Delineating Democracy: A Look At Wisconsin’s Voting Districts
Delineating Democracy: A Look at Wisconsin’s Voting Districts
Related Articles: Delineating Democracy: A Look at Wisconsin’s Voting Districts
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delineating Democracy: A Look at Wisconsin’s Voting Districts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delineating Democracy: A Look at Wisconsin’s Voting Districts

The act of drawing electoral boundaries, known as redistricting, is a fundamental aspect of democratic governance. It ensures fair representation and allows for the equitable distribution of political power. In the United States, this process occurs every ten years following the decennial census, with each state tasked with redrawing its congressional and state legislative districts.
Wisconsin, a state with a rich history of political engagement, is no exception. The state’s voting districts, which determine the allocation of seats in the U.S. House of Representatives and the Wisconsin State Legislature, have been the subject of intense scrutiny and debate over the years. This scrutiny stems from the inherent power of redistricting to influence electoral outcomes, potentially leading to gerrymandering – the manipulation of district boundaries to favor a particular political party or group.
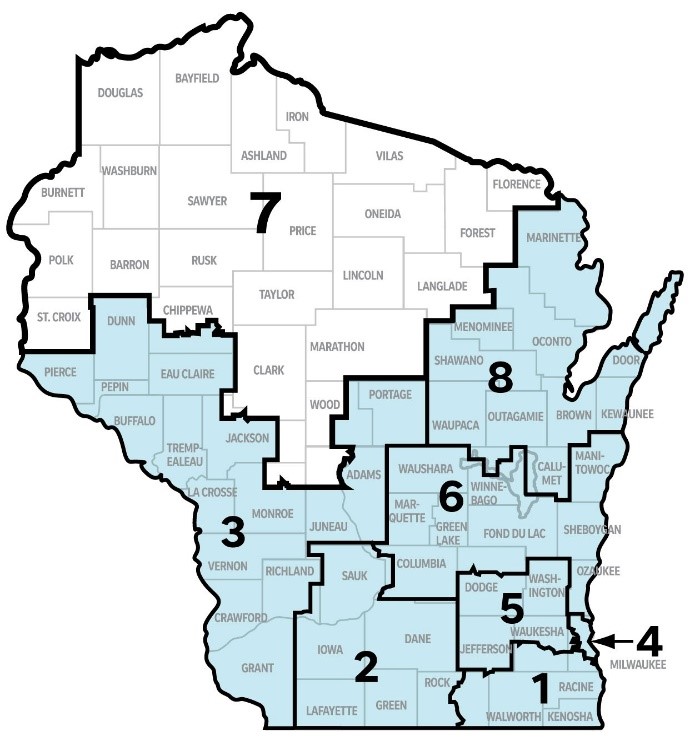
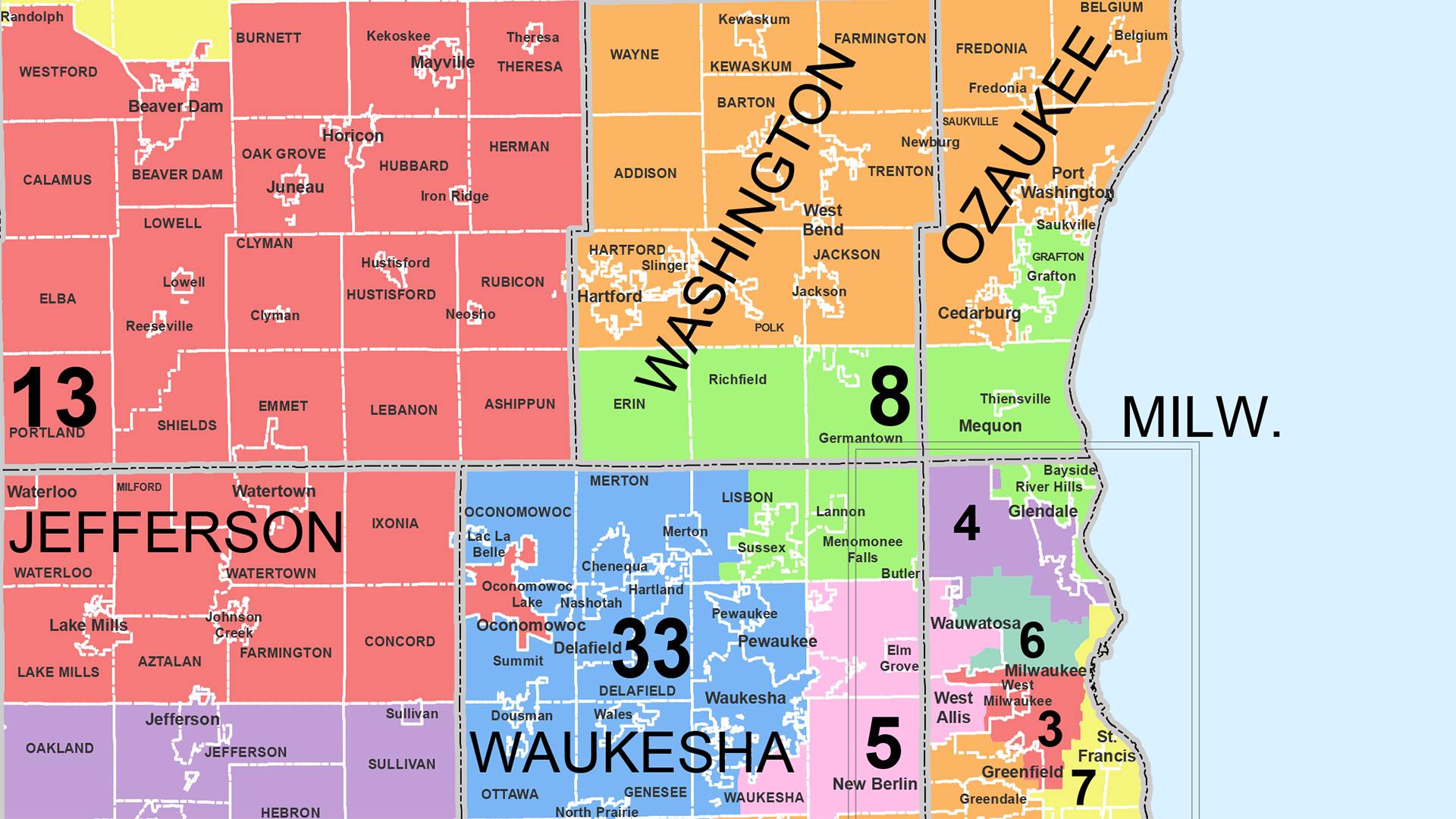
Understanding the Map: A Visual Representation of Political Power
The map of Wisconsin’s voting districts provides a visual representation of the state’s political landscape. Each district, delineated by distinct boundaries, represents a specific geographical area and its corresponding population. These districts are not static entities; they are subject to change every decade to reflect population shifts and ensure equal representation.
The map’s significance lies in its ability to reveal patterns of political representation and potential imbalances in electoral power. By analyzing the distribution of districts across the state, one can gain insights into the voting preferences of different regions, the concentration of specific demographics within certain districts, and the potential impact of redistricting on electoral outcomes.
Navigating the Complexities of Redistricting
Redistricting is a complex process governed by a set of legal principles and practical considerations. The guiding principles include:
- Equal Population: Districts must contain roughly equal populations, ensuring that each voter has an equal say in the electoral process.
- Contiguity: Districts must be geographically connected, preventing the fragmentation of communities and ensuring that residents share a common interest.
- Compactness: Districts should be as compact as possible, minimizing the distortion of electoral boundaries and preventing the creation of oddly shaped districts.
- Respect for Communities of Interest: Redistricting should avoid dividing communities with shared interests, such as racial or ethnic minorities, ensuring their representation.
However, these principles are often challenged by political pressures and the desire to maintain partisan advantage. This tension can lead to gerrymandering, where districts are drawn to benefit a particular party or group, potentially undermining fair representation and the integrity of the electoral process.
The Wisconsin Experience: A Case Study in Redistricting
Wisconsin has experienced a long history of redistricting controversies, with accusations of gerrymandering surfacing in both congressional and state legislative districts. The state’s political landscape, characterized by a close division between Democrats and Republicans, has contributed to the intensity of these debates.
In recent years, several lawsuits have challenged the fairness of Wisconsin’s redistricting process. These legal challenges have centered on allegations of partisan gerrymandering, where district lines are drawn to give one party an unfair advantage in elections. While the courts have ruled against some of these challenges, the debate continues, highlighting the complexities of balancing the principles of fair representation with the potential for partisan manipulation.
FAQs about Wisconsin’s Voting Districts
1. How often are Wisconsin’s voting districts redrawn?
Wisconsin’s voting districts are redrawn every ten years following the decennial census, ensuring that they reflect changes in population distribution.
2. Who is responsible for drawing Wisconsin’s voting districts?
In Wisconsin, the responsibility for drawing congressional and state legislative districts lies with the Wisconsin Legislature.
3. How does the process of redistricting work in Wisconsin?
The Wisconsin Legislature is responsible for drawing new district lines based on the decennial census data. The process involves public hearings, expert input, and ultimately, legislative approval.
4. What are the legal challenges to Wisconsin’s redistricting process?
Legal challenges to Wisconsin’s redistricting process often center on allegations of partisan gerrymandering, arguing that district lines are drawn to favor one political party over another.
5. How does the map of Wisconsin’s voting districts impact elections?
The map of Wisconsin’s voting districts can significantly impact elections by determining the concentration of voters with specific political preferences within each district. This can influence the outcome of elections and the representation of different political viewpoints.
Tips for Understanding Wisconsin’s Voting Districts
- Consult Official Sources: Refer to official maps and data published by the Wisconsin Elections Commission for accurate information on district boundaries and demographics.
- Engage with Local Resources: Contact your local election officials or community organizations to learn more about your specific district and its representation.
- Stay Informed about Redistricting: Follow the news and participate in public discussions about redistricting to understand the process and its potential impact on your community.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Quest for Fair Representation
The map of Wisconsin’s voting districts serves as a powerful symbol of the ongoing quest for fair representation in a democratic society. While redistricting is an essential process for ensuring equal representation, it remains a complex and often contentious issue. The ongoing debate surrounding gerrymandering highlights the need for transparency, accountability, and public engagement in the redistricting process. By understanding the principles and challenges of redistricting, citizens can actively participate in shaping the political landscape and ensuring that their voices are heard in the electoral arena.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delineating Democracy: A Look at Wisconsin’s Voting Districts. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!