A Comprehensive Look At The Geography Of Wisconsin And Michigan
A Comprehensive Look at the Geography of Wisconsin and Michigan
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Look at the Geography of Wisconsin and Michigan
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Look at the Geography of Wisconsin and Michigan. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Look at the Geography of Wisconsin and Michigan
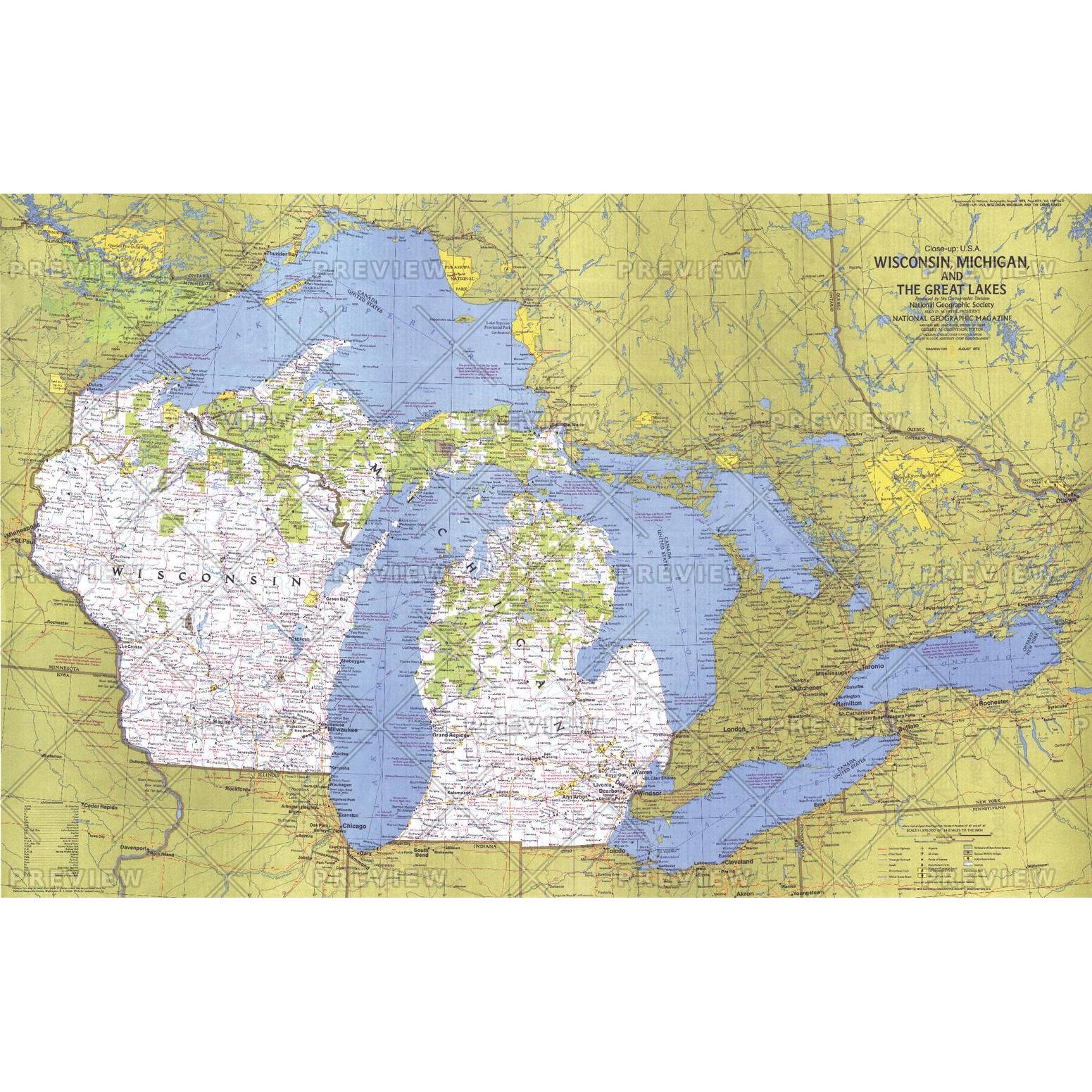
The states of Wisconsin and Michigan, nestled in the heart of the Great Lakes region, share a unique geographical tapestry woven from rolling hills, sprawling forests, and the majestic presence of the Great Lakes. Understanding their individual landscapes and shared characteristics is crucial for appreciating their natural beauty, economic activity, and cultural identity.
Wisconsin: The Badger State
Wisconsin, known as the "Badger State," is a land of diverse landscapes. Its geography is characterized by:
-
The Driftless Area: This unique region in the southwest corner of the state escaped the last glacial advance, resulting in a rugged, hilly terrain with deep river valleys. The Driftless Area is a haven for unique flora and fauna, making it a popular destination for hikers and outdoor enthusiasts.
-
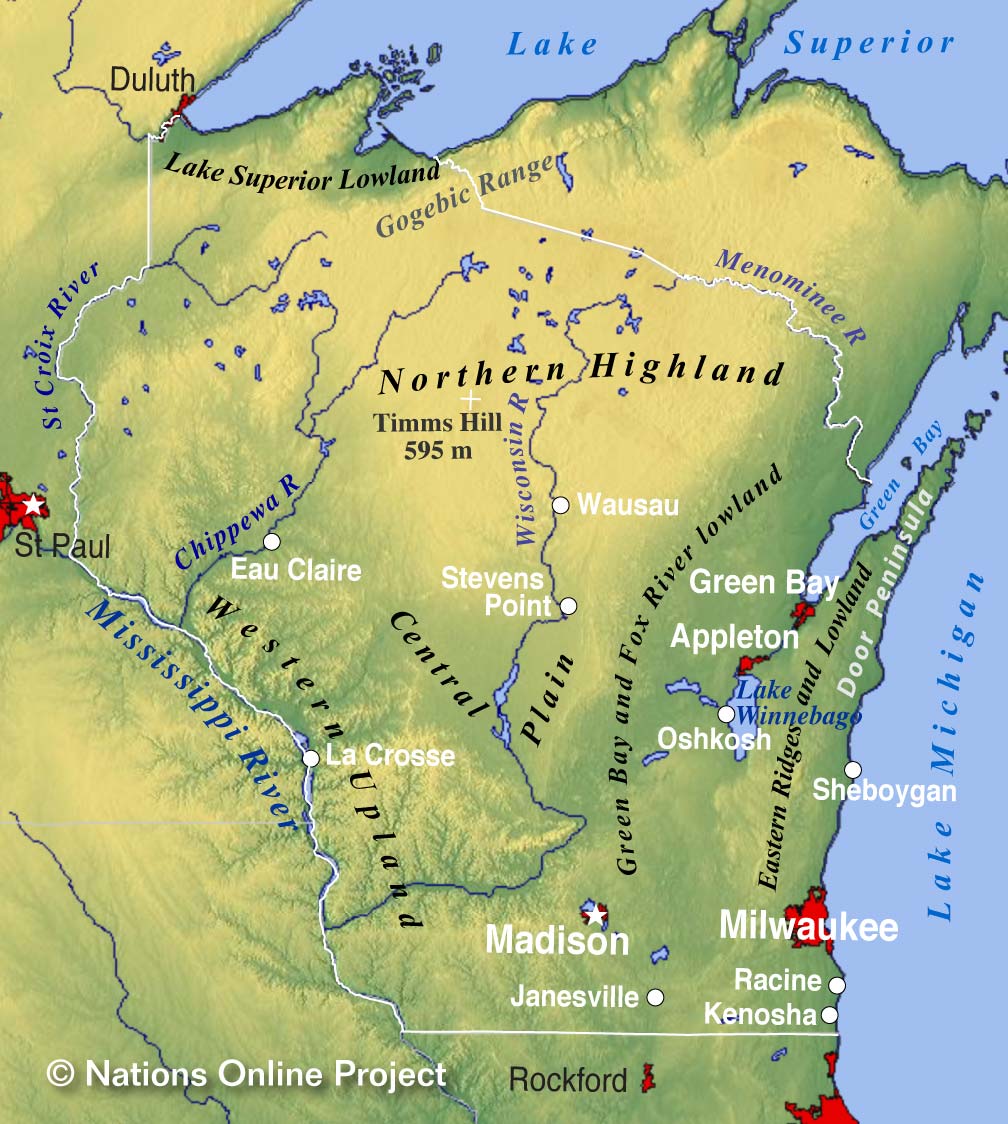
The Northern Highlands: Covering much of northern Wisconsin, this region boasts a landscape of rolling hills, forested areas, and numerous lakes and rivers. It is known for its pristine wilderness, abundant wildlife, and numerous recreational opportunities, including fishing, boating, and hiking.
-
The Central Sands: This region, located in central Wisconsin, is dominated by a vast expanse of sandy soils. It is home to extensive agricultural lands, primarily dedicated to growing potatoes, cranberries, and other crops.
-
The Lake Michigan Shore: The eastern edge of Wisconsin is defined by the stunning Lake Michigan shoreline. This area features picturesque beaches, charming coastal towns, and a vibrant tourism industry.
Michigan: The Great Lakes State
Michigan, aptly named the "Great Lakes State," is defined by its vast shoreline and numerous inland lakes. Its geography is distinguished by:
-
The Upper Peninsula: This northern region, separated from the Lower Peninsula by the Straits of Mackinac, is characterized by rugged terrain, dense forests, and numerous inland lakes. It is a haven for outdoor recreation, including hiking, fishing, and hunting.
-
The Lower Peninsula: Shaped like a mitten, the Lower Peninsula boasts a diverse landscape, ranging from rolling hills and farmland in the south to forested areas and numerous inland lakes in the north. The western side of the Lower Peninsula features the iconic Lake Michigan shoreline, while the eastern side is bordered by Lake Huron and Lake Erie.
-
The Great Lakes Shoreline: Michigan boasts the longest freshwater coastline in the contiguous United States. Its vast shoreline offers numerous opportunities for water-based activities, including boating, fishing, and swimming.
Shared Geographic Features and Their Importance
Wisconsin and Michigan share several geographical features that have shaped their history, culture, and economy:
-
The Great Lakes: The presence of the Great Lakes has been instrumental in the development of both states. They provided transportation routes, facilitated trade, and fostered industries such as fishing, shipping, and tourism. The Great Lakes also play a crucial role in regulating the climate and providing recreational opportunities.
-
Glacial History: The last glacial advance significantly shaped the landscapes of both states. The retreating glaciers left behind vast deposits of glacial till, creating fertile soils that support agriculture. The glacial activity also carved out valleys, created lakes, and formed the distinctive rolling hills that define much of the region.
-
Forestry: Both Wisconsin and Michigan are heavily forested, with vast areas of pine, hardwood, and mixed forests. These forests have historically provided lumber for construction, paper production, and other industries. They also play a crucial role in supporting biodiversity and regulating the environment.
-
Agriculture: The fertile soils and favorable climate have made both states important agricultural producers. Wisconsin is known for its dairy industry, while Michigan is a leading producer of fruits, vegetables, and grains.
The Importance of Understanding the Geography
Understanding the geography of Wisconsin and Michigan is crucial for several reasons:
-
Environmental Stewardship: Recognizing the importance of the Great Lakes, forests, and other natural resources is essential for developing sustainable practices and protecting the environment.
-
Economic Development: Understanding the region’s resources, climate, and infrastructure is vital for attracting new businesses, supporting existing industries, and promoting economic growth.
-
Tourism and Recreation: The diverse landscapes and recreational opportunities offered by both states attract visitors from across the globe. Understanding the geography helps in developing tourism infrastructure, promoting outdoor activities, and ensuring the preservation of natural beauty.
-
Cultural Identity: The geography of Wisconsin and Michigan has played a significant role in shaping their cultures. The Great Lakes, forests, and agricultural lands have inspired art, music, literature, and traditions that define the region’s identity.
FAQs about the Geography of Wisconsin and Michigan
-
What is the highest point in Wisconsin? The highest point in Wisconsin is Timms Hill, at 1,951 feet above sea level.
-
What is the highest point in Michigan? The highest point in Michigan is Mount Arvon, at 1,979 feet above sea level, located in the Upper Peninsula.
-
What are the major rivers in Wisconsin and Michigan? Some of the major rivers in Wisconsin include the Wisconsin River, the Mississippi River, and the Fox River. Major rivers in Michigan include the Grand River, the Saginaw River, and the Muskegon River.
-
What are the major cities in Wisconsin and Michigan? Major cities in Wisconsin include Milwaukee, Madison, and Green Bay. Major cities in Michigan include Detroit, Grand Rapids, and Lansing.
-
What are the major industries in Wisconsin and Michigan? Major industries in Wisconsin include manufacturing, agriculture, tourism, and healthcare. Major industries in Michigan include manufacturing, automotive, tourism, and healthcare.
Tips for Exploring the Geography of Wisconsin and Michigan
-
Visit the Great Lakes: Take a ferry ride across Lake Michigan or Lake Huron, explore the stunning shorelines, and enjoy the beauty of the region’s largest water bodies.
-
Explore the forests: Hike through the forests of the Upper Peninsula or the Northern Highlands, enjoy the peace and tranquility of the wilderness, and observe the diverse flora and fauna.
-
Visit the Driftless Area: Hike or bike through the rugged hills and deep valleys of the Driftless Area, experiencing the unique landscape shaped by glacial forces.
-
Learn about the history: Visit historical sites, museums, and landmarks to learn about the region’s rich history and how it was shaped by its geography.
-
Enjoy the local culture: Experience the unique cultures of Wisconsin and Michigan by visiting local festivals, sampling regional cuisine, and listening to traditional music.
Conclusion
The geography of Wisconsin and Michigan is a testament to the power of nature, shaping the landscape, influencing the economy, and contributing to the region’s unique cultural identity. From the rolling hills and fertile farmlands to the majestic Great Lakes and pristine forests, these states offer a diverse and captivating landscape for exploration, recreation, and appreciation. Understanding their geography provides a deeper understanding of the region’s history, its people, and its future.

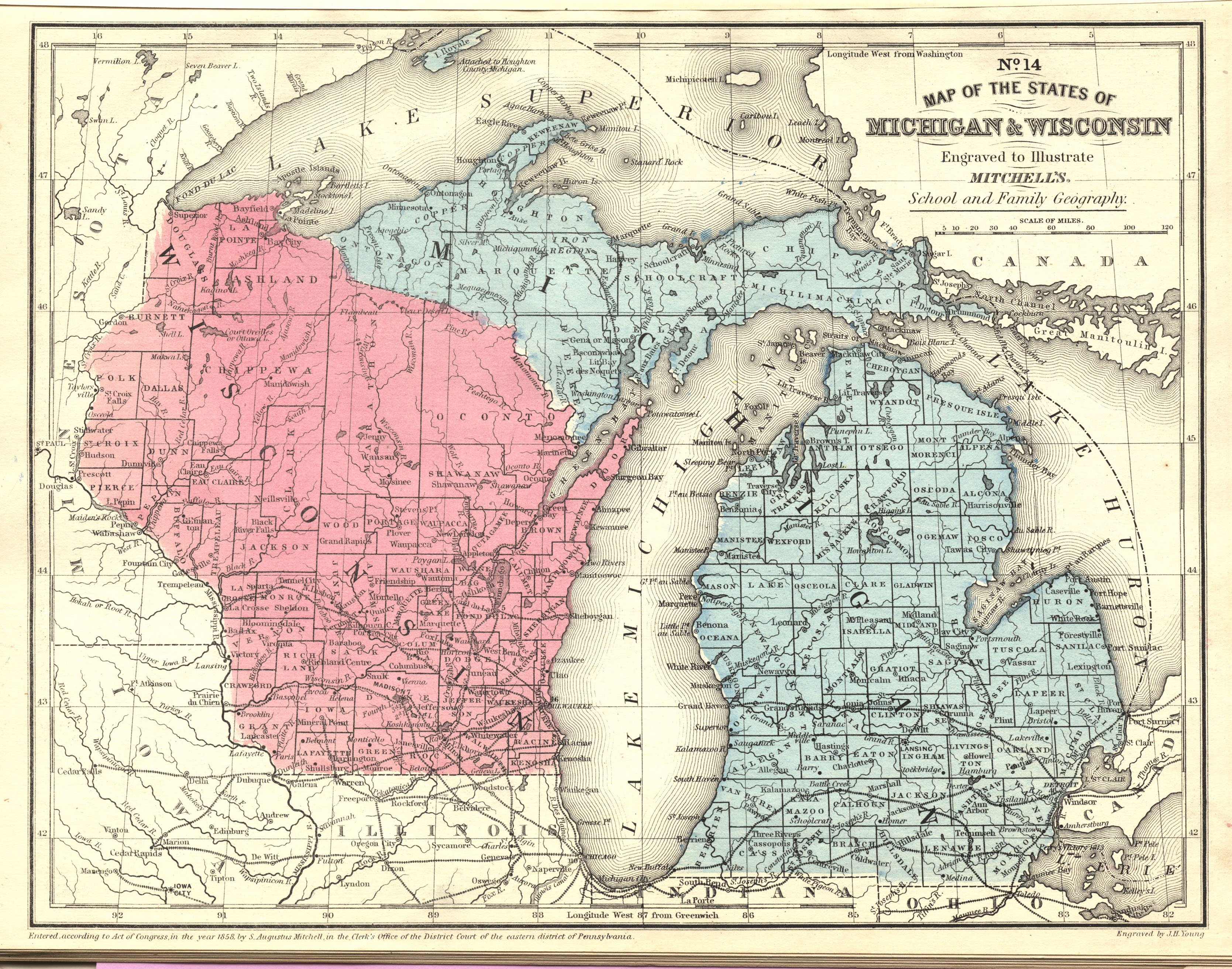
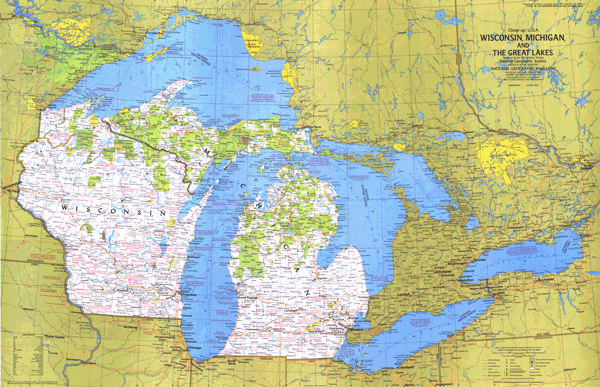
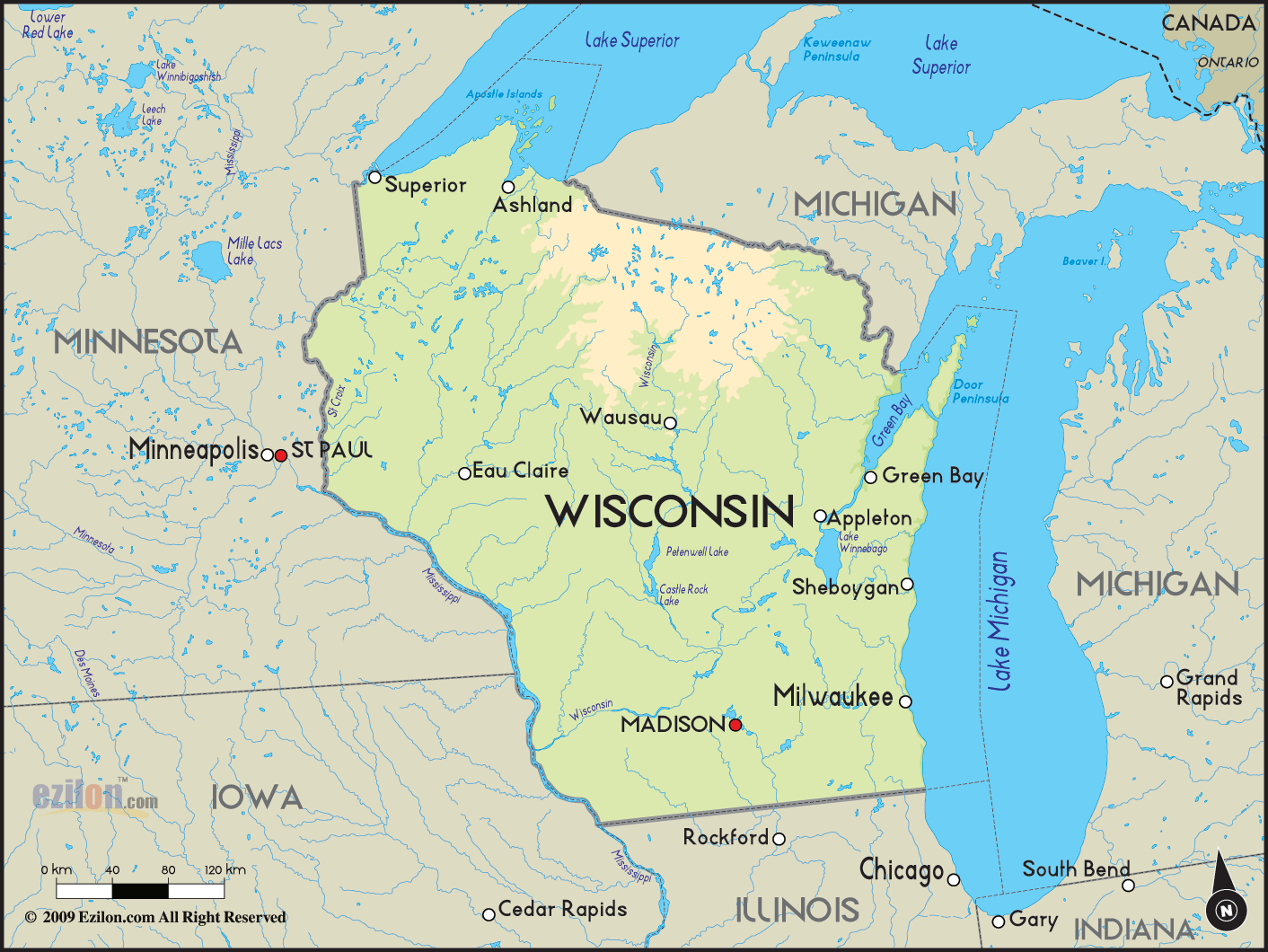



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Look at the Geography of Wisconsin and Michigan. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!