Mapping Representation: An Examination Of Wisconsin’s Legislative Districts
Mapping Representation: An Examination of Wisconsin’s Legislative Districts
Related Articles: Mapping Representation: An Examination of Wisconsin’s Legislative Districts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping Representation: An Examination of Wisconsin’s Legislative Districts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Representation: An Examination of Wisconsin’s Legislative Districts

The intricate tapestry of American democracy is woven with threads of representation, each thread representing a constituency, a voice, and a stake in the political process. In Wisconsin, this tapestry is vividly illustrated by the state’s legislative districts, a complex network of geographically defined areas that determine how citizens connect with their elected officials. These districts, the subject of ongoing debate and scrutiny, play a pivotal role in shaping the political landscape of the state.
A Framework for Representation:
Wisconsin’s legislative districts are the foundation upon which the state’s political structure rests. They are the tangible manifestation of the principle of "one person, one vote," ensuring that each citizen’s voice carries equal weight in the political arena. The state is divided into 33 Senate districts and 99 Assembly districts, each encompassing a specific geographic area with a defined population. This division, while seemingly straightforward, is the result of a complex process that involves demographic analysis, political considerations, and legal requirements.
The Importance of Districting:
The manner in which legislative districts are drawn has profound implications for the democratic process. Fair and equitable districting ensures that all citizens have an equal opportunity to elect representatives who reflect their values and interests. Conversely, gerrymandering, the practice of manipulating district boundaries for partisan advantage, undermines the principles of fair representation and can lead to unrepresentative outcomes.
Historical Context and Evolution:
The process of drawing legislative districts in Wisconsin, like in many other states, has evolved over time, reflecting societal changes and political shifts. In the early 20th century, districts were often drawn with little regard for population equality, leading to disparities in representation. The landmark Supreme Court case, Reynolds v. Sims (1964), established the principle of "one person, one vote," ushering in an era of redistricting based on population equality.
The Redistricting Process:
The process of redrawing legislative districts in Wisconsin is a complex undertaking that involves multiple stakeholders and legal considerations. Every ten years, following the decennial census, the state’s legislative districts are redrawn to reflect population shifts and ensure equal representation. This process is overseen by the Wisconsin Government Accountability Board (GAB), an independent body responsible for administering elections and overseeing redistricting.
Challenges and Controversies:
Despite the legal framework designed to ensure fair and equitable redistricting, the process remains fraught with challenges and controversies. Partisan politics often play a significant role in shaping district boundaries, leading to accusations of gerrymandering and manipulation. The balance between maintaining communities of interest and ensuring equal representation presents a constant challenge for redistricting officials.
The Impact of Districting on Policy:
The manner in which legislative districts are drawn has a direct impact on the policy-making process. Districts with a high concentration of voters with similar political views can lead to the election of representatives who are more likely to support policies aligned with those views. This can create a situation where certain interests are overrepresented while others are underrepresented, potentially leading to policy outcomes that do not reflect the broader interests of the state.
The Future of Districting in Wisconsin:
The issue of legislative districting is a constant topic of debate and scrutiny in Wisconsin, as in many other states. Ongoing efforts to reform the redistricting process aim to address concerns about partisan manipulation and ensure that districts are drawn in a fair and transparent manner. Technological advancements, such as the use of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and sophisticated data analysis techniques, are playing an increasingly important role in the redistricting process, enabling more precise and data-driven approaches to district design.
FAQs about Wisconsin’s Legislative Districts:
Q: How are legislative districts drawn in Wisconsin?
A: The process of drawing legislative districts in Wisconsin is governed by state law and involves a combination of demographic analysis, political considerations, and legal requirements. The Wisconsin Government Accountability Board (GAB) oversees the redistricting process, which occurs every ten years following the decennial census.
Q: What are the criteria used to draw legislative districts in Wisconsin?
A: The primary criteria for drawing legislative districts in Wisconsin are:
- Population Equality: Districts must be as equal in population as possible, adhering to the principle of "one person, one vote."
- Contiguity: Districts must be geographically contiguous, meaning that all parts of the district must be connected.
- Communities of Interest: Districts should respect communities of interest, ensuring that residents with shared interests are represented together.
Q: How often are legislative districts redrawn in Wisconsin?
A: Legislative districts in Wisconsin are redrawn every ten years, following the decennial census, to reflect population shifts and ensure equal representation.
Q: What is the role of the Wisconsin Government Accountability Board (GAB) in redistricting?
A: The GAB is responsible for overseeing the redistricting process in Wisconsin. This includes receiving and reviewing proposed district maps, holding public hearings, and ultimately approving the final district maps.
Q: What is gerrymandering, and how does it affect Wisconsin’s legislative districts?
A: Gerrymandering is the practice of manipulating district boundaries for partisan advantage. This can lead to unrepresentative outcomes, where one party has a disproportionate number of seats in the legislature despite not receiving a majority of the votes statewide.
Tips for Understanding Wisconsin’s Legislative Districts:
- Consult Official Resources: The Wisconsin Government Accountability Board (GAB) website provides comprehensive information about redistricting, including maps, data, and reports.
- Engage with Local Officials: Contact your local elected officials and ask questions about the redistricting process and its impact on your community.
- Participate in Public Hearings: Attend public hearings on redistricting to voice your concerns and provide input on proposed district maps.
- Stay Informed: Follow news coverage and analysis of redistricting issues to stay informed about the latest developments.
Conclusion:
Wisconsin’s legislative districts are the building blocks of the state’s political system, shaping the representation and policy outcomes that impact the lives of all citizens. While the process of redistricting is complex and often controversial, it remains a crucial element of a healthy democracy. By understanding the principles and challenges associated with districting, citizens can actively engage in the process and advocate for fair and equitable representation in the state legislature. As the state continues to evolve and its population shifts, the ongoing debate over districting will undoubtedly remain a critical part of the political landscape, ensuring that the voices of all Wisconsin residents are heard and represented.

![]()

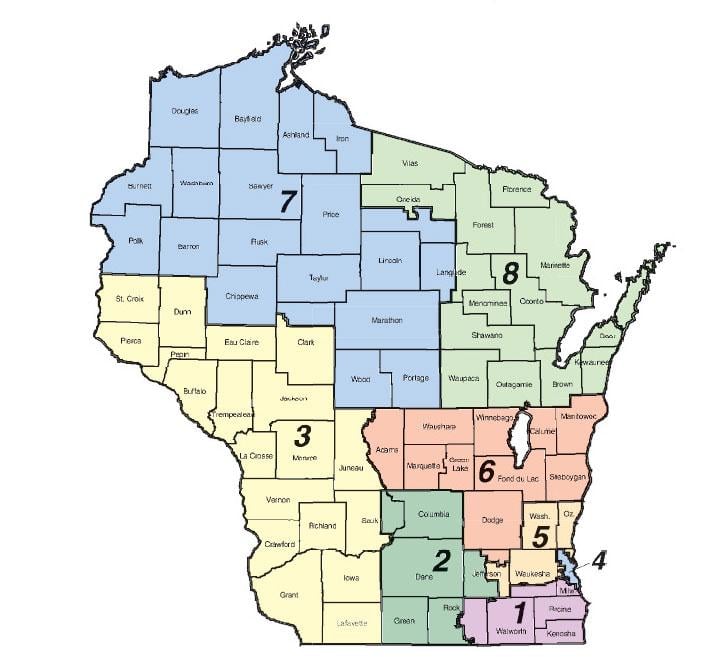
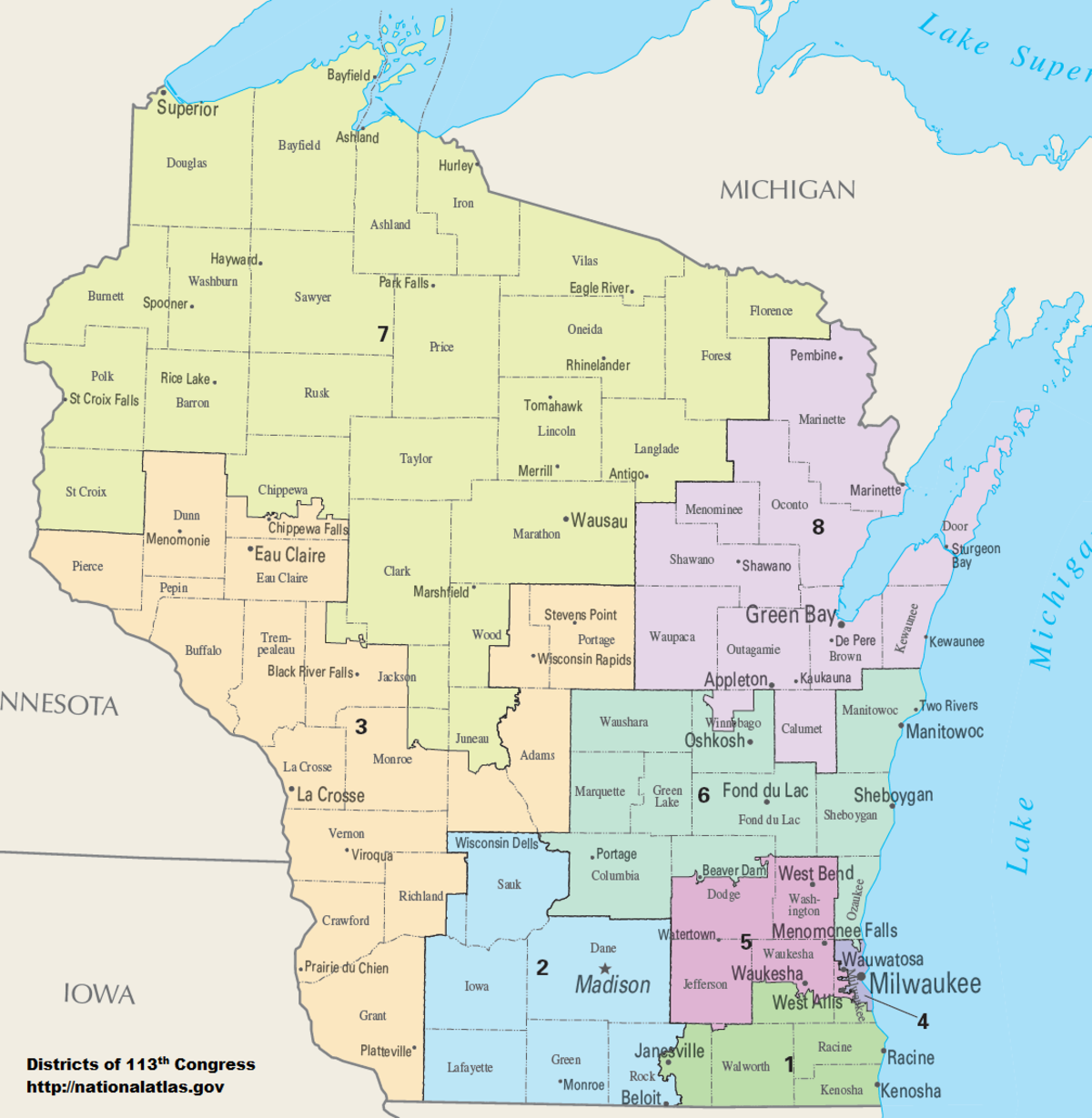
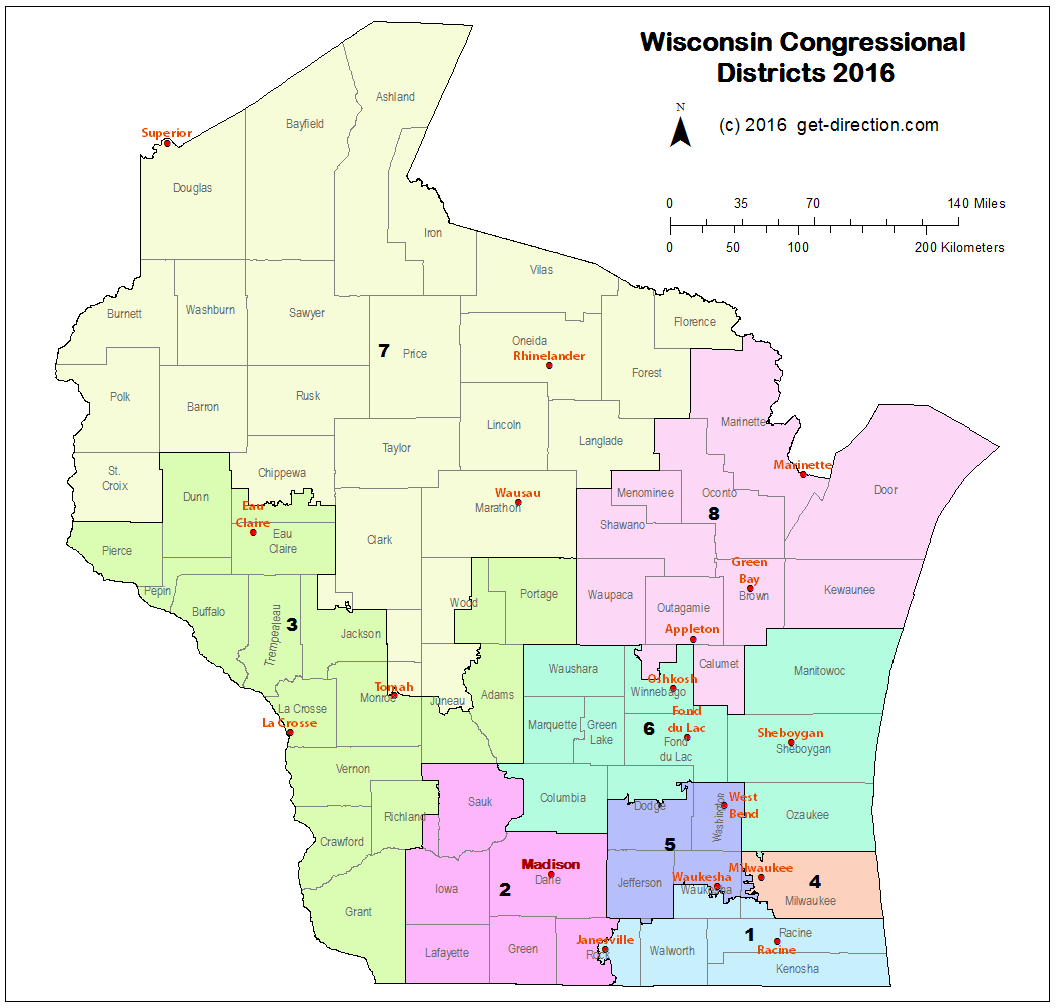


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Representation: An Examination of Wisconsin’s Legislative Districts. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!