A Look At Nuclear Power In Washington State: A Vital Component Of The Energy Landscape
A Look at Nuclear Power in Washington State: A Vital Component of the Energy Landscape
Related Articles: A Look at Nuclear Power in Washington State: A Vital Component of the Energy Landscape
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Look at Nuclear Power in Washington State: A Vital Component of the Energy Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Look at Nuclear Power in Washington State: A Vital Component of the Energy Landscape
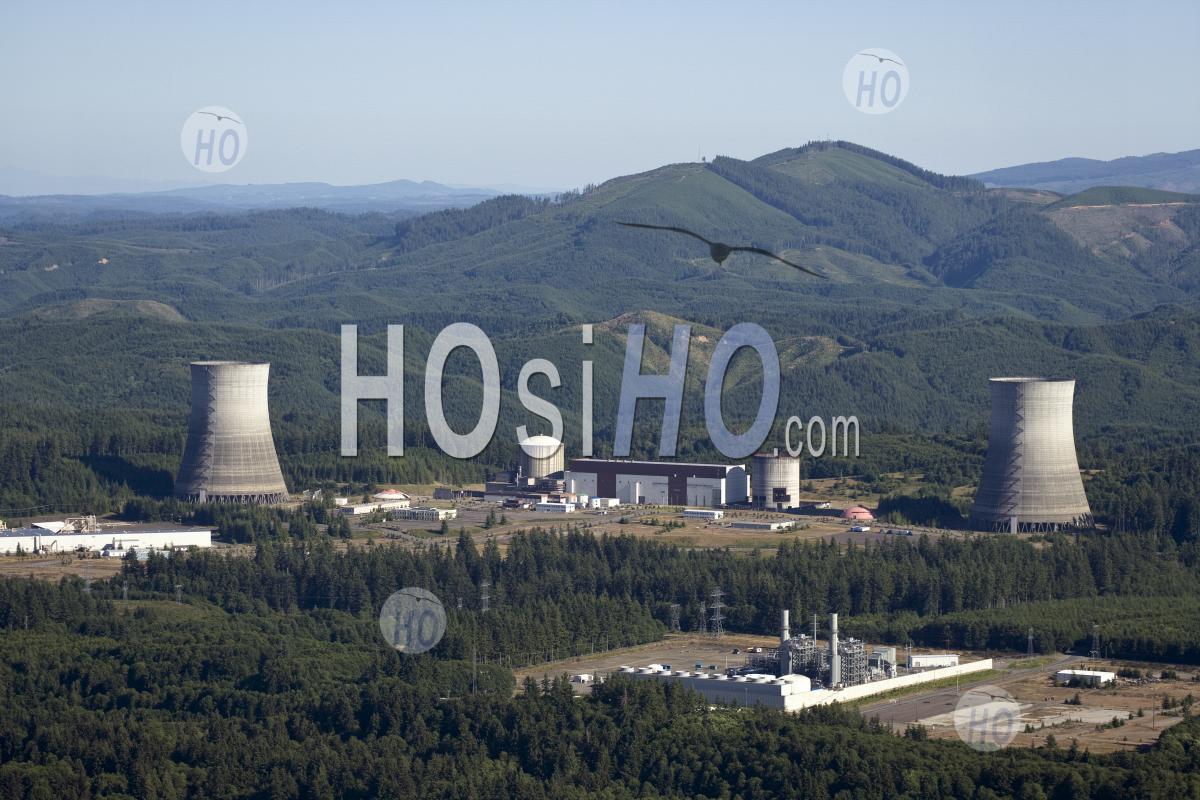

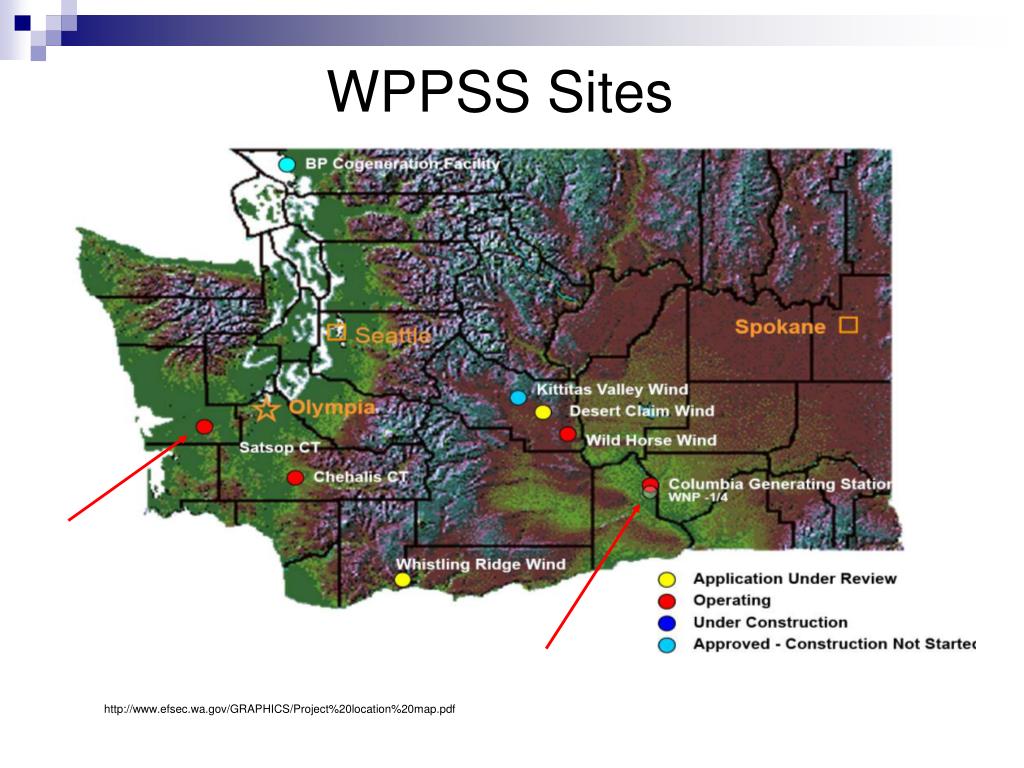
Washington State, renowned for its scenic beauty and progressive environmental policies, also boasts a significant presence in the nuclear energy sector. While the state currently operates only one nuclear power plant, the Columbia Generating Station, its history with nuclear energy is rich and complex, reflecting the evolving national debate surrounding this technology.
The Columbia Generating Station: A Powerhouse in the Pacific Northwest
Located near Richland, Washington, the Columbia Generating Station is a pressurized water reactor owned and operated by Energy Northwest, a public power consortium. It began commercial operation in 1984 and remains a crucial source of electricity for the state and the region, generating enough power to serve over 800,000 homes. The plant’s significance extends beyond its immediate contribution to the energy grid.
Economic and Environmental Contributions:
- Economic Engine: The Columbia Generating Station is a significant economic driver for the region, employing hundreds of skilled workers and generating millions in tax revenue. Its operations support a network of local businesses and contribute to the overall prosperity of the surrounding communities.
- Environmental Benefits: Nuclear power is a low-carbon energy source, emitting significantly fewer greenhouse gases than fossil fuel plants. The Columbia Generating Station plays a vital role in reducing the state’s carbon footprint and mitigating climate change.
- Reliability and Stability: Nuclear power plants are known for their consistent and reliable energy production, providing a stable and predictable source of electricity for the grid. This reliability is particularly crucial in a region susceptible to fluctuating energy demands and weather patterns.
A Historical Perspective: The Legacy of Nuclear Power in Washington
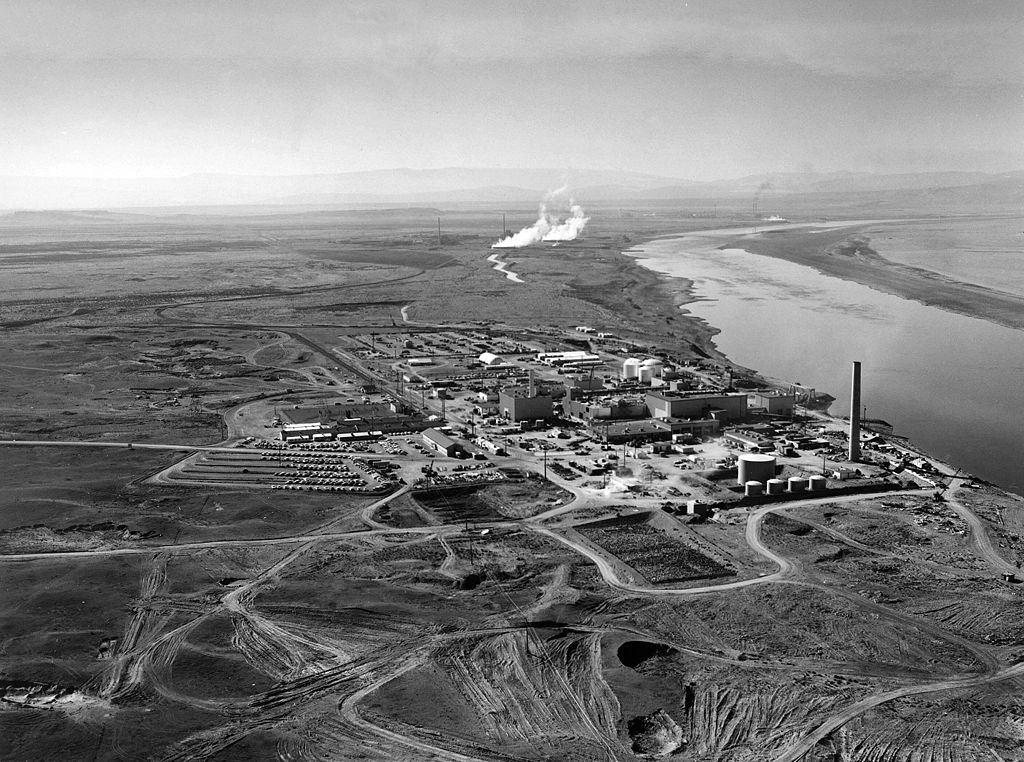
Washington State’s relationship with nuclear power began in the mid-20th century, driven by the nation’s post-World War II pursuit of atomic energy. The state saw the construction of several nuclear reactors, including the Hanford Site, which played a pivotal role in the Manhattan Project and later transitioned to a focus on plutonium production.
However, the state’s enthusiasm for nuclear power waned in the 1970s and 80s, influenced by public concerns about safety, waste disposal, and the proliferation of nuclear weapons. The WPPSS (Washington Public Power Supply System), a consortium responsible for several nuclear projects, faced financial difficulties and ultimately abandoned several reactors, leaving the state with a legacy of unfinished projects and unresolved environmental issues.
The Future of Nuclear Power in Washington: A Balancing Act
The future of nuclear power in Washington State remains a complex and debated topic. While the Columbia Generating Station is currently licensed to operate until 2045, its future beyond that date is uncertain.
- Renewables and Energy Transition: The state has set ambitious goals for transitioning to a clean energy future, with a strong focus on renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. This push for renewables may necessitate the eventual phasing out of nuclear power, even with its low-carbon emissions.
- Safety and Waste Management: Nuclear power remains a controversial topic due to concerns about safety and the long-term management of radioactive waste. Addressing these concerns will be crucial for the continued viability of nuclear power in the state.
- Technological Advancements: Emerging technologies, such as small modular reactors (SMRs), offer potential solutions to some of the challenges associated with traditional nuclear power plants. The development and deployment of these technologies could influence the future of nuclear energy in Washington.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Nuclear Power in Washington
Q: Is nuclear power safe?
A: Nuclear power plants are designed with multiple layers of safety systems and undergo rigorous regulatory oversight. While accidents are possible, the probability of a major incident is extremely low. However, the long-term management of radioactive waste remains a significant concern.
Q: What are the environmental impacts of nuclear power?
A: Nuclear power plants do not emit greenhouse gases during operation, making them a low-carbon energy source. However, the mining and processing of uranium fuel, as well as the disposal of radioactive waste, have environmental impacts that need to be carefully considered.
Q: What are the economic benefits of nuclear power?
A: Nuclear power plants create jobs, generate tax revenue, and provide a stable source of electricity. They also contribute to energy security by reducing reliance on imported fuels.
Q: Is nuclear power a viable solution for climate change?
A: Nuclear power can play a significant role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. However, its long-term sustainability depends on addressing concerns about safety, waste management, and the cost-effectiveness of new technologies.
Tips for Understanding Nuclear Power in Washington
- Engage with local communities: Learn about the history and impact of nuclear power in your region by connecting with local organizations and individuals.
- Seek out credible information: Consult reliable sources like scientific journals, government agencies, and independent research organizations.
- Stay informed about policy developments: Keep abreast of state and federal policies related to nuclear power and their potential implications.
- Consider the full life cycle: When evaluating the environmental impacts of nuclear power, assess the entire process, from uranium mining to waste disposal.
- Engage in thoughtful discussions: Participate in constructive conversations about the future of nuclear energy, acknowledging the diverse perspectives and potential trade-offs.
Conclusion: A Complex and Evolving Landscape
Nuclear power in Washington State represents a complex and evolving landscape, shaped by historical legacies, technological advancements, and evolving societal priorities. While the state currently relies on one operating nuclear power plant, the future of this technology remains uncertain, subject to ongoing debates about safety, waste management, and the role of nuclear energy in a transitioning energy landscape. Engaging in informed discussions, seeking credible information, and understanding the diverse perspectives surrounding nuclear power will be crucial for navigating this complex issue and shaping the future of energy in Washington State.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Look at Nuclear Power in Washington State: A Vital Component of the Energy Landscape. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
