A Geographic Overview Of The Middle East: Unpacking A Complex Region
A Geographic Overview of the Middle East: Unpacking a Complex Region
Related Articles: A Geographic Overview of the Middle East: Unpacking a Complex Region
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Overview of the Middle East: Unpacking a Complex Region. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Overview of the Middle East: Unpacking a Complex Region
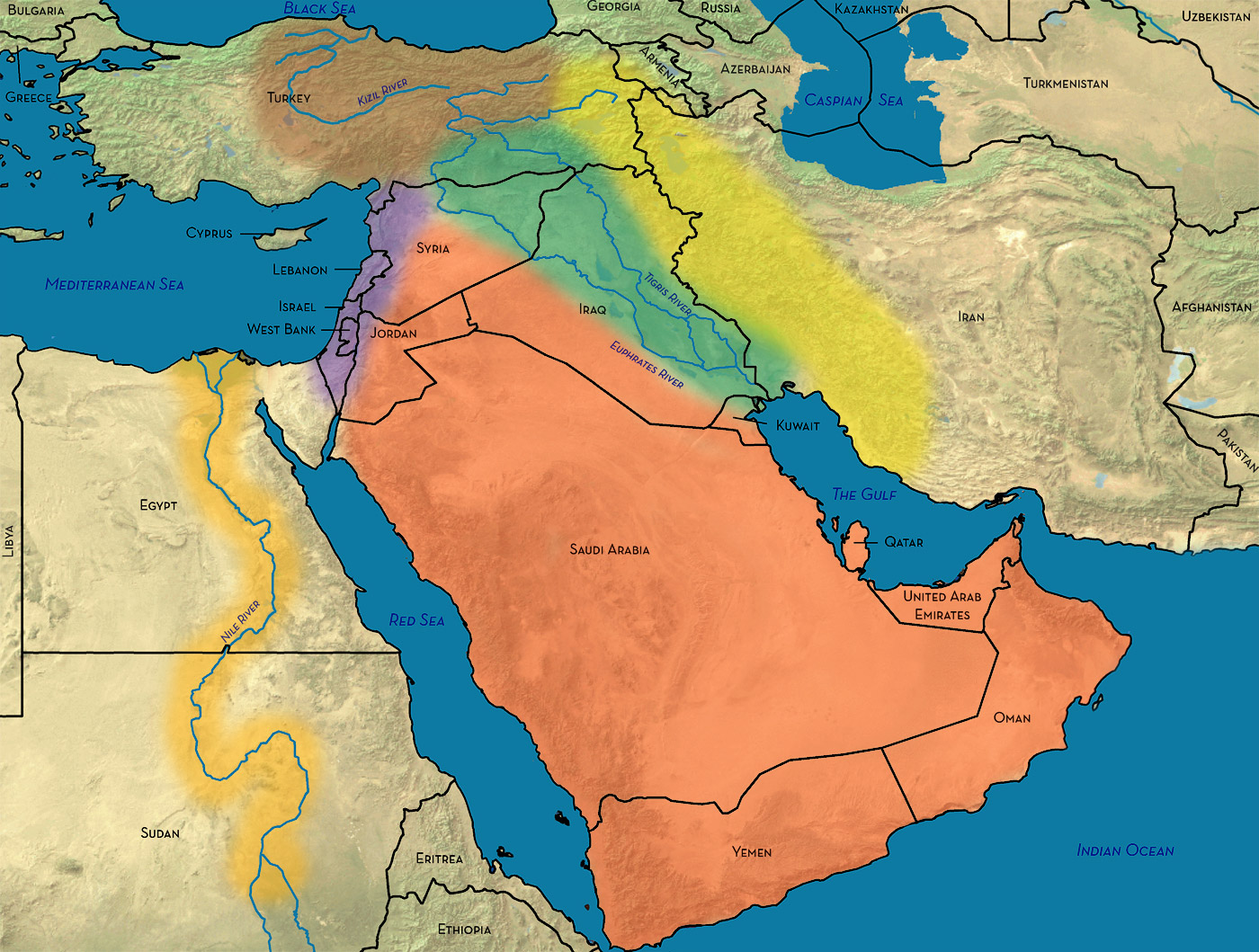
The Middle East, a geographically and culturally diverse region, occupies a pivotal position on the global stage. Its strategic location at the crossroads of continents, its vast oil reserves, and its rich history have shaped its political landscape and influenced world events for centuries. Understanding the region’s intricate tapestry of nations, cultures, and challenges requires a comprehensive understanding of its geographic composition.
Defining the Middle East: A Geographic Perspective
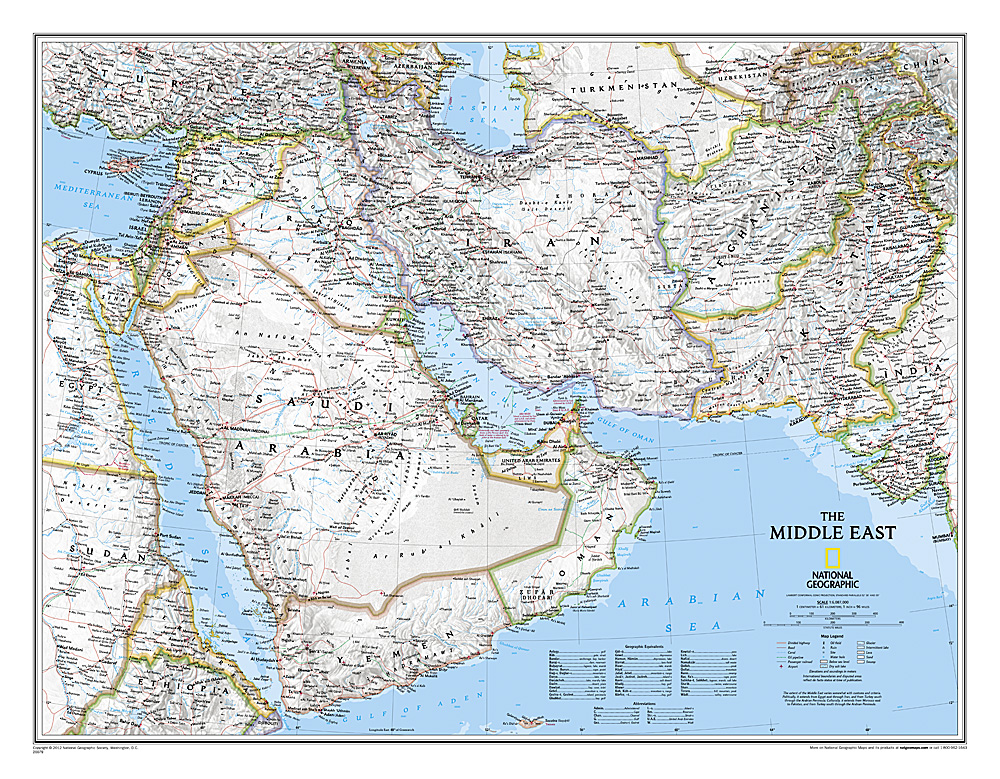
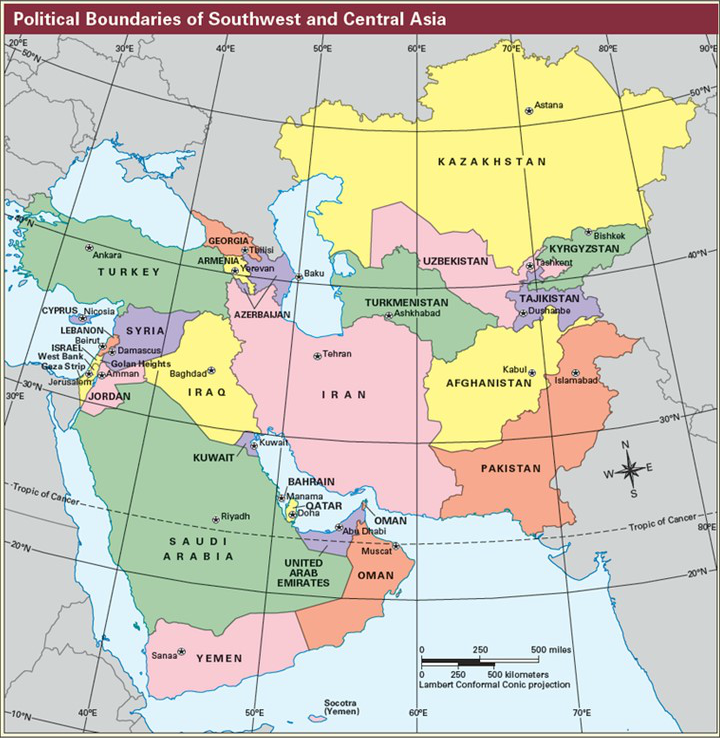
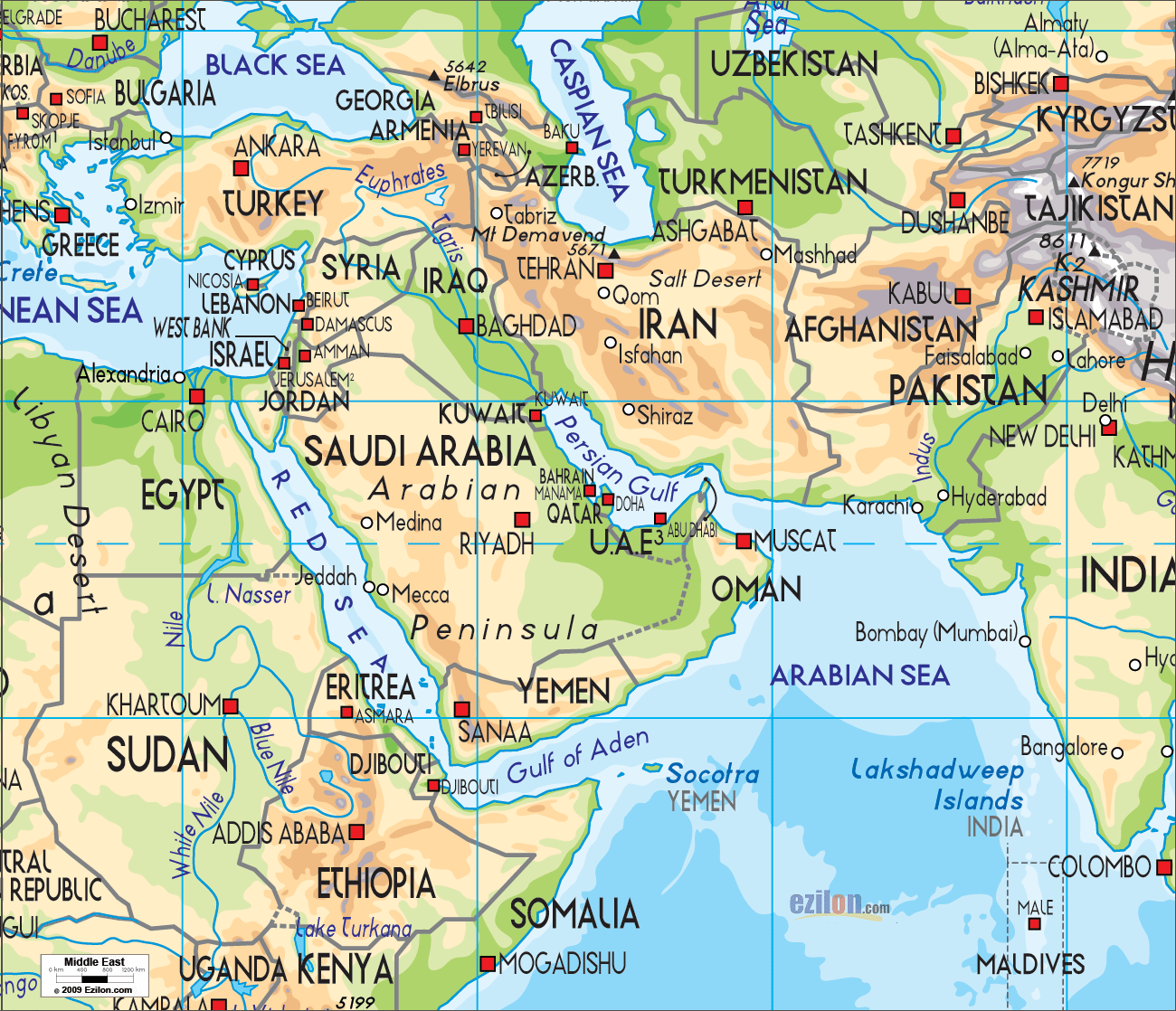
The Middle East, also referred to as Western Asia, is a geographically diverse region encompassing a vast expanse of land stretching from the eastern Mediterranean Sea to the Arabian Sea. It is bordered by North Africa to the west, the Caucasus region to the north, and South Asia to the east. However, defining its precise boundaries can be challenging due to the complex interplay of geopolitical, cultural, and historical factors.
Key Countries and Territories
The Middle East is home to a diverse range of countries, each with its unique history, culture, and political system. Some of the most prominent nations include:
- Arabian Peninsula: Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Kuwait, and Bahrain.
- Levant: Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Israel, and Palestine.
- Mesopotamia: Iraq.
- Caucasus: Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia.
- North Africa: Egypt.
The Importance of Geographic Features
The Middle East’s geography plays a crucial role in shaping its history, culture, and economy. Key features include:
- Deserts: Vast desert landscapes like the Arabian Desert and the Syrian Desert dominate the region, influencing its climate, agriculture, and population distribution.
- Waterways: Major rivers such as the Nile, Tigris, and Euphrates have supported civilizations for millennia, providing vital water resources and facilitating trade.
- Mountains: Mountain ranges like the Zagros Mountains and the Taurus Mountains offer natural barriers and contribute to the region’s diverse ecosystems.
- Coastal Zones: The Mediterranean Sea, the Red Sea, and the Persian Gulf provide access to international trade routes and support vibrant coastal economies.
Navigating the Political Landscape
The Middle East’s political landscape is characterized by complex and often volatile dynamics. Historical rivalries, religious differences, and the struggle for resources have contributed to a history marked by conflict and instability.
- Political Systems: The region encompasses a range of political systems, from monarchies to republics to authoritarian regimes.
- Religious Diversity: Islam is the dominant religion in the Middle East, with various denominations including Sunni Islam, Shia Islam, and others. However, other religions like Christianity, Judaism, and Zoroastrianism also hold significant historical and cultural importance.
- Ethnic Groups: The Middle East is home to a diverse range of ethnic groups, including Arabs, Kurds, Persians, Turks, and others. This diversity contributes to the region’s cultural richness but also poses challenges for achieving political stability.
Economic and Resource Dynamics
The Middle East is a region of immense economic importance, primarily due to its vast reserves of oil and natural gas. The region’s oil wealth has fueled economic growth and development, but it has also created economic imbalances and social inequalities.
- Energy Resources: The Middle East holds the world’s largest oil reserves, making it a crucial player in the global energy market.
- Diversification: Many countries are seeking to diversify their economies beyond oil and gas, focusing on sectors like tourism, technology, and agriculture.
- Economic Challenges: The region faces challenges such as unemployment, poverty, and infrastructure development.
Understanding the Middle East: A Crucial Task
The Middle East is a complex region with a rich history, diverse cultures, and a dynamic political landscape. Understanding its geography, political systems, economic dynamics, and historical context is crucial for comprehending global events and fostering peaceful dialogue and cooperation.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between the Middle East and the Near East?
A: The terms "Middle East" and "Near East" are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct historical and geographic connotations. "Near East" is an older term that typically refers to the region closer to Europe, including Turkey, Greece, and the Levant. "Middle East" is a broader term that encompasses a wider geographic area, including the Arabian Peninsula and North Africa.
Q: What are the main languages spoken in the Middle East?
A: Arabic is the most widely spoken language in the Middle East, with various dialects spoken across different countries. Other prominent languages include Persian, Turkish, Kurdish, and Hebrew.
Q: What are some of the major challenges facing the Middle East today?
A: The Middle East faces a number of challenges, including political instability, armed conflict, terrorism, economic inequality, climate change, and social unrest.
Tips for Learning More about the Middle East
- Read books and articles: Explore the region’s history, culture, and politics through reputable sources.
- Watch documentaries: Visual media can provide a deeper understanding of the region’s people, landscapes, and challenges.
- Travel to the Middle East: Experiencing the region firsthand can provide invaluable insights into its diverse cultures and landscapes.
- Engage in dialogue: Discuss the Middle East with people from different backgrounds and perspectives.
Conclusion
The Middle East is a region of immense historical, cultural, and geopolitical significance. Its geography, political systems, and economic dynamics continue to shape the region’s destiny and influence global events. By understanding the complexities of this region, we can foster greater understanding, cooperation, and peaceful resolution of conflicts.
![Geography of the Middle East - [PPT Powerpoint]](https://static.documents.pub/img/1200x630/reader020/image/20190910/56812a7c550346895d8e08d6.png?t=1618574315)
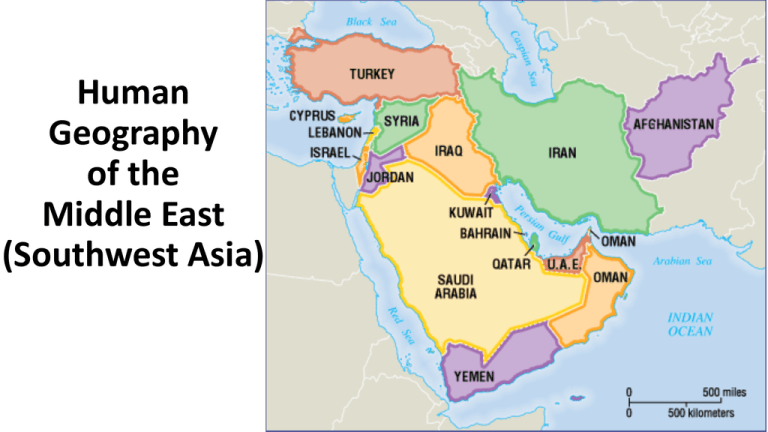
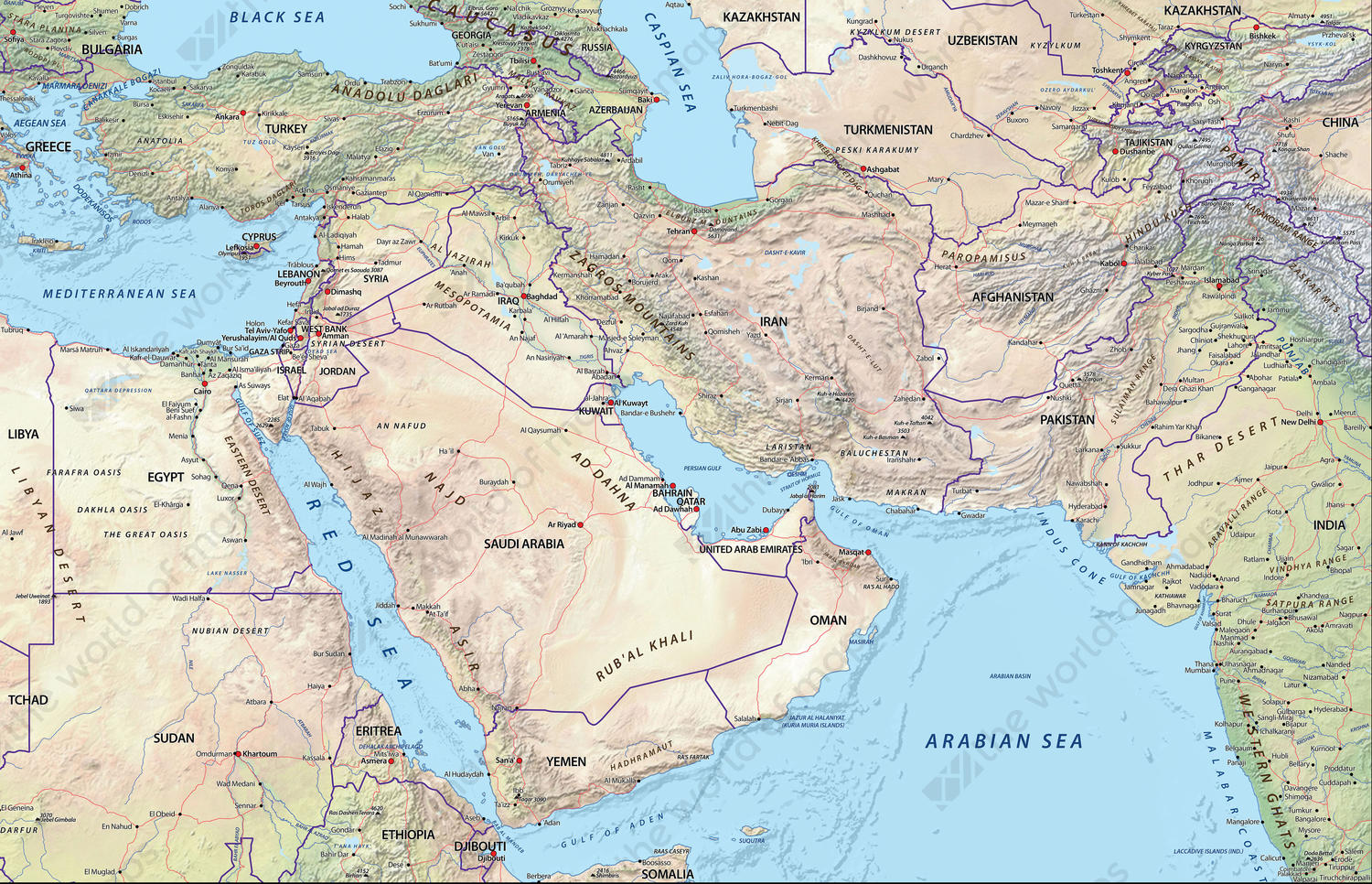

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Overview of the Middle East: Unpacking a Complex Region. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!