A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring The Topography Of Vietnam
A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Topography of Vietnam
Related Articles: A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Topography of Vietnam
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Topography of Vietnam. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Topography of Vietnam

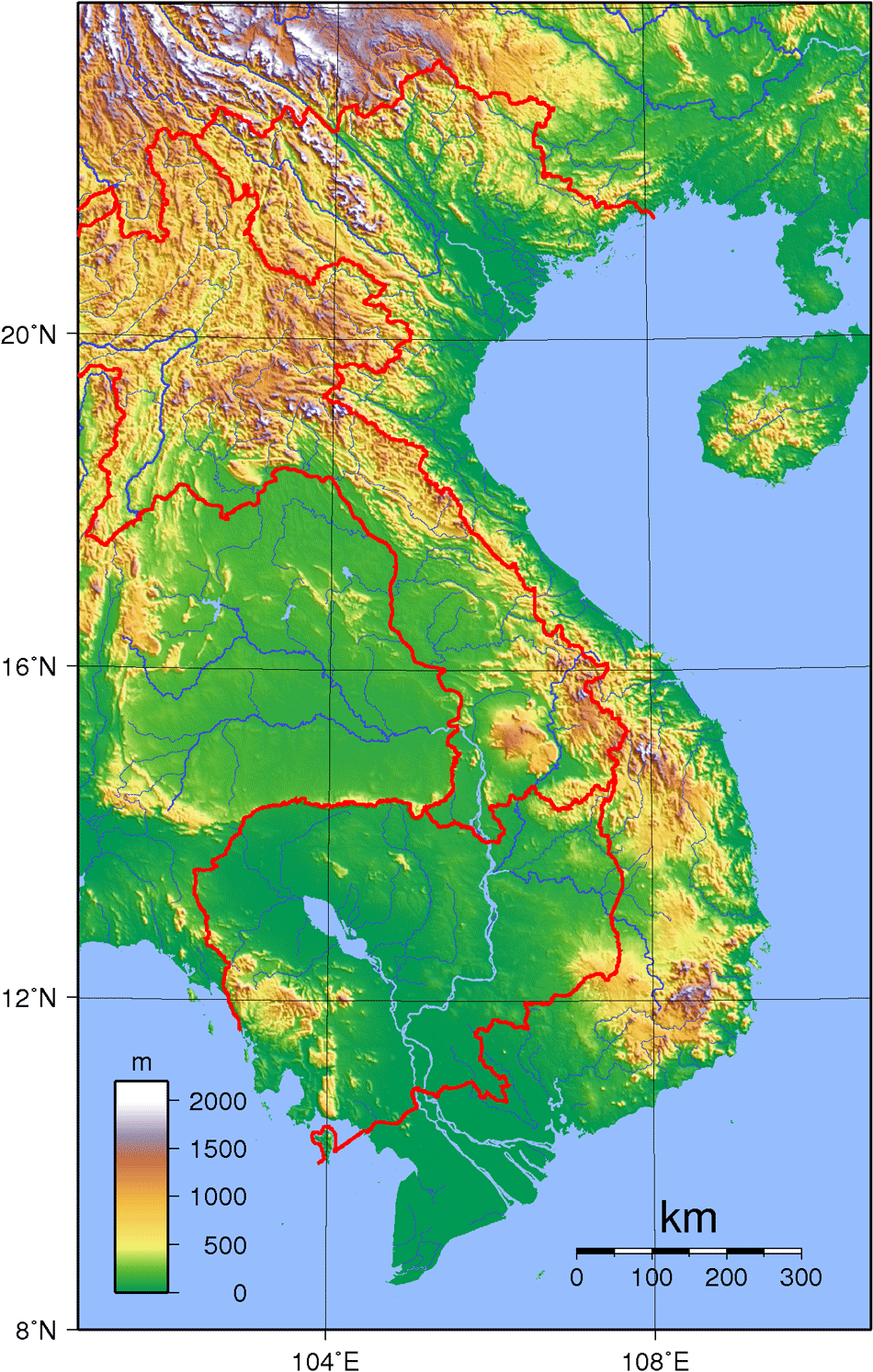
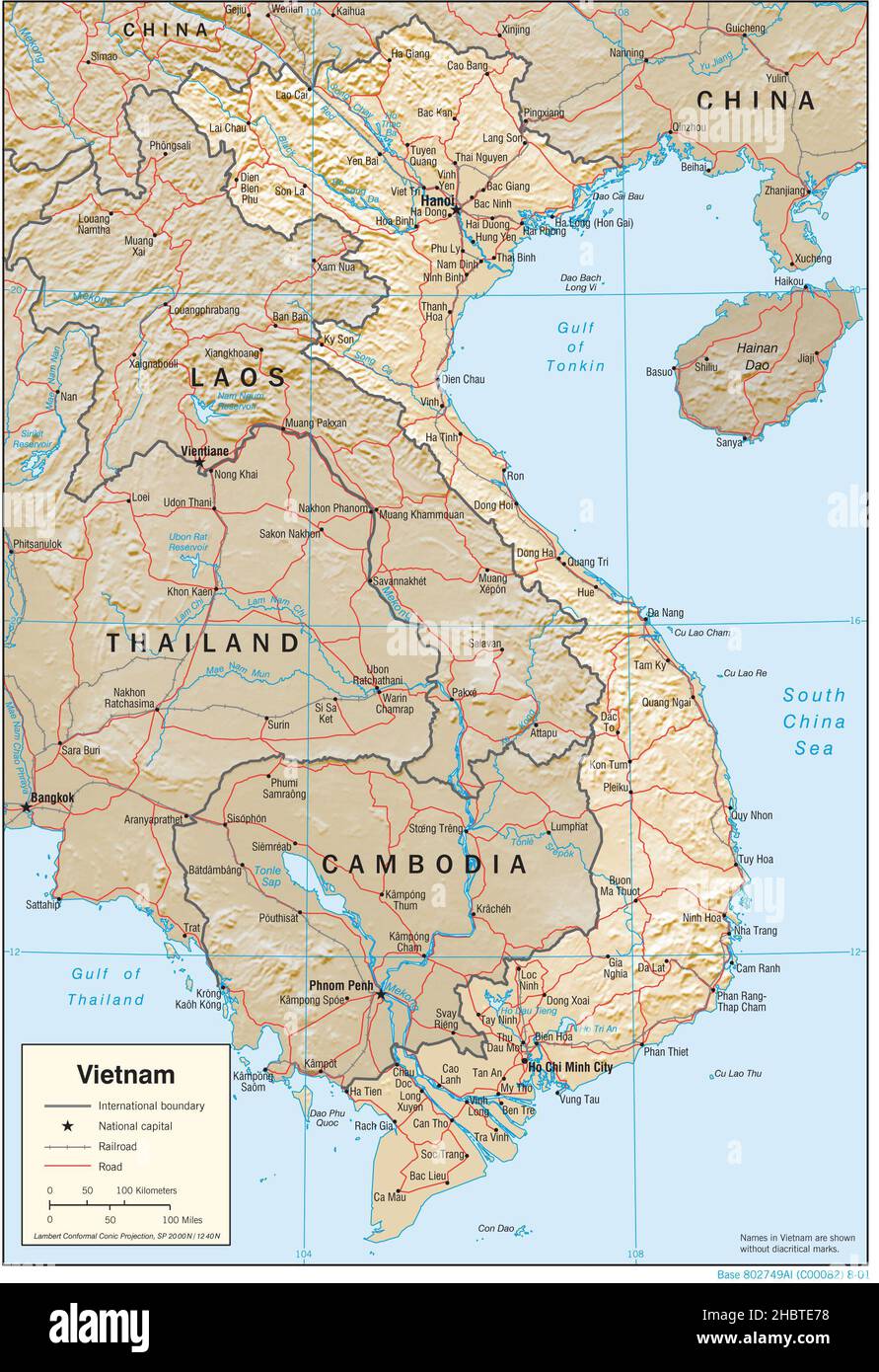
Vietnam, a Southeast Asian nation stretching over 1,650 kilometers along the eastern coast of the Indochinese Peninsula, is a land of remarkable topographic diversity. Its landscape, sculpted by millennia of geological forces, presents a fascinating tapestry of mountains, rivers, plains, and coastlines, each contributing to the country’s unique character and rich cultural heritage.
A Landscape of Contrasts:
The topography of Vietnam is characterized by a striking contrast between its mountainous north and the vast, fertile Mekong Delta in the south. The northern region is dominated by the Annamite Chain, a formidable mountain range running parallel to the coast, reaching elevations exceeding 3,000 meters. This rugged terrain, interspersed with deep valleys and verdant forests, presents significant challenges for infrastructure development and agricultural activities.
Moving south, the landscape gradually transitions into the Central Highlands, a plateau region characterized by rolling hills, volcanic lakes, and extensive coffee plantations. This region, with its unique climate and soil conditions, has become a vital agricultural hub for Vietnam.
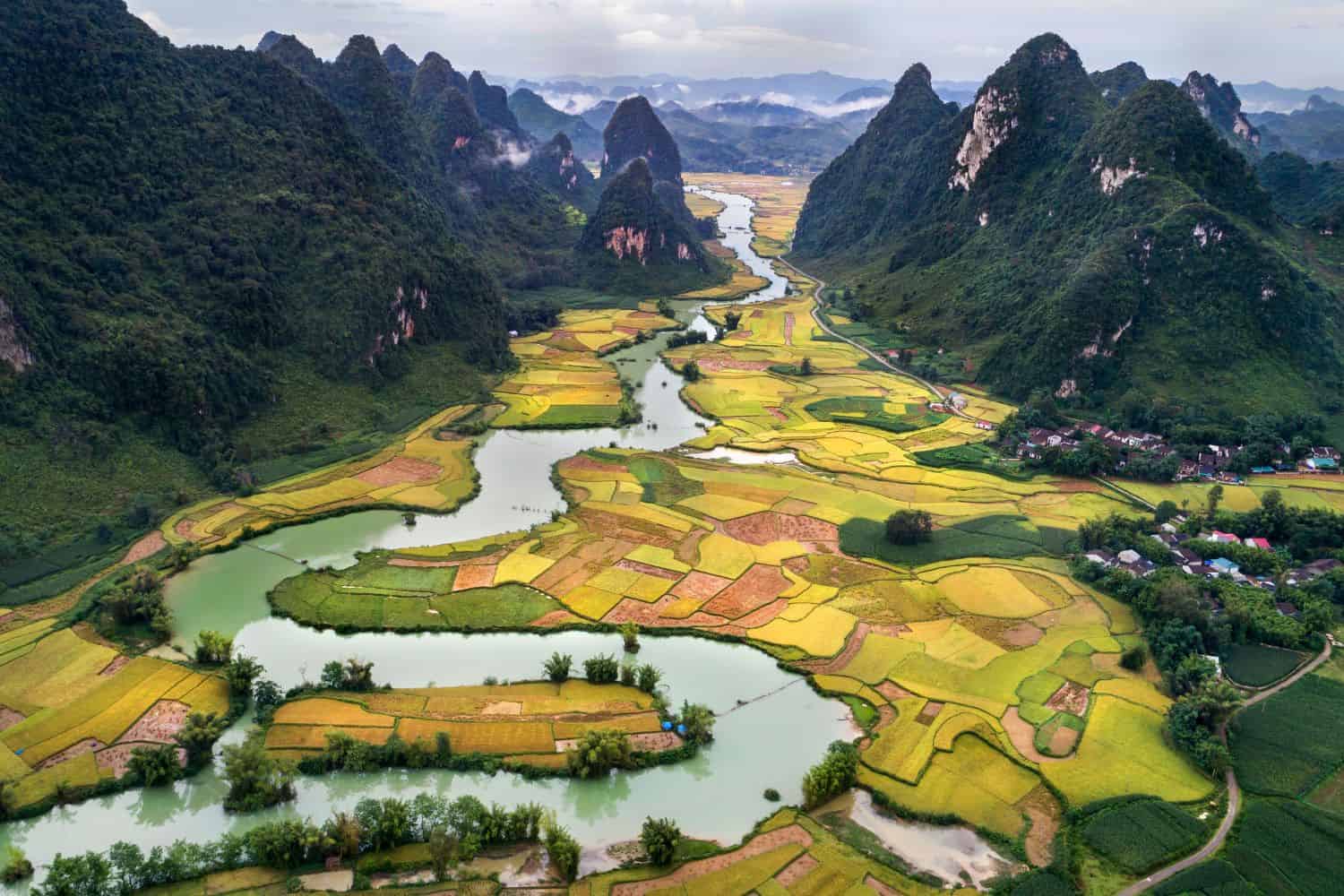
The Mekong Delta, in the southernmost region, is a vast alluvial plain formed by the deposition of sediment from the Mekong River. This fertile delta, crisscrossed by a network of waterways, is the heart of Vietnamese rice production, supporting a dense population and playing a crucial role in the country’s food security.
Coastal Dynamics and Biodiversity:
Vietnam boasts a long coastline of over 3,444 kilometers, punctuated by numerous bays, estuaries, and islands. This extensive coastline, shaped by the forces of erosion and deposition, has played a significant role in shaping the country’s history, culture, and economy.
The coastline is home to a diverse array of ecosystems, including mangrove forests, coral reefs, and seagrass meadows. These ecosystems are vital for marine biodiversity, providing habitat for a multitude of species and contributing to the livelihoods of coastal communities.
The Importance of Topographic Understanding:
Understanding the topography of Vietnam is crucial for various reasons:
- Resource Management: Topographic data provides insights into the distribution of natural resources, such as water, minerals, and fertile land. This information is essential for sustainable resource management, ensuring their availability for present and future generations.
- Infrastructure Development: The rugged terrain of Vietnam presents significant challenges for transportation and infrastructure development. Topographic maps are indispensable for planning roads, railways, and other infrastructure projects, ensuring their feasibility and minimizing environmental impact.
- Disaster Risk Management: Understanding the topography of Vietnam is vital for disaster risk management. Topographic data helps identify areas prone to natural hazards such as landslides, floods, and typhoons, enabling the development of early warning systems and mitigation strategies.
- Environmental Conservation: Topographic information is essential for monitoring and managing protected areas, ensuring the conservation of biodiversity and ecological integrity. It also aids in understanding the impacts of human activities on the environment, facilitating informed decision-making for sustainable development.
- Tourism Development: Vietnam’s diverse topography attracts tourists from around the world. Topographic maps help tourists explore the country’s natural beauty, from the majestic mountains to the serene beaches, enhancing their travel experience.
Exploring Vietnam’s Topographic Features:
Mountains:
- Fansipan: The highest peak in Indochina, located in the Hoang Lien Son range, stands at 3,143 meters above sea level.
- Truong Son Range: This mountain range, also known as the Annamite Chain, stretches over 1,000 kilometers, forming a natural barrier between the coastal lowlands and the interior highlands.
- Langbian Plateau: Located in the Central Highlands, this plateau is characterized by rolling hills, volcanic lakes, and coffee plantations.
Rivers:
- Mekong River: The Mekong River, one of the longest rivers in Southeast Asia, flows through Vietnam for over 1,200 kilometers, forming the Mekong Delta in the south.
- Red River: The Red River, originating in China, flows through Vietnam for over 500 kilometers, irrigating the Red River Delta, a major agricultural region.
- Thu Bon River: This river flows through the Central Highlands and the coastal lowlands, supporting a diverse ecosystem and contributing to the region’s agricultural productivity.
Plains:
- Red River Delta: This fertile plain, located in northern Vietnam, is one of the most densely populated areas in the country, supporting a significant agricultural sector.
- Mekong Delta: The Mekong Delta, formed by the Mekong River, is the largest rice-producing region in Vietnam, contributing significantly to the country’s food security.
- Coastal Lowlands: These lowlands, stretching along the eastern coast of Vietnam, are characterized by fertile soils and a favorable climate, making them suitable for agriculture and urban development.
Coastline:
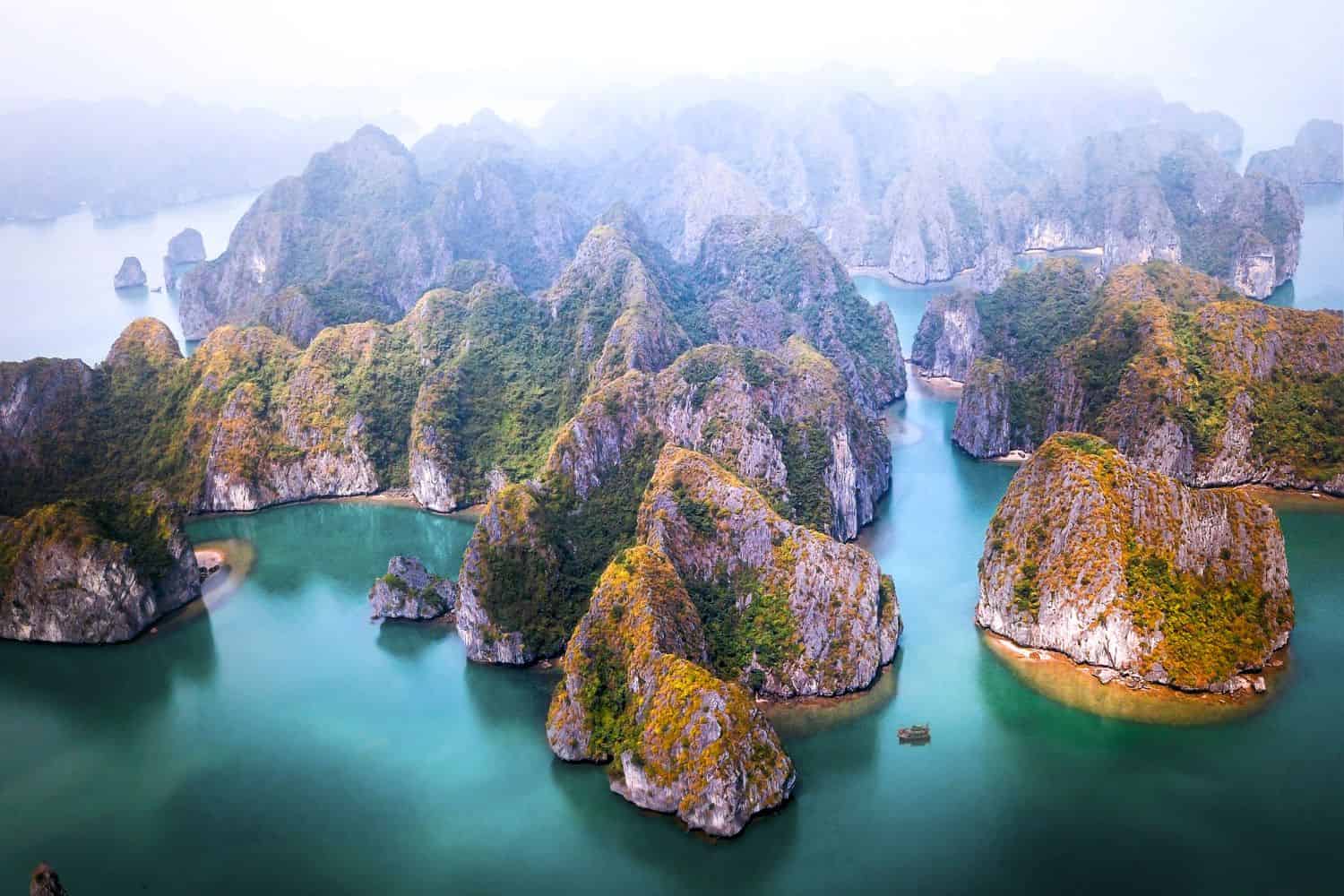
- Ha Long Bay: A UNESCO World Heritage site, Ha Long Bay is renowned for its stunning limestone islands rising from the turquoise waters.
- Nha Trang Bay: This bay, located on the central coast, is a popular tourist destination, known for its pristine beaches and vibrant coral reefs.
- Mekong Delta Coastline: The Mekong Delta coastline is characterized by a network of waterways, mangroves, and rice paddies, offering a unique and picturesque landscape.
Topographic Data Sources:
Various sources provide topographic information about Vietnam:
- Government Agencies: The Vietnamese Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment and the General Department of Surveying and Mapping are responsible for collecting and disseminating topographic data.
- International Organizations: Organizations such as the World Bank, the Asian Development Bank, and the United Nations provide topographic data and support for infrastructure development and resource management in Vietnam.
- Commercial Providers: Private companies offer topographic data and mapping services, catering to various sectors, including engineering, construction, and tourism.
FAQs on Vietnam’s Topography:
Q: How does Vietnam’s topography influence its climate?
A: Vietnam’s topography significantly influences its climate. The Annamite Chain acts as a natural barrier, blocking moisture from the Pacific Ocean, resulting in a drier climate in the interior highlands compared to the coastal regions. The Mekong Delta, with its vast network of waterways, experiences a humid tropical climate, while the Central Highlands enjoys a cooler climate with distinct dry and wet seasons.
Q: What are the challenges of infrastructure development in Vietnam?
A: The rugged terrain of Vietnam poses significant challenges for infrastructure development. Mountainous regions require extensive road construction and bridge building, while the Mekong Delta’s intricate network of waterways necessitates sophisticated engineering solutions for transportation and flood control.
Q: How does topography affect agricultural practices in Vietnam?
A: The topography of Vietnam influences agricultural practices. The fertile plains of the Red River Delta and the Mekong Delta are ideal for rice cultivation, while the sloping hills of the Central Highlands are suitable for coffee and tea plantations. The mountainous regions are often used for forestry and livestock grazing.
Q: How is Vietnam’s topography important for its biodiversity?
A: Vietnam’s diverse topography supports a wide range of ecosystems, contributing to its rich biodiversity. The Annamite Chain is home to a variety of endemic species, while the Mekong Delta’s waterways provide habitat for numerous aquatic species. The coastal regions are known for their coral reefs and mangrove forests, which are vital for marine biodiversity.
Tips for Understanding Vietnam’s Topography:
- Consult topographic maps: Utilize topographic maps, available online or in printed form, to visualize the country’s terrain and identify key features.
- Explore satellite imagery: Explore satellite imagery of Vietnam to gain a broader perspective on its topography and identify patterns in land use and natural features.
- Read about regional geography: Research the geography of specific regions in Vietnam to gain a deeper understanding of their unique topographic characteristics and associated challenges and opportunities.
- Visit Vietnam: Experiencing Vietnam firsthand allows for a deeper appreciation of its diverse topography and its impact on the country’s culture, economy, and environment.
Conclusion:
The topography of Vietnam, with its intricate interplay of mountains, rivers, plains, and coastlines, is a defining feature of the country. Understanding this geographic tapestry is crucial for sustainable development, resource management, disaster preparedness, and environmental conservation. By appreciating the unique characteristics of Vietnam’s topography, we can gain valuable insights into its rich history, vibrant culture, and remarkable biodiversity. As Vietnam continues to develop, its topographic features will continue to shape its future, presenting both challenges and opportunities for its people and environment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Topography of Vietnam. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!