Navigating The Landscape: An Exploration Of Wisconsin’s Topographic Map
Navigating the Landscape: An Exploration of Wisconsin’s Topographic Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: An Exploration of Wisconsin’s Topographic Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: An Exploration of Wisconsin’s Topographic Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: An Exploration of Wisconsin’s Topographic Map
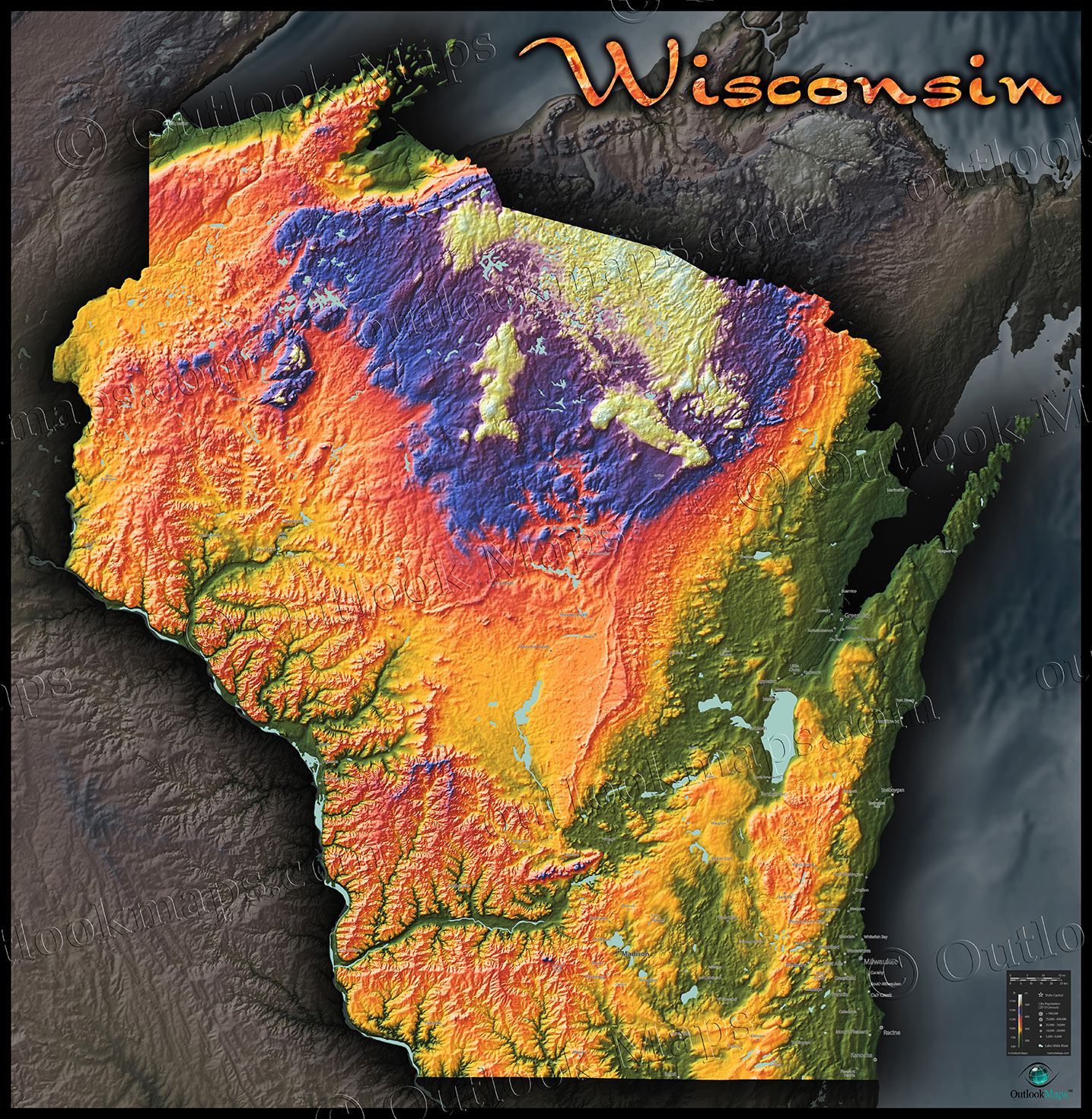
Wisconsin, a state known for its diverse geography, from the rolling hills of the Driftless Area to the vast expanse of Lake Superior, presents a fascinating landscape to explore. Understanding the intricate details of this terrain is crucial for various activities, from outdoor recreation to resource management. This is where topographic maps, detailed representations of the Earth’s surface, become indispensable tools.
Understanding Topographic Maps: A Visual Representation of Terrain
Topographic maps, also known as "topo maps," are visual representations of the Earth’s surface, capturing not just the location of features but also their elevation. They provide a comprehensive understanding of the land’s shape, including hills, valleys, rivers, and other natural and man-made features.
Key Elements of a Wisconsin Topographic Map
1. Contour Lines: These are the most prominent feature of a topo map, depicting lines of equal elevation. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the terrain. The difference in elevation between contour lines, known as the contour interval, is crucial for understanding the slope of the land.
2. Elevation Points: These points, marked with numbers, indicate the exact elevation of specific locations on the map. They provide a reference point for understanding the overall elevation profile of the area.
3. Relief Shading: This technique uses shading to create a three-dimensional effect, enhancing the visualization of hills and valleys.
4. Symbols: Topo maps utilize a standardized set of symbols to represent various features, including roads, buildings, water bodies, vegetation, and even cultural landmarks. Understanding these symbols is essential for accurate interpretation of the map.
5. Coordinate Grid: Topo maps are overlaid with a grid system, typically using the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) system, to provide precise geographic coordinates for any location. This is crucial for accurate navigation and location identification.
The Benefits of Utilizing Wisconsin Topographic Maps
1. Navigation and Exploration: Topo maps are invaluable for outdoor enthusiasts, hikers, and anyone navigating unfamiliar terrain. They provide a detailed understanding of the landscape, allowing for safe and efficient route planning.
2. Resource Management: Topographic maps are vital for land management and resource conservation. They help in identifying areas prone to erosion, flooding, or other environmental hazards, aiding in the development of sustainable practices.
3. Infrastructure Planning: Topo maps play a crucial role in the planning and construction of infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and pipelines. They provide essential data on terrain, elevation, and existing infrastructure, facilitating informed decision-making.
4. Environmental Studies: Topo maps are essential tools for researchers studying various environmental processes, including landform evolution, hydrological cycles, and biodiversity. They provide a baseline for understanding the dynamics of the natural world.
5. Educational Value: Topo maps offer a valuable educational tool for students learning about geography, geology, and environmental science. They provide a hands-on approach to understanding the complexities of the Earth’s surface.
Wisconsin Topographic Maps: A Detailed Look at the State’s Terrain
Wisconsin’s topography is a fascinating tapestry of diverse landscapes, each with its unique characteristics.
1. The Driftless Area: Located in the southwestern corner of the state, this region is characterized by rolling hills, deep valleys, and a lack of glacial deposits, hence its name. The Driftless Area is renowned for its scenic beauty and unique ecosystems, making it a popular destination for hiking, camping, and other outdoor activities.
2. The Northern Highlands: This region, encompassing the northernmost parts of the state, features a mix of forested areas, lakes, and rivers. The terrain is generally hilly, with some areas reaching elevations of over 1,000 feet. The Northern Highlands are a haven for wildlife and offer excellent opportunities for fishing, boating, and wildlife viewing.
3. The Central Sands: This region, located in central Wisconsin, is characterized by extensive sand plains and rolling hills. The Central Sands are home to a unique ecosystem, including a variety of plants and animals adapted to the sandy soil.
4. The Lake Superior Lowlands: This region, bordering Lake Superior, features a unique combination of rugged shoreline, forested areas, and numerous rivers and streams. The Lake Superior Lowlands are a popular destination for fishing, boating, and scenic drives.
5. The Wisconsin River Valley: This region, stretching across the central part of the state, is defined by the Wisconsin River and its tributaries. The valley is characterized by rolling hills, fertile farmland, and numerous small towns. The Wisconsin River Valley is a popular destination for canoeing, kayaking, and fishing.
Accessing Wisconsin Topographic Maps
Topographic maps for Wisconsin are available from various sources, including:
1. United States Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS provides free access to a vast collection of topographic maps, including those covering Wisconsin. Their website, https://www.usgs.gov/, offers a user-friendly interface for searching and downloading maps.
2. National Geographic: National Geographic offers a range of topographic maps, including those specifically designed for outdoor recreation. Their website, https://www.nationalgeographic.com/, provides information on available maps and purchase options.
3. Online Mapping Services: Various online mapping services, such as Google Maps and MapQuest, offer limited topographic information. However, specialized mapping platforms like CalTopo and Gaia GPS provide more detailed topographic data, including contour lines, elevation profiles, and other relevant information.
4. Local Outdoor Stores: Many outdoor stores specializing in hiking, camping, and other outdoor activities carry a selection of topographic maps for Wisconsin.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the contour interval for Wisconsin topographic maps?
The contour interval for USGS topographic maps covering Wisconsin is typically 20 feet, meaning each contour line represents a 20-foot change in elevation.
2. How do I use a topographic map for navigation?
To use a topo map for navigation, you need to understand the symbols, contour lines, and elevation points. Use a compass and a ruler to measure distances and calculate bearings. Always carry a backup navigation tool, such as a GPS device or a smartphone with a mapping app.
3. What are some safety tips for using topographic maps in the wilderness?
Always inform someone of your planned route and expected return time. Carry a map and compass, even if you use a GPS device. Be aware of weather conditions and potential hazards. Dress appropriately for the terrain and weather.
4. How can I contribute to the creation of topographic maps?
Citizen science projects, such as the USGS’s "The National Map," allow volunteers to contribute data and imagery, helping to improve the accuracy and detail of topographic maps.
Conclusion
Wisconsin’s topographic map is a valuable tool for understanding and exploring the state’s diverse landscape. It provides a detailed representation of the terrain, aiding in navigation, resource management, infrastructure planning, and environmental studies. By understanding the key elements of a topo map and utilizing it responsibly, individuals can unlock the secrets of Wisconsin’s natural beauty and navigate its diverse terrain with confidence.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: An Exploration of Wisconsin’s Topographic Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!