A Landscape Of Diversity: Understanding Vietnam’s Topographic Map
A Landscape of Diversity: Understanding Vietnam’s Topographic Map
Related Articles: A Landscape of Diversity: Understanding Vietnam’s Topographic Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Landscape of Diversity: Understanding Vietnam’s Topographic Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A Landscape of Diversity: Understanding Vietnam’s Topographic Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A Landscape of Diversity: Understanding Vietnam’s Topographic Map
- 3.1 Unveiling Vietnam’s Topographic Tapestry
- 3.2 The Importance of a Topographic Map
- 3.3 Decoding the Features of a Topographic Map
- 3.4 Exploring the Benefits of a Topographic Map
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions about Topographic Maps of Vietnam
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
A Landscape of Diversity: Understanding Vietnam’s Topographic Map
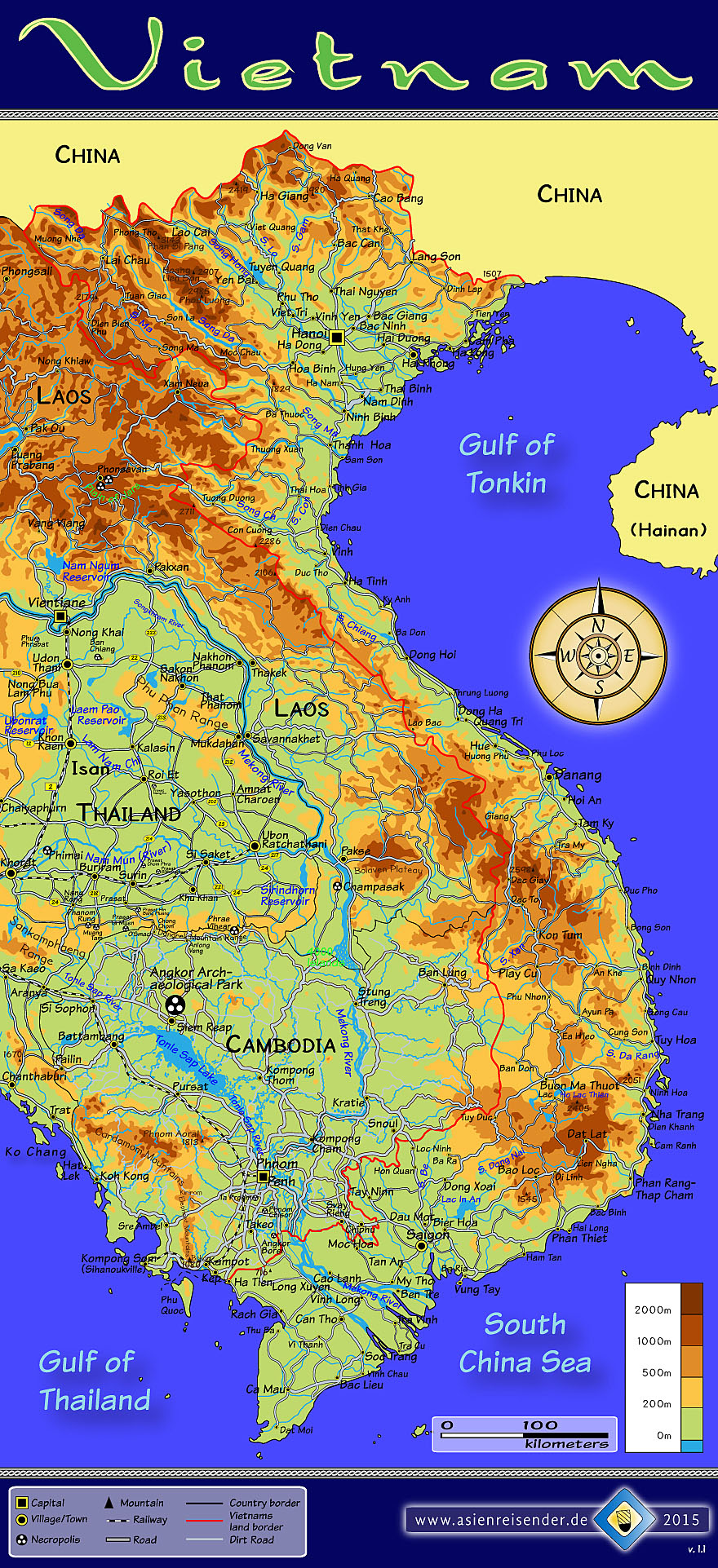
Vietnam’s topography is a tapestry woven from mountains, rivers, deltas, and coastlines, resulting in a breathtaking and diverse landscape. Understanding this topography is crucial for various sectors, from agriculture and infrastructure development to disaster preparedness and tourism. A topographic map of Vietnam provides a detailed visual representation of this diverse terrain, serving as an invaluable tool for navigating, understanding, and managing the country’s unique environment.
Unveiling Vietnam’s Topographic Tapestry
The Vietnamese landscape is characterized by a striking interplay of contrasting elements:
- The Majestic Mountains: The Annamite Cordillera, running parallel to the coast, forms the backbone of Vietnam, reaching heights of over 3,000 meters. These mountains are home to dense forests, diverse flora and fauna, and numerous ethnic minority groups.
- The Mighty Rivers: Vietnam’s rivers are lifelines, shaping the landscape and providing essential resources. The Mekong River, one of the world’s largest, flows through the Mekong Delta, creating fertile land for agriculture and supporting a vibrant ecosystem. Other important rivers include the Red River, the Thu Bon River, and the Song Ba River, each contributing to the country’s hydrological network.
- The Fertile Deltas: The Mekong Delta and the Red River Delta are vital agricultural regions, renowned for their rice production and abundance of freshwater resources. These deltas are also densely populated, serving as hubs of economic activity and cultural centers.
- The Expansive Coastline: Vietnam boasts a long and varied coastline stretching over 3,260 kilometers, offering diverse landscapes from sandy beaches to rocky cliffs. This coastline is home to numerous coastal cities, fishing communities, and pristine islands, contributing to the country’s tourism industry.
The Importance of a Topographic Map
A topographic map of Vietnam offers a comprehensive and detailed representation of this diverse landscape, providing crucial information for various sectors:
- Infrastructure Development: Topographic maps are essential for planning and implementing infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, dams, and power lines. They provide data on elevation, slopes, and terrain features, allowing engineers to design structures that are safe, efficient, and environmentally sustainable.
- Resource Management: Topographic maps are vital for managing natural resources, including water, forests, and minerals. They help identify potential areas for agriculture, forestry, and mining, while also informing sustainable management practices to prevent environmental degradation.
- Disaster Preparedness: Topographic maps are crucial for disaster preparedness and response. They provide information on flood-prone areas, earthquake zones, and landslide risks, enabling authorities to develop effective disaster management plans and evacuation routes.
- Tourism and Recreation: Topographic maps are invaluable for tourists and outdoor enthusiasts. They provide information on hiking trails, camping sites, and points of interest, allowing travelers to explore Vietnam’s diverse landscapes safely and enjoyably.
- Scientific Research: Topographic maps are essential for scientific research, particularly in fields like geology, ecology, and climatology. They provide data on landforms, vegetation, and elevation, enabling researchers to understand the complex interactions between the environment and human activities.
Decoding the Features of a Topographic Map
Topographic maps utilize a specific set of symbols and conventions to represent various features of the terrain. Understanding these features is crucial for interpreting the information presented on the map:
- Contour Lines: Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s shape. Closely spaced contour lines indicate steep slopes, while widely spaced lines suggest gentle slopes.
- Elevation: Elevation is typically shown using contour lines and spot heights, which indicate the precise elevation of specific points on the map.
- Water Features: Rivers, lakes, and oceans are represented using blue lines and symbols, indicating the direction of flow and the presence of water bodies.
- Vegetation: Different types of vegetation, such as forests, grasslands, and agricultural areas, are represented using distinct colors and symbols.
- Cultural Features: Cities, towns, roads, and other cultural features are marked on the map, providing context and information on human settlements and infrastructure.
Exploring the Benefits of a Topographic Map
The benefits of using a topographic map of Vietnam extend beyond providing information about the landscape. They offer a comprehensive understanding of the country’s unique geographical features, enabling informed decision-making in various sectors:
- Sustainable Development: Topographic maps promote sustainable development by providing data on environmental sensitivities, resource availability, and potential risks, allowing for informed planning and minimizing environmental impact.
- Improved Infrastructure: Topographic maps enable the construction of resilient infrastructure that is better adapted to the terrain and minimizes environmental disruption.
- Effective Disaster Response: Topographic maps contribute to improved disaster response by providing crucial information on evacuation routes, vulnerable areas, and potential hazards, facilitating timely and efficient aid delivery.
- Enhanced Tourism Experience: Topographic maps empower tourists to explore Vietnam’s diverse landscapes safely and confidently, enriching their travel experience and promoting responsible tourism practices.
- Scientific Advancements: Topographic maps facilitate scientific research by providing a detailed understanding of the landscape, enabling researchers to analyze environmental processes, understand the impact of human activities, and develop solutions for sustainable management.
Frequently Asked Questions about Topographic Maps of Vietnam
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a geographical map?
A: A geographical map shows general features like countries, cities, and major landforms, while a topographic map focuses on the terrain’s elevation, slopes, and other physical features in detail.
Q: Where can I find a topographic map of Vietnam?
A: Topographic maps of Vietnam are available from various sources, including government agencies, mapping companies, and online platforms like Google Maps.
Q: How can I use a topographic map to plan a hiking trip?
A: By studying contour lines, elevation data, and trail markings, you can identify suitable trails, estimate the difficulty level, and plan your route accordingly.
Q: What are some essential tips for using a topographic map?
A: Always carry a compass and know how to use it for navigation. Understand the scale of the map and the elevation intervals represented by contour lines. Be aware of potential hazards like steep slopes, water bodies, and wildlife.
Q: What are the limitations of a topographic map?
A: Topographic maps are static representations and may not reflect real-time changes in the landscape, such as flooding or landslides. They also don’t provide information on vegetation density, soil type, or other factors that may be relevant for specific applications.
Conclusion
A topographic map of Vietnam is a powerful tool for understanding and managing the country’s unique landscape. It provides a detailed and comprehensive representation of the terrain, enabling informed decision-making in various sectors, from infrastructure development and resource management to disaster preparedness and tourism. By utilizing the information provided by topographic maps, individuals and organizations can contribute to sustainable development, enhance infrastructure, improve disaster response, and enrich the experience of exploring Vietnam’s breathtaking landscapes.
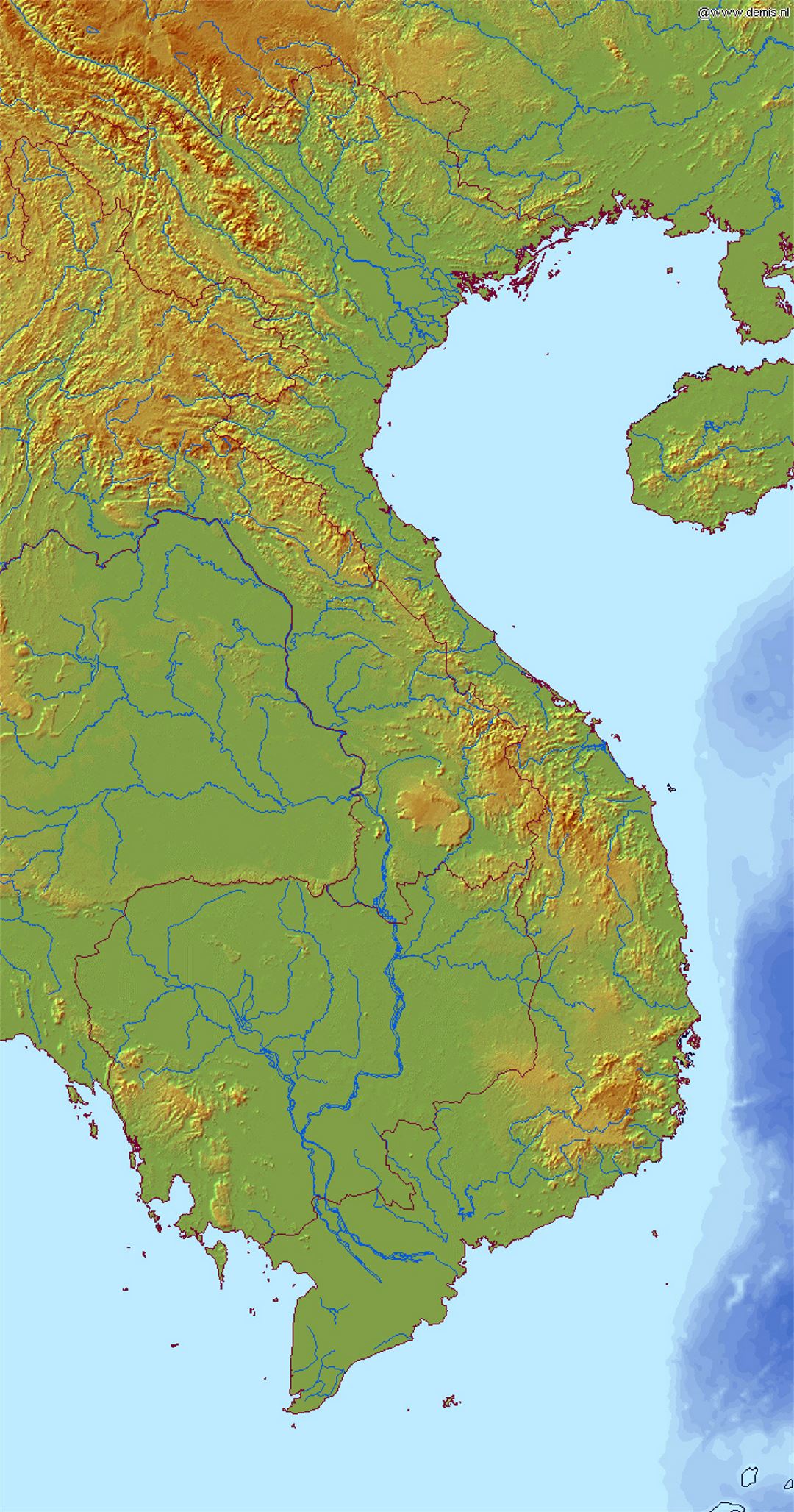

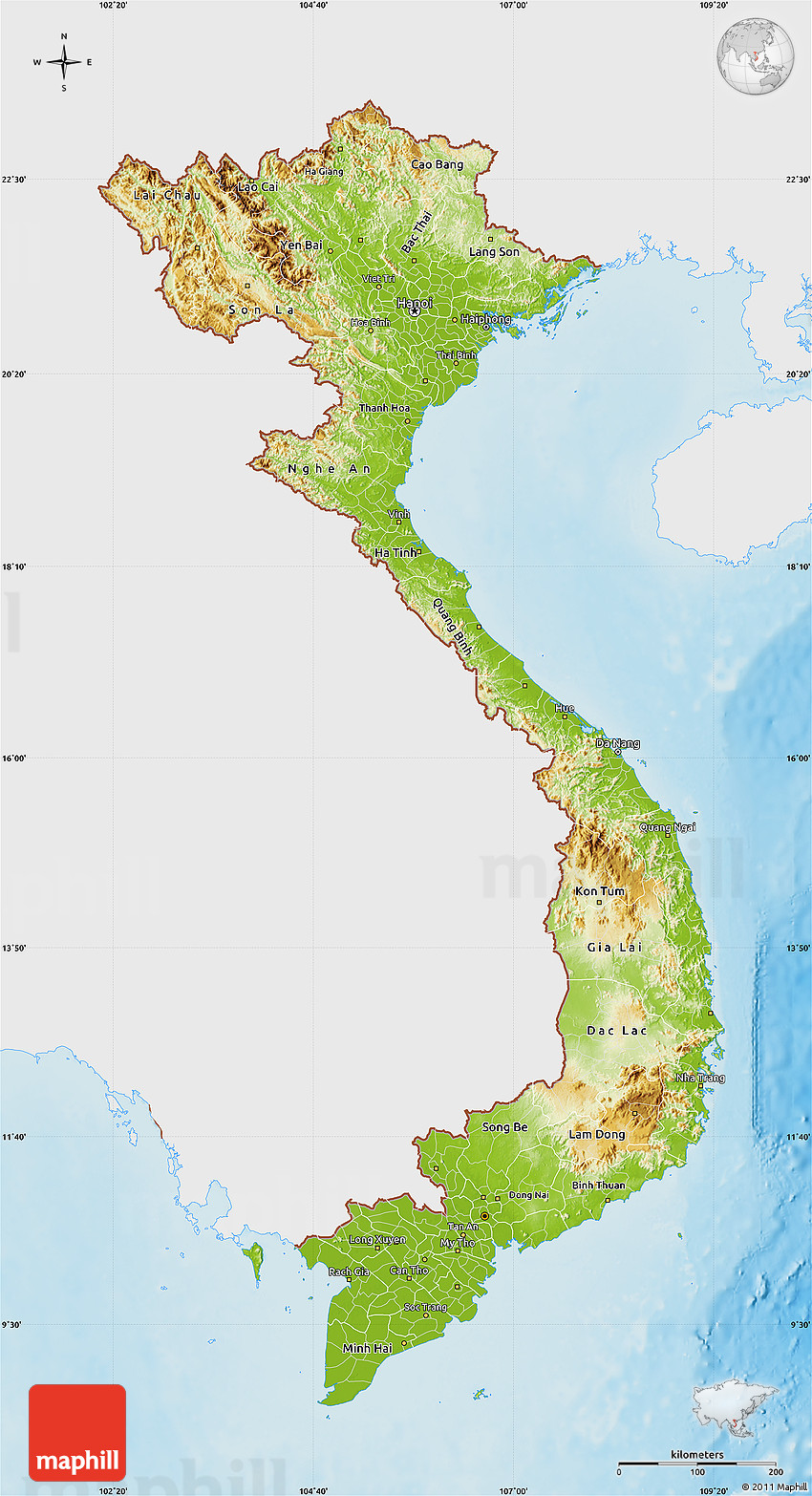



![[OC] Human Development Index in Vietnam by Province and Region : r/geography](https://i.redd.it/oo8hso6pahd51.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Landscape of Diversity: Understanding Vietnam’s Topographic Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!