Navigating The Continent: A Comprehensive Look At The African Countries Map
Navigating the Continent: A Comprehensive Look at the African Countries Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Continent: A Comprehensive Look at the African Countries Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Continent: A Comprehensive Look at the African Countries Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Continent: A Comprehensive Look at the African Countries Map
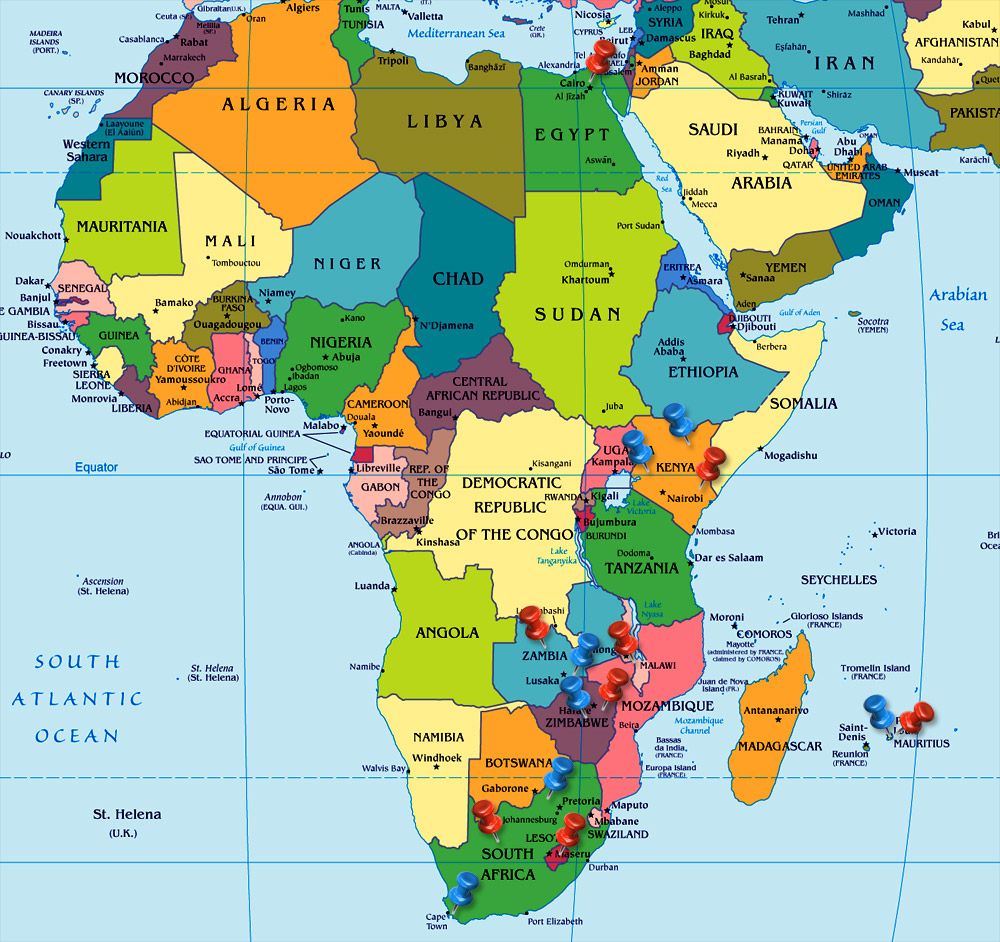
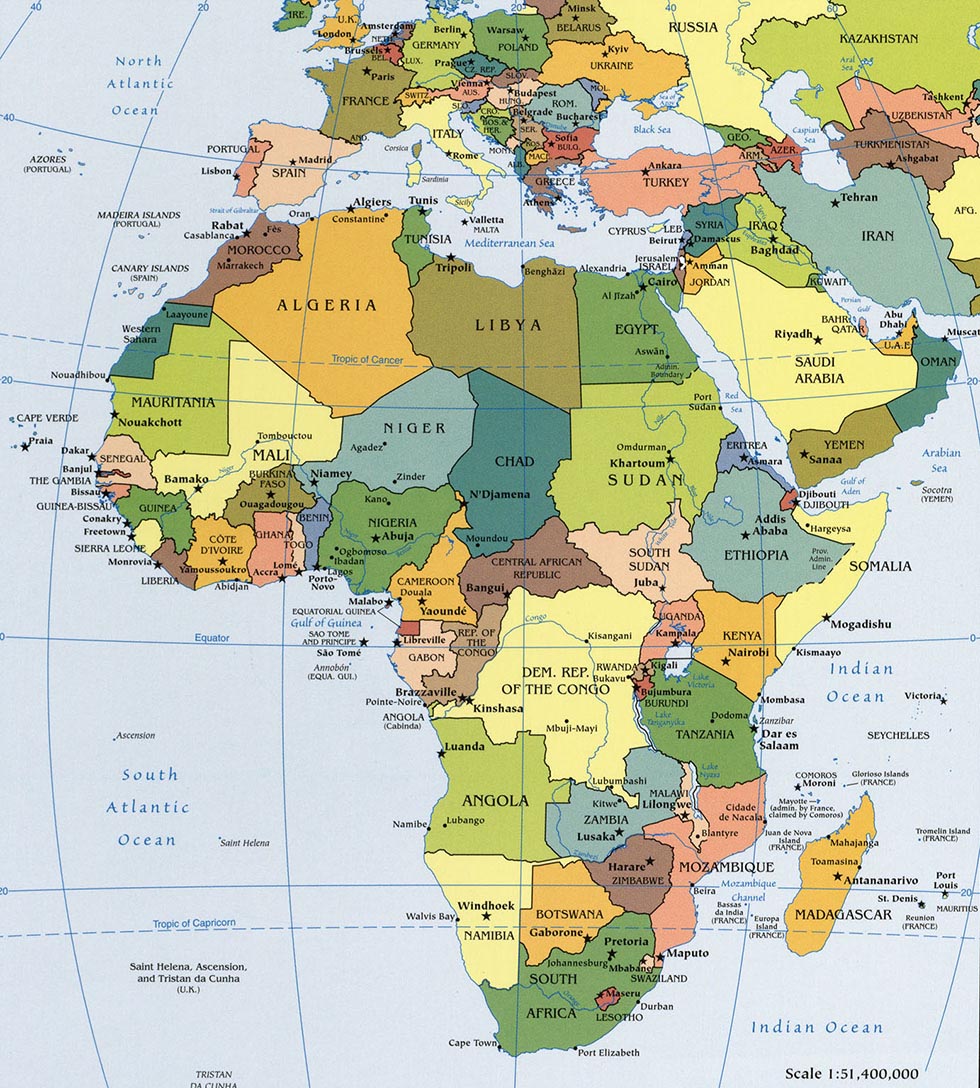
The African continent, a sprawling landmass teeming with diverse landscapes, cultures, and histories, is often perceived as a monolithic entity. However, beneath the surface of this vast expanse lie 54 distinct nations, each with its own unique story to tell. Understanding the intricate tapestry of African countries, their geographical boundaries, and their interconnectedness is paramount for comprehending the continent’s multifaceted dynamics. This article delves into the African countries map, exploring its significance and providing a comprehensive overview of its constituent parts.
A Tapestry of Nations: Demarcating Boundaries and Identities
The African countries map is more than just a visual representation of political divisions; it is a reflection of complex historical processes, cultural exchanges, and evolving identities. The current configuration of African states is a product of colonial legacies, independence movements, and post-colonial struggles for self-determination.
Colonial Legacies and the Scramble for Africa:
The late 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed the "Scramble for Africa," a period of intense European colonization that carved up the continent into arbitrary territories. This process largely disregarded existing ethnic, linguistic, and cultural boundaries, leading to the creation of artificial states that often lacked internal cohesion.
Independence Movements and the Rise of New Nations:
Following World War II, a wave of independence movements swept across Africa, culminating in the emergence of numerous sovereign states. This period saw the dismantling of colonial empires and the establishment of new national identities. However, the legacy of colonial boundaries continued to shape political and economic realities, often leading to internal conflict and instability.
Post-Colonial Challenges and the Quest for Unity:
The post-colonial era presented African nations with a myriad of challenges, including economic development, political stability, and the resolution of inter-state conflicts. The continent grappled with issues of poverty, inequality, and the legacies of colonial exploitation. This period also witnessed the emergence of pan-African movements, seeking to foster unity and cooperation among African states.
Understanding the Map: A Journey Through Diverse Landscapes and Cultures
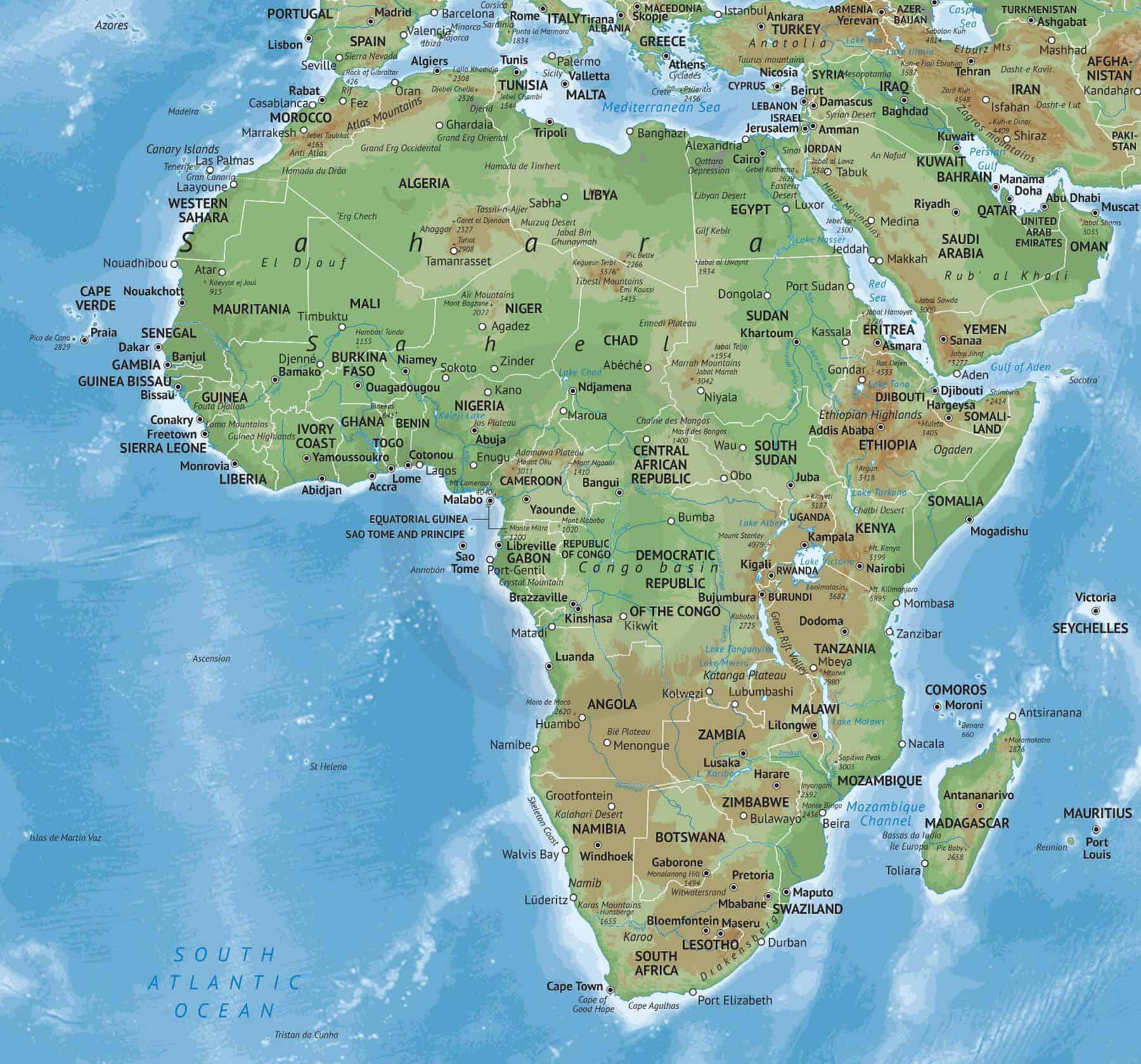
The African countries map provides a visual framework for exploring the continent’s diverse landscapes and cultures. From the towering peaks of Mount Kilimanjaro to the lush rainforests of the Congo Basin, from the arid deserts of the Sahara to the fertile plains of the Nile Valley, Africa offers a stunning array of geographical wonders.
Regional Variations and Geographic Diversity:
The continent can be broadly divided into five major regions: North Africa, West Africa, Central Africa, East Africa, and Southern Africa. Each region boasts distinct geographical features, climates, and cultural identities.
- North Africa: Characterized by the Sahara Desert, the Atlas Mountains, and a predominantly Arab and Berber population.
- West Africa: Known for its coastal savannas, rainforests, and a rich cultural heritage influenced by trans-Saharan trade routes.
- Central Africa: Home to the Congo Basin, a vast rainforest region with diverse indigenous cultures.
- East Africa: Characterized by the Great Rift Valley, volcanic mountains, and a blend of cultures influenced by Arab and Indian traders.
- Southern Africa: Known for its diverse landscapes, including the Kalahari Desert, the Drakensberg Mountains, and a rich history of indigenous cultures.
Cultural Tapestry: A Mosaic of Traditions and Beliefs
The African countries map is a testament to the continent’s remarkable cultural diversity. From the vibrant traditions of the Maasai in East Africa to the ancient rituals of the Dogon people in West Africa, from the intricate art of the Yoruba in Nigeria to the rich musical heritage of South Africa, Africa boasts a kaleidoscope of cultural expressions.
Language Diversity: A Symphony of Sounds
Africa is home to over 2,000 languages, making it one of the most linguistically diverse continents in the world. The official languages of African countries reflect the historical influences of colonialism, migration patterns, and cultural exchanges.
Religion and Belief Systems:
Africa is a continent of diverse religious beliefs, with Islam, Christianity, traditional African religions, and other faiths coexisting. The dominant religions vary across regions, reflecting historical influences and cultural dynamics.
Economic Landscapes: A Spectrum of Development
The African countries map reveals a wide spectrum of economic realities. While some nations have experienced significant economic growth in recent years, others continue to grapple with poverty, inequality, and a lack of infrastructure.
Natural Resources and Economic Development:
Africa is rich in natural resources, including oil, diamonds, gold, and minerals. However, the equitable distribution and sustainable management of these resources remain significant challenges.
Challenges and Opportunities: Shaping the Future of Africa
The African countries map serves as a reminder of the continent’s potential and the challenges it faces. The map highlights the interconnectedness of African nations and the need for cooperation and collaboration to address common challenges.
Political Stability and Conflict Resolution:
Political instability and conflict continue to plague many African nations, hindering economic development and undermining peace and security. Addressing these issues requires robust governance, inclusive political systems, and effective conflict resolution mechanisms.
Economic Development and Poverty Reduction:
Addressing poverty and promoting sustainable economic growth are crucial priorities for African nations. This requires investments in education, healthcare, infrastructure, and the diversification of economies.
Regional Integration and Cooperation:
Strengthening regional integration and cooperation among African countries is vital for achieving shared goals. This involves fostering trade, promoting investment, and coordinating policies to address common challenges.
Sustainability and Environmental Conservation:
Africa’s vast natural resources and ecosystems require careful management and conservation. Sustainable practices are crucial for protecting biodiversity, mitigating climate change, and ensuring the well-being of future generations.
FAQs: A Deeper Dive into the African Countries Map
1. How many countries are there in Africa?
There are 54 sovereign states recognized by the United Nations as African countries.
2. What is the largest country in Africa?
Algeria is the largest country in Africa by land area, spanning over 2,381,741 square kilometers.
3. What is the smallest country in Africa?
The Seychelles, an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, is the smallest country in Africa, with a land area of just 455 square kilometers.
4. What is the most populous country in Africa?
Nigeria is the most populous country in Africa, with an estimated population of over 200 million.
5. What are the official languages of African countries?
The official languages of African countries vary widely, reflecting the continent’s linguistic diversity. Some countries have multiple official languages, often reflecting colonial legacies and cultural influences.
6. What are the major religions in Africa?
Islam, Christianity, and traditional African religions are the dominant religions in Africa. The distribution of religions varies across regions, reflecting historical influences and cultural dynamics.
7. What are the major economic sectors in Africa?
Africa’s economies are diverse, with major sectors including agriculture, mining, tourism, and services. The specific economic activities vary across countries, reflecting their natural resources, infrastructure, and development levels.
8. What are the major challenges facing African countries?
African countries face a myriad of challenges, including poverty, inequality, political instability, conflict, climate change, and a lack of infrastructure.
9. What are the opportunities for development in Africa?
Africa presents significant opportunities for development, driven by its growing population, abundant natural resources, and a burgeoning middle class. The continent’s potential for economic growth, technological advancement, and social progress is immense.
10. What is the role of the African Union in promoting development and cooperation?
The African Union (AU) is a continental organization that aims to promote peace, security, and development in Africa. The AU plays a crucial role in fostering cooperation, resolving conflicts, and coordinating economic development initiatives.
Tips for Navigating the African Countries Map:
1. Utilize Interactive Maps: Explore online interactive maps that provide detailed information about African countries, including their borders, capitals, major cities, and geographical features.
2. Focus on Regional Variations: Recognize that Africa is a continent of diverse regions, each with distinct characteristics. Explore the unique features and challenges of each region to gain a comprehensive understanding.
3. Engage with Cultural Diversity: Immerse yourself in the rich cultural tapestry of Africa by exploring its languages, traditions, arts, and music.
4. Consider Historical Context: Understand the historical influences that have shaped the African countries map, including colonialism, independence movements, and post-colonial struggles.
5. Stay Informed about Current Events: Keep abreast of current events in Africa, including political developments, economic trends, and social issues.
Conclusion: A Journey of Discovery and Understanding
The African countries map is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s complex dynamics. It reveals a tapestry of nations, each with its own unique story and challenges. By engaging with the map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the continent’s diversity, its historical legacies, and its potential for growth and progress. Understanding the African countries map is not just about memorizing geographical boundaries; it is about embracing the richness and complexity of the continent, its people, and its stories.
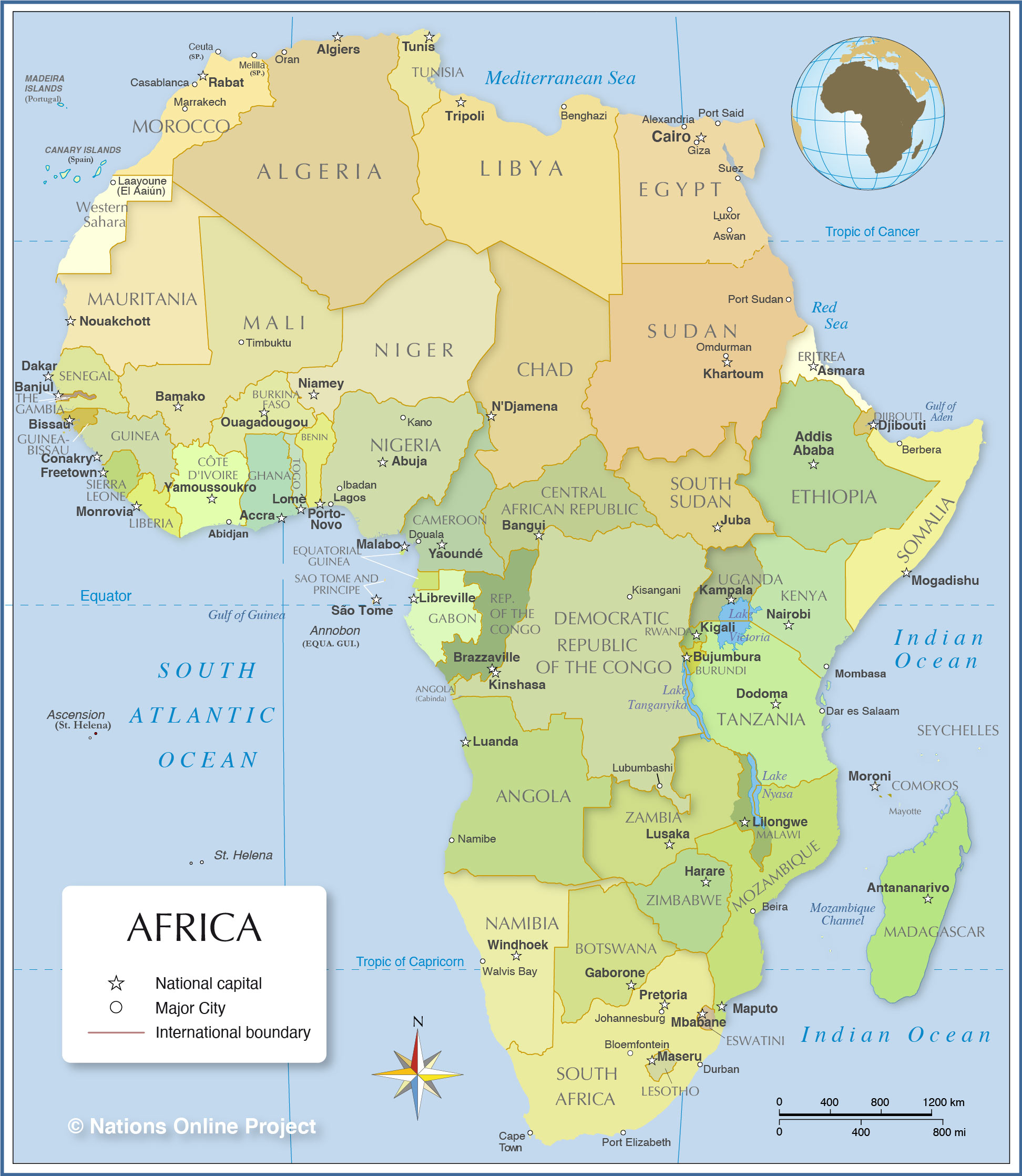
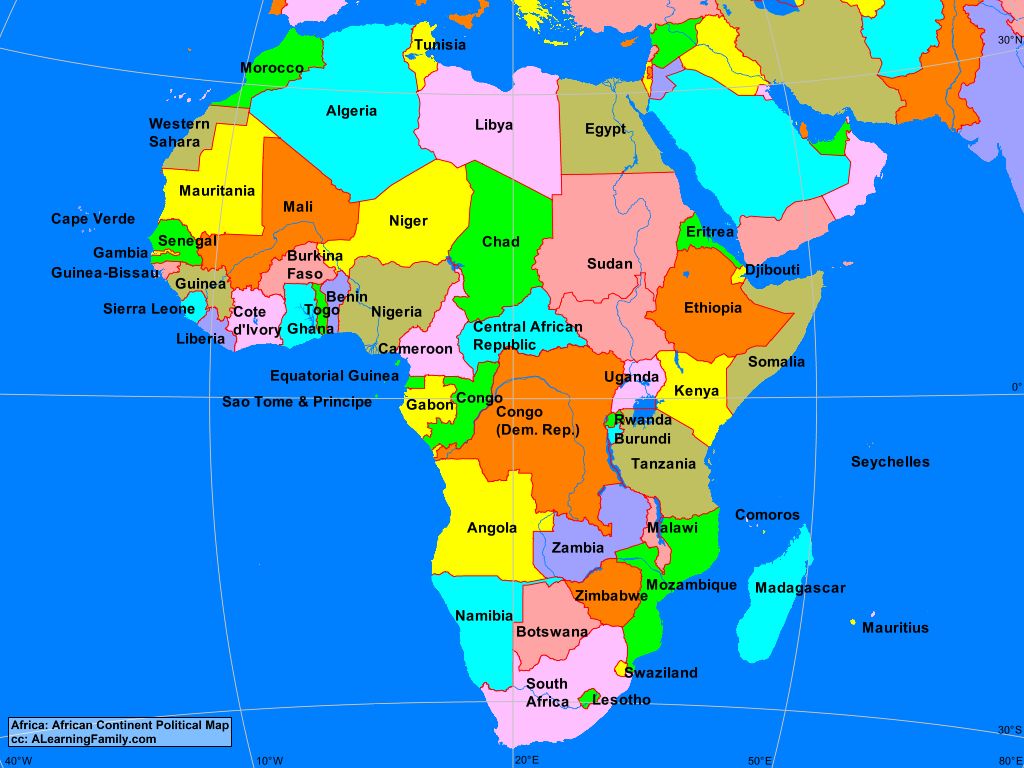
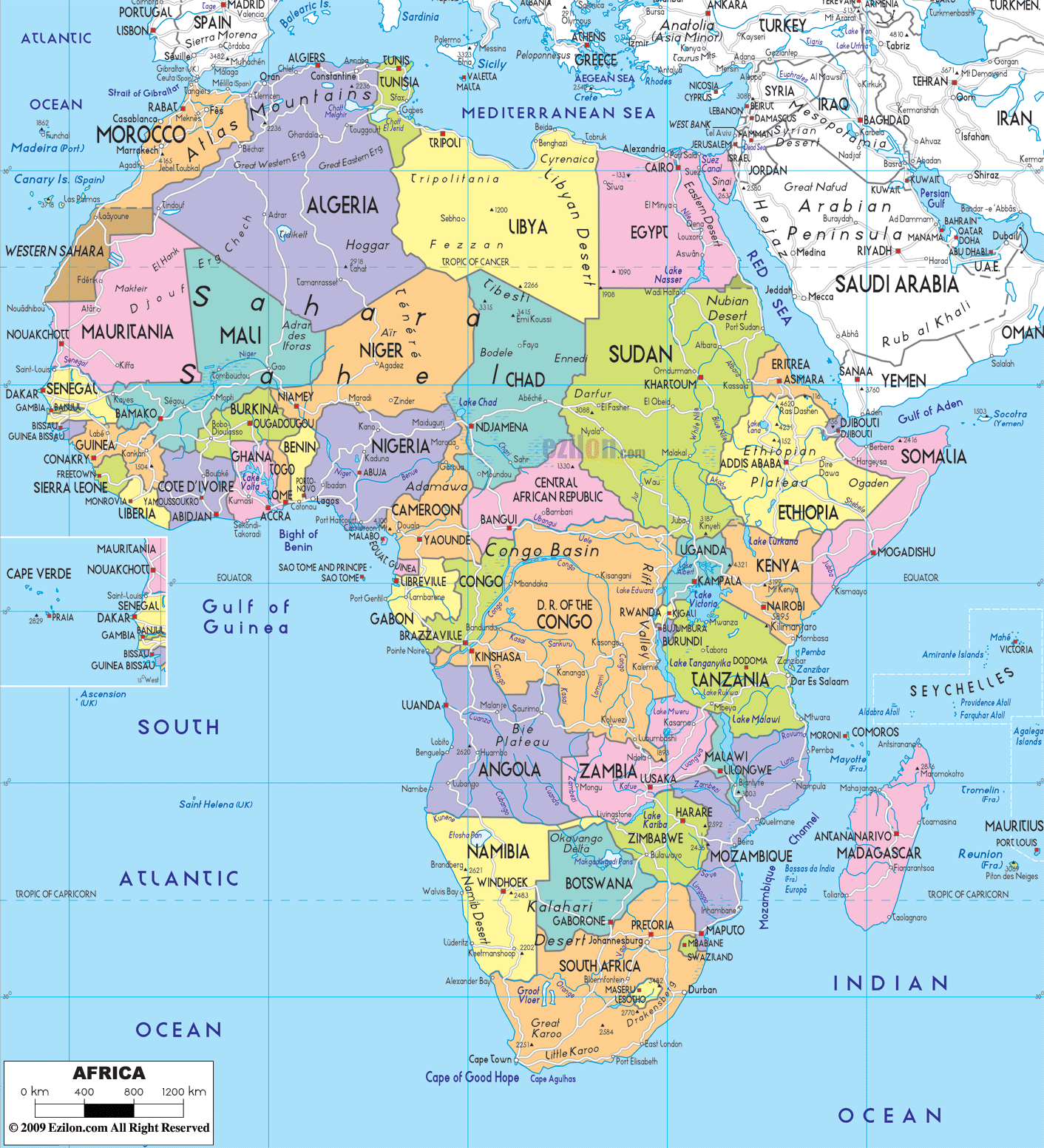



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Continent: A Comprehensive Look at the African Countries Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!