A Geographic Overview: Vietnam And Its Neighbors
A Geographic Overview: Vietnam and Its Neighbors
Related Articles: A Geographic Overview: Vietnam and Its Neighbors
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Overview: Vietnam and Its Neighbors. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Overview: Vietnam and Its Neighbors

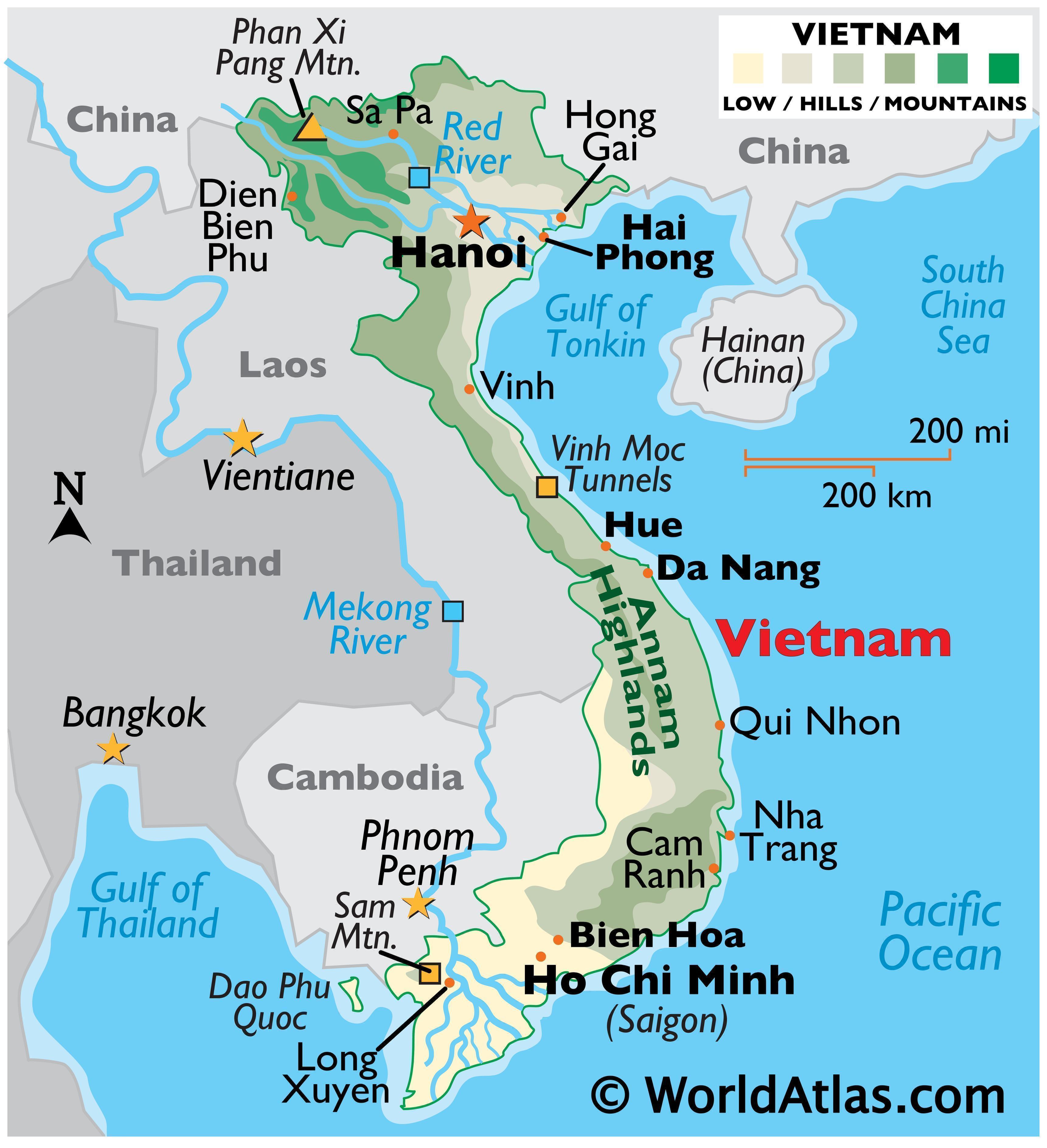
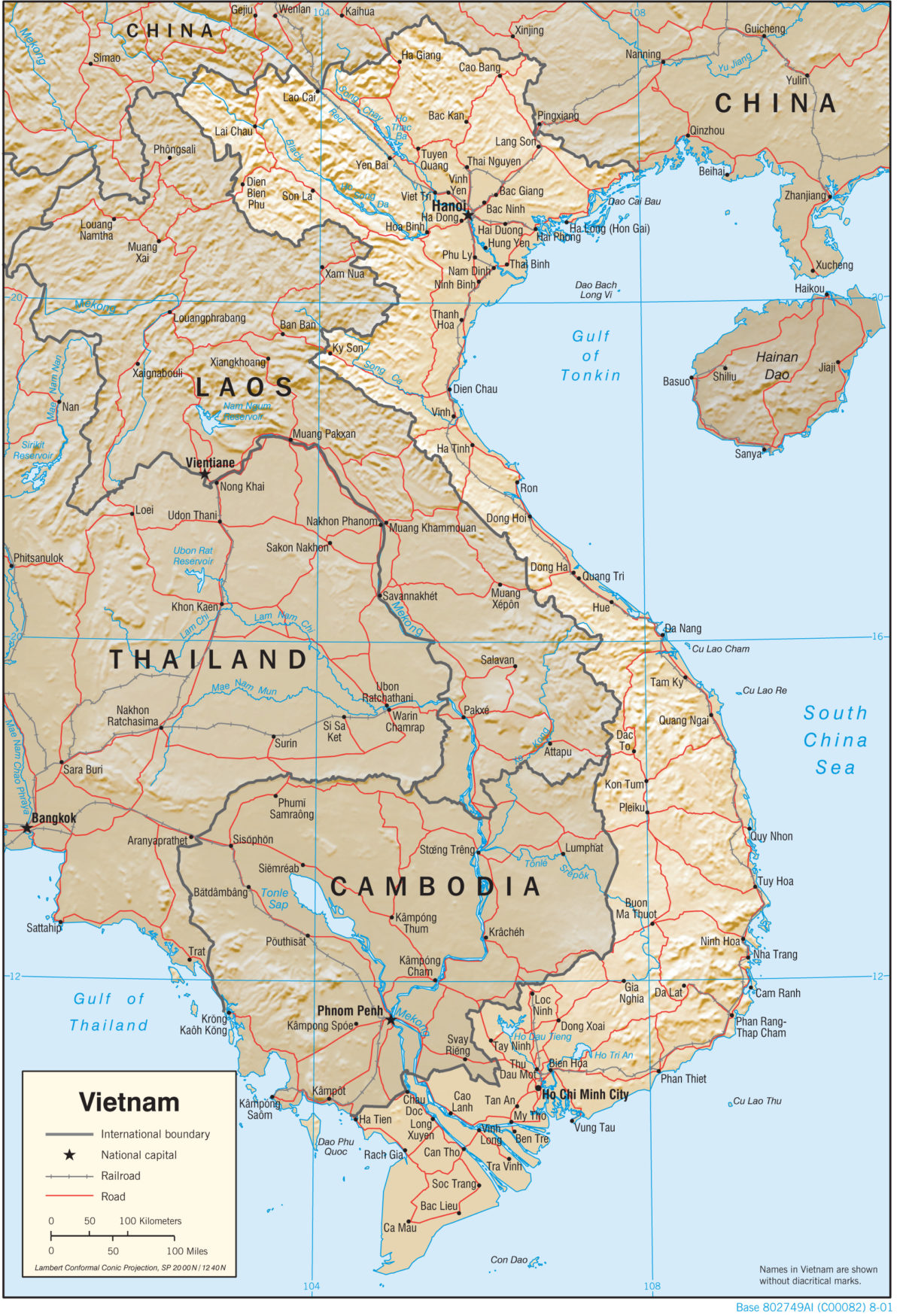
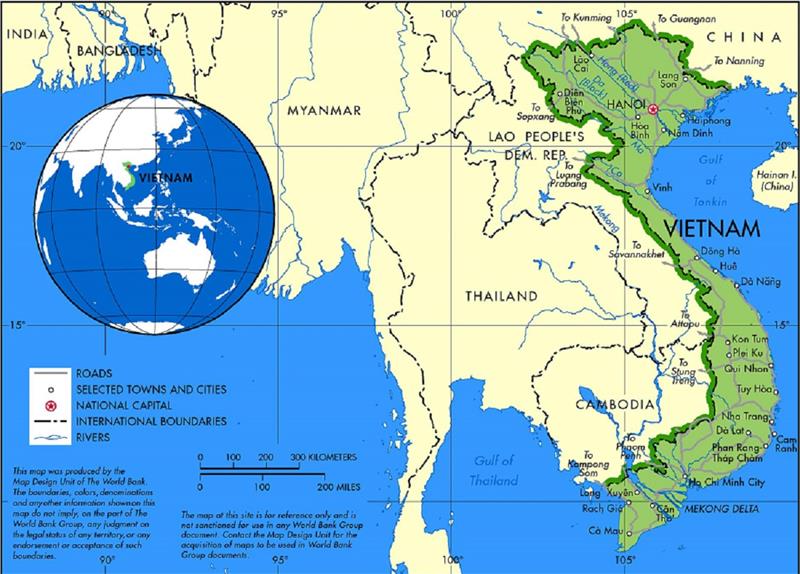
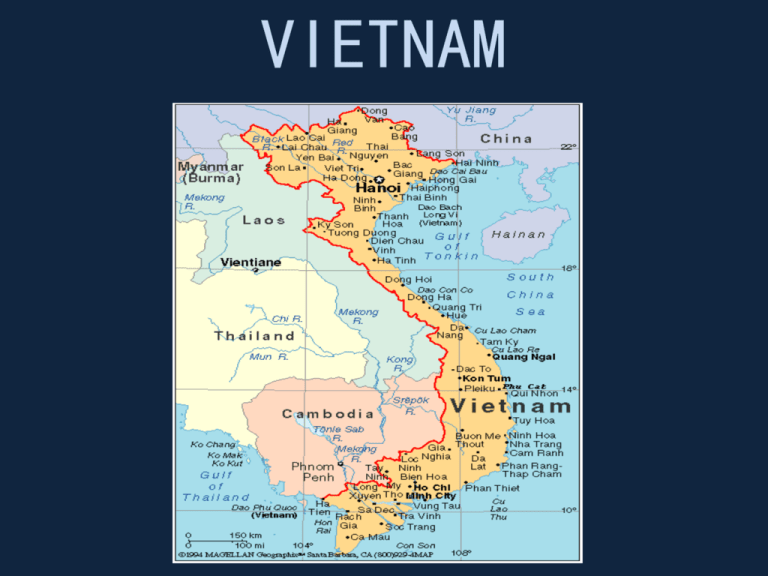
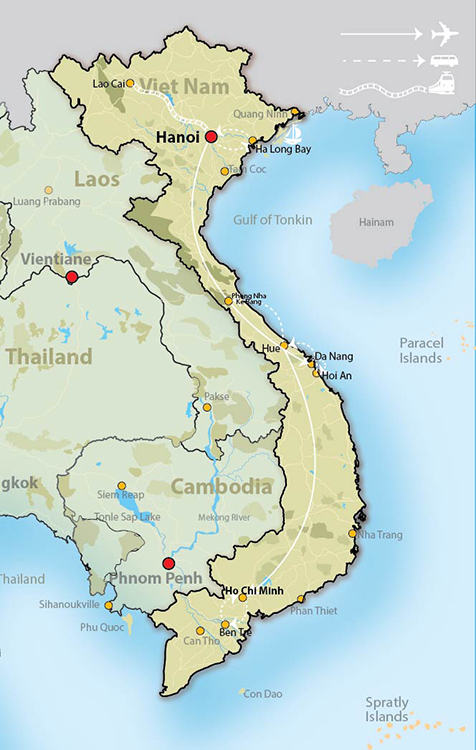
The Southeast Asian nation of Vietnam, a narrow strip of land stretching along the eastern edge of the Indochinese peninsula, holds a geographically strategic position. Its landscape, a captivating blend of mountains, rivers, and coastlines, is a testament to the interplay of tectonic forces and climatic influences. Understanding Vietnam’s geography necessitates a broader perspective, encompassing its relationship with neighboring countries – China, Laos, Cambodia, and Thailand – each contributing to the intricate tapestry of Southeast Asia.
A Tapestry of Landscapes:
Vietnam’s geography is characterized by distinct regional variations:
-
The Red River Delta: This fertile region in the north is a vital agricultural hub, fed by the Red River, a lifeline for irrigation and transportation. It is also home to Hanoi, the nation’s capital, and a historical center of Vietnamese culture.
-
The North Central Coast: This region, marked by rugged mountains and narrow coastal plains, experiences a harsh climate with frequent typhoons. Its landscape is dotted with ancient trading ports and remnants of historical empires.
-
The Central Highlands: This mountainous region, known for its diverse ethnic groups and lush forests, is a significant source of natural resources, including coffee, rubber, and timber.
-
The Mekong Delta: This vast delta in the south, formed by the Mekong River, is Vietnam’s rice bowl, producing a substantial portion of the country’s agricultural output. It is also a crucial fishing ground and a major economic center.
Neighbors Shaping Vietnam’s Destiny:
The intricate web of geography extends beyond Vietnam’s borders. Its neighbors, each with their own distinct characteristics, influence Vietnam’s economic, cultural, and political landscape:
-
China: Vietnam’s northern neighbor, China, shares a long and complex history with Vietnam. The two nations share a common cultural heritage, but also a history of territorial disputes. The mountainous border region remains a sensitive area, with occasional tensions arising from historical claims and resource disputes.
-
Laos: Sharing a mountainous border with Vietnam, Laos is a landlocked country with a predominantly mountainous terrain. The two nations enjoy a close relationship, with strong economic and cultural ties. The Mekong River, a vital waterway for both countries, serves as a connecting artery, facilitating trade and cultural exchange.
-
Cambodia: Vietnam shares a border with Cambodia in the southwest, a region marked by the Mekong River and the Cardamom Mountains. The two nations have a long history of interaction, with cultural and linguistic influences flowing across the border. Their shared history, however, also includes periods of conflict and territorial disputes.
-
Thailand: While not directly bordering Vietnam, Thailand plays a significant role in the region’s economic and cultural landscape. Both countries are members of ASEAN, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, promoting regional cooperation and integration. Thailand’s influence on Vietnamese culture is evident in the popularity of Thai cuisine and music.
The Significance of Geography:
The geography of Vietnam and its neighboring countries is not merely a collection of physical features. It shapes the region’s history, culture, and economic development.
-
Trade and Connectivity: The Mekong River, traversing through Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, and Thailand, serves as a vital trade route, connecting the interior with coastal regions and facilitating economic growth.
-
Cultural Exchange: The porous borders and historical interactions between Vietnam and its neighbors have fostered cultural exchange and linguistic influences. This shared heritage is evident in the diverse ethnic groups, languages, and traditions found in the region.
-
Resource Management: The region’s shared natural resources, including forests, rivers, and mineral deposits, require collaborative management to ensure sustainable development and environmental protection.
-
Political Stability: The complex geopolitical landscape, marked by historical tensions and territorial disputes, necessitates regional cooperation to maintain stability and foster economic growth.
FAQs by Map of Vietnam and Neighboring Countries:
1. What are the main geographical features of Vietnam?
Vietnam’s landscape is diverse, encompassing a narrow coastal plain, a mountainous interior, and a vast delta. It features the Red River Delta in the north, the Central Highlands, and the Mekong Delta in the south.
2. What are the major rivers in Vietnam?
The Red River and the Mekong River are the two most significant rivers in Vietnam. They play vital roles in agriculture, transportation, and cultural life.
3. What are the major mountains in Vietnam?
Vietnam’s mountainous regions include the Hoang Lien Son Range, the Truong Son Range, and the Annamite Range. These ranges are home to diverse ethnic groups and valuable natural resources.
4. What are the major cities in Vietnam?
Major cities in Vietnam include Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City, Da Nang, Hai Phong, and Can Tho. These cities serve as economic and cultural hubs.
5. What are the major neighboring countries of Vietnam?
Vietnam shares borders with China, Laos, Cambodia, and Thailand. These countries play significant roles in Vietnam’s economic, cultural, and political landscape.
Tips by Map of Vietnam and Neighboring Countries:
-
Use a physical map: A physical map, showcasing elevation and terrain, provides a comprehensive understanding of the region’s geography.
-
Study the major rivers: Understanding the course and significance of major rivers, such as the Mekong and Red River, helps grasp the flow of resources and cultural connections.
-
Identify major cities and regions: Familiarize yourself with major cities and regions to understand the distribution of population and economic activities.
-
Research historical interactions: Understanding historical interactions between Vietnam and its neighbors provides context for present-day relationships and cultural influences.
-
Explore cultural diversity: Appreciate the rich cultural diversity of the region, reflecting the influence of different ethnic groups and historical interactions.
Conclusion by Map of Vietnam and Neighboring Countries:
The map of Vietnam and its neighboring countries is not just a visual representation of physical features. It is a window into the region’s rich history, diverse culture, and complex political landscape. Understanding the geography of this interconnected region is crucial for appreciating the historical, cultural, and economic factors that shape the lives of millions. It underscores the importance of regional cooperation and understanding for promoting sustainable development, fostering cultural exchange, and ensuring peace and stability in Southeast Asia.

vietnam.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Overview: Vietnam and Its Neighbors. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!