A Geographic Exploration Of Russia: Understanding Its Borders And Neighbors
A Geographic Exploration of Russia: Understanding its Borders and Neighbors
Related Articles: A Geographic Exploration of Russia: Understanding its Borders and Neighbors
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Exploration of Russia: Understanding its Borders and Neighbors. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Exploration of Russia: Understanding its Borders and Neighbors
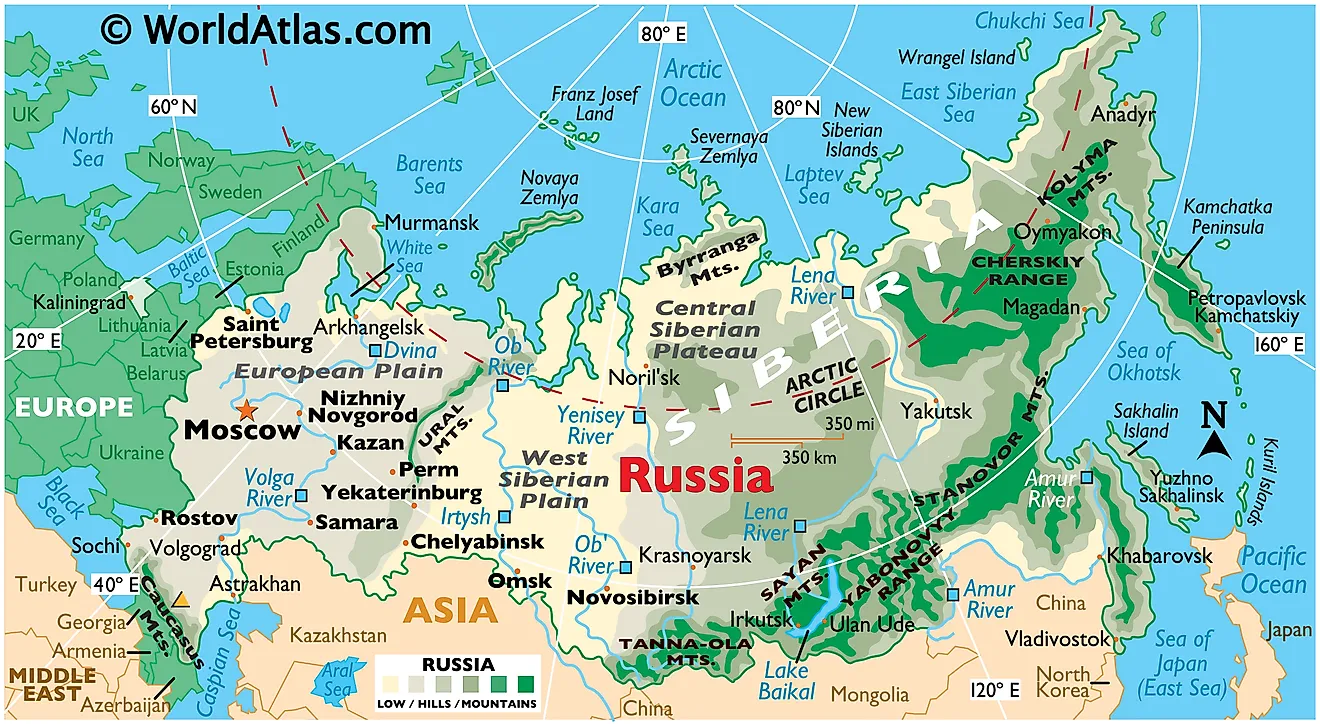
Russia, the largest country in the world by land area, spans eleven time zones and encompasses a vast and diverse landscape. Its borders are a complex tapestry, reflecting centuries of historical interactions, territorial shifts, and geopolitical complexities. Understanding Russia’s map and its neighboring countries is crucial for comprehending its cultural, economic, and political dynamics.
A Land of Extremes: Exploring Russia’s Geographic Boundaries
Russia’s geographic expanse is truly remarkable. It stretches from the Baltic Sea in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east, and from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Black Sea and the Caucasus Mountains in the south. This vast territory encompasses diverse environments, including vast plains, towering mountains, dense forests, and frozen tundra.
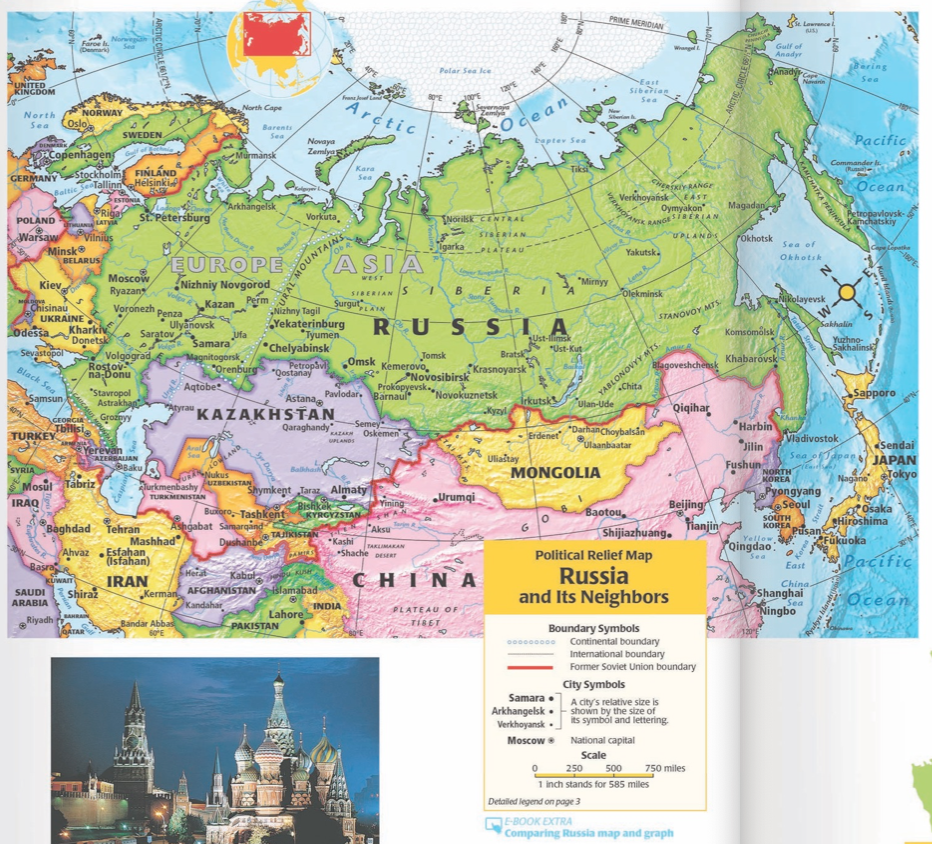
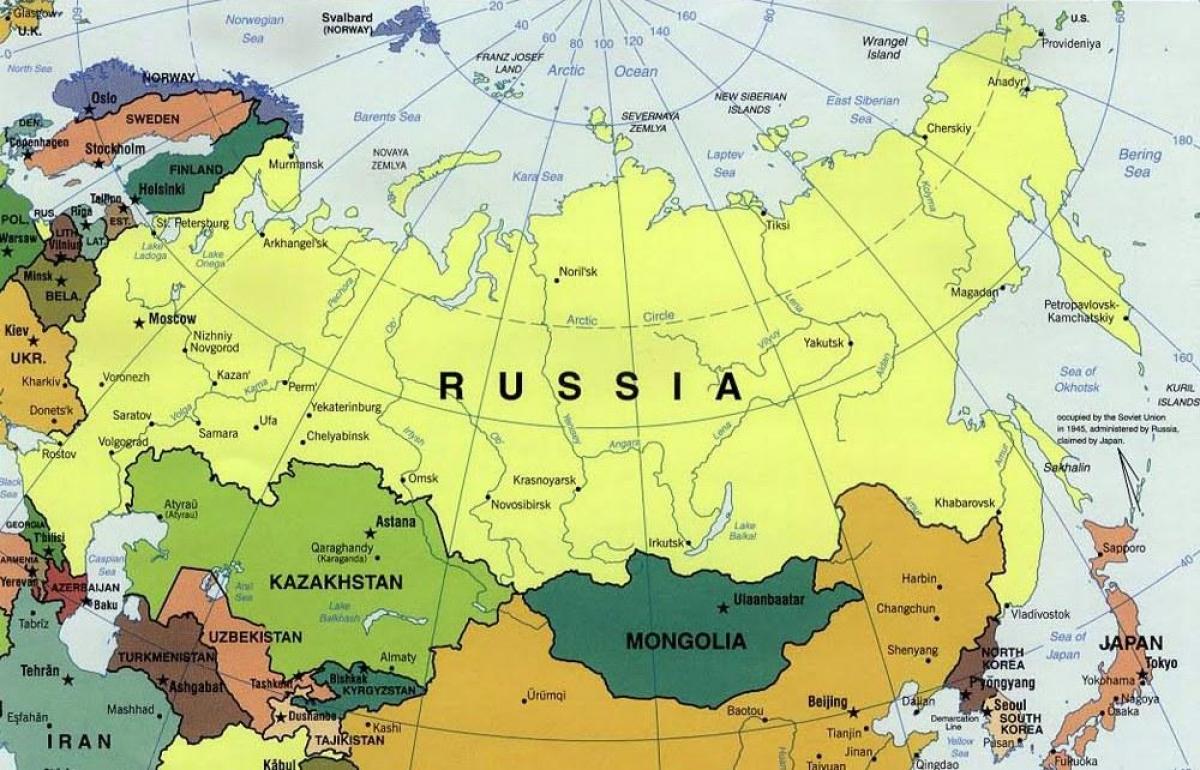
Russia’s Land Borders: A Mosaic of Relationships
Russia shares land borders with fourteen countries, each relationship imbued with unique historical, cultural, and economic ties.
Eastern Europe:
- Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania: These Baltic states, former republics of the Soviet Union, are located to the west of Russia. Their borders have been a source of tension in recent years, particularly in the context of Russia’s annexation of Crimea and its military intervention in Ukraine.
- Belarus: A close ally of Russia, Belarus shares a long and porous border, facilitating economic and cultural exchange.
- Ukraine: The conflict in Ukraine has cast a long shadow over Russia’s relationship with its southern neighbor. The annexation of Crimea and the ongoing war in eastern Ukraine have significantly impacted the two countries’ relations.
- Poland, Slovakia, and the Czech Republic: These countries, formerly part of the Warsaw Pact, share a history of complex relations with Russia, marked by periods of cooperation and conflict.
Caucasus Region:
- Georgia: The relationship between Russia and Georgia has been strained since the 2008 war over the breakaway regions of Abkhazia and South Ossetia.
- Azerbaijan: While sharing a complex history with Russia, Azerbaijan has maintained closer economic and political ties with the country in recent years.
- Armenia: Armenia has a strong historical and cultural connection with Russia, and the two countries maintain close political and military ties.
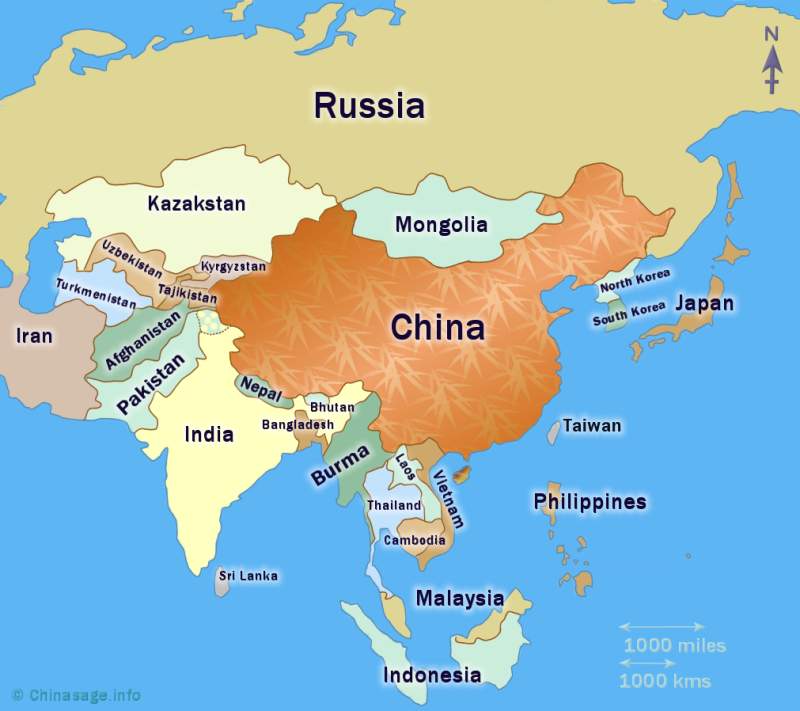
Asia:
- Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan: These Central Asian republics, formerly part of the Soviet Union, share close economic and cultural ties with Russia.
- China: Russia’s eastern border with China is the world’s longest land border. The two countries have a complex relationship, marked by historical tensions and growing economic cooperation.
- Mongolia: Russia and Mongolia share a long border and have historically enjoyed close relations.
Navigating the Seas: Russia’s Maritime Borders
Russia’s maritime borders extend across the Arctic Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, and the Black Sea. These borders are crucial for Russia’s access to international trade routes and its strategic positioning in the global arena.
- Arctic Ocean: Russia claims a vast portion of the Arctic Ocean, including the North Pole, based on its continental shelf. This claim has generated controversy and sparked territorial disputes with other Arctic nations.
- Pacific Ocean: Russia’s Pacific coast is home to several key ports, including Vladivostok, and plays a vital role in its economic and military strategy.
- Black Sea: The Black Sea is a strategic waterway for Russia, connecting it to the Mediterranean Sea and the Middle East.
The Importance of Russia’s Borders
Understanding Russia’s borders is essential for comprehending its geopolitical significance. Its vast landmass and its strategic location have made it a key player in global affairs.
- Resource Abundance: Russia is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, and timber. Its borders provide access to these resources and facilitate their export to international markets.
- Strategic Positioning: Russia’s borders with Europe and Asia give it a unique geopolitical advantage, allowing it to influence regional dynamics and maintain strategic partnerships.
- Security Concerns: Russia’s borders are often seen as a source of security concerns, particularly in light of its historical conflicts with neighboring countries.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Russia’s Borders
1. What are the main challenges facing Russia’s borders?
Russia faces several challenges related to its borders, including:
- Security Threats: Russia’s borders are subject to various security threats, including terrorism, organized crime, and border disputes.
- Economic Integration: Integrating its vast territory and fostering economic development across its diverse regions is a significant challenge for Russia.
- Demographic Trends: Russia’s population is declining, and its borders are often seen as a source of migration and demographic change.
2. How do Russia’s borders impact its international relations?
Russia’s borders play a crucial role in shaping its international relations. Its complex relationships with its neighbors are influenced by historical conflicts, economic interdependence, and geopolitical rivalry.
3. What are the implications of Russia’s Arctic claims?
Russia’s claims to a vast portion of the Arctic Ocean have significant implications for global governance, resource extraction, and environmental protection. The issue has sparked controversy and territorial disputes with other Arctic nations.
4. How does Russia manage its borders?
Russia has a complex border management system, involving various agencies and institutions. The Federal Security Service (FSB) is responsible for border security, while other agencies are involved in customs, immigration, and environmental protection.
Tips for Understanding Russia’s Map and its Borders
- Use Interactive Maps: Utilize online interactive maps that provide detailed information about Russia’s borders, including political boundaries, major cities, and geographic features.
- Explore Historical Context: Understanding the historical context of Russia’s borders is crucial for comprehending its current geopolitical situation.
- Engage with News and Analysis: Stay informed about current events and geopolitical developments related to Russia and its neighbors.
- Study Regional Dynamics: Focus on the specific relationships between Russia and its neighboring countries, taking into account their cultural, economic, and political ties.
Conclusion: A Continuous Evolution
Russia’s map and its borders are not static entities. They are constantly evolving, shaped by historical events, political shifts, and economic forces. Understanding these dynamics is essential for comprehending the complexities of Russia’s role in the world. By examining the historical and contemporary context of Russia’s borders, we gain a deeper understanding of its cultural, economic, and geopolitical significance.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Exploration of Russia: Understanding its Borders and Neighbors. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!