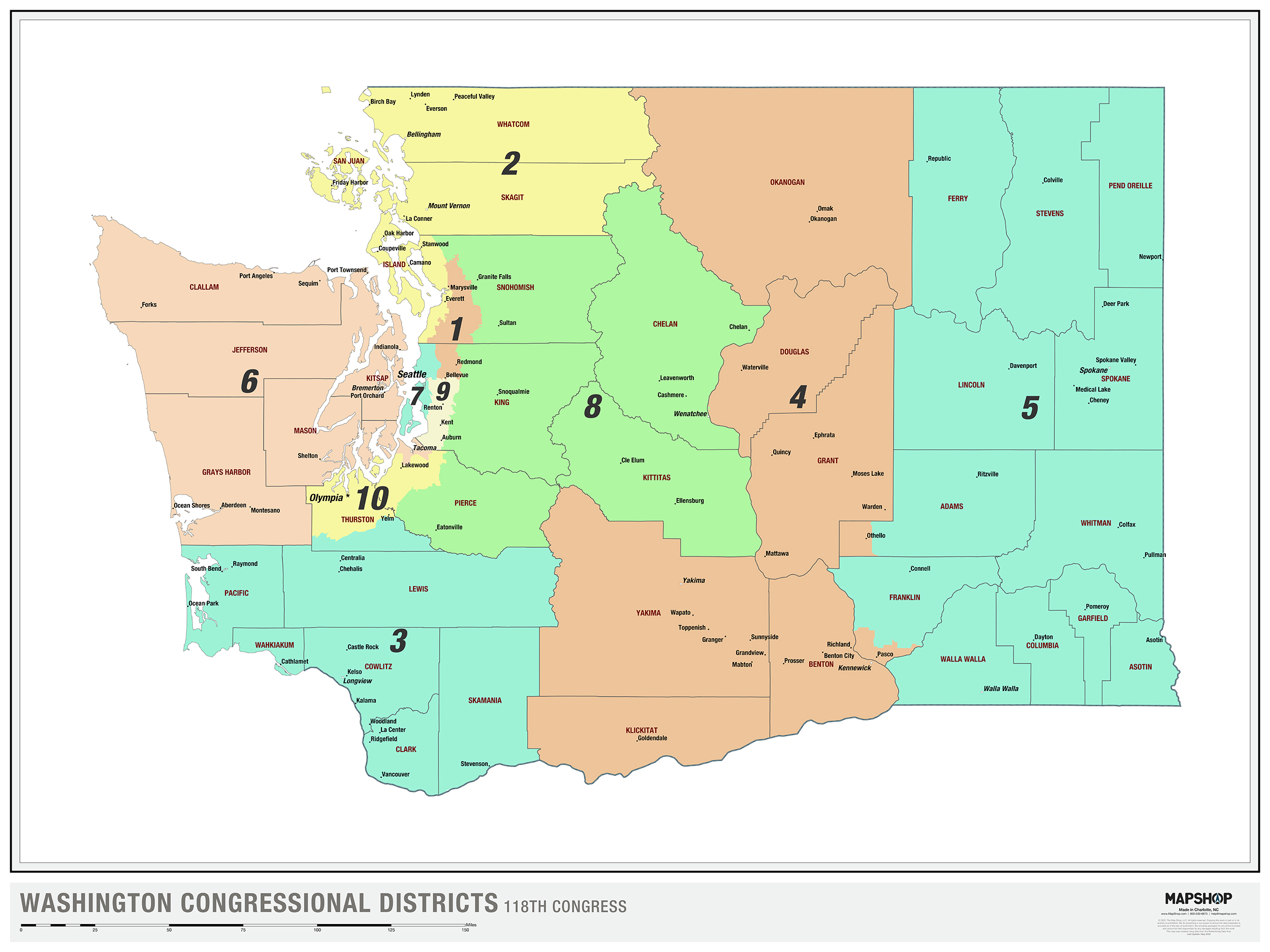

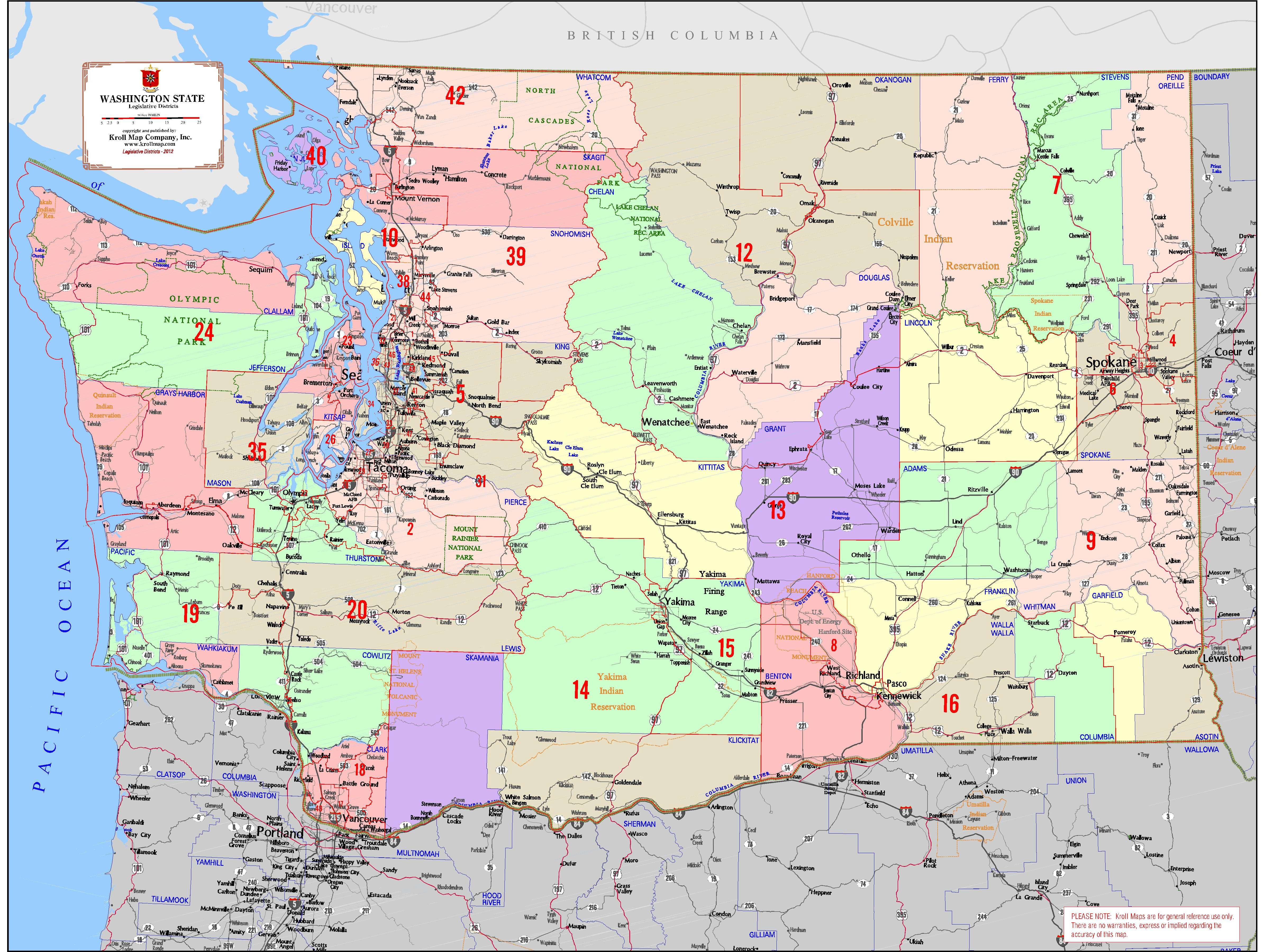
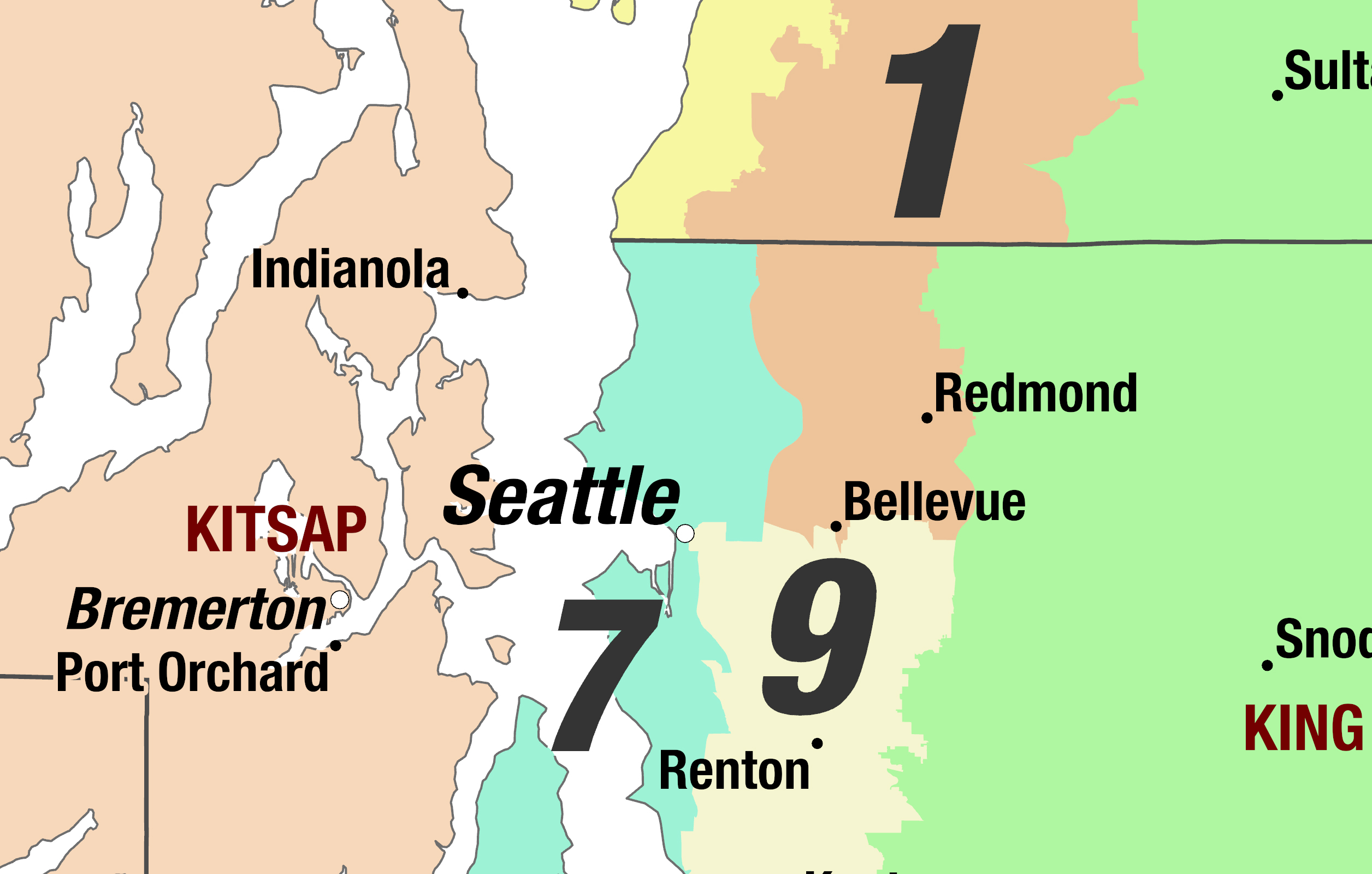

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Washington State’s Voting Districts. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!