A Comprehensive Guide To Wisconsin Assembly Districts: Understanding The Building Blocks Of Representation
A Comprehensive Guide to Wisconsin Assembly Districts: Understanding the Building Blocks of Representation
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Wisconsin Assembly Districts: Understanding the Building Blocks of Representation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Wisconsin Assembly Districts: Understanding the Building Blocks of Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Wisconsin Assembly Districts: Understanding the Building Blocks of Representation

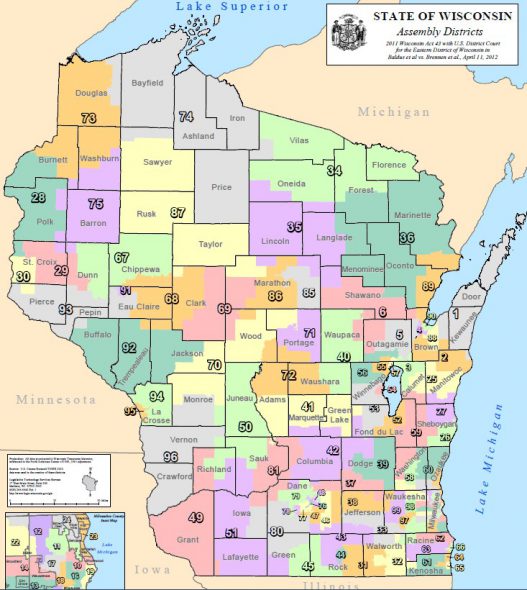
The Wisconsin Assembly, one of the two houses of the Wisconsin State Legislature, is composed of 99 members, each representing a distinct geographical area known as an Assembly District. These districts serve as the foundational units of political representation in the state, shaping the electoral landscape and influencing the voices heard in state government. Understanding the map of Wisconsin Assembly Districts is crucial for comprehending the intricacies of Wisconsin’s political system and the representation of its diverse population.
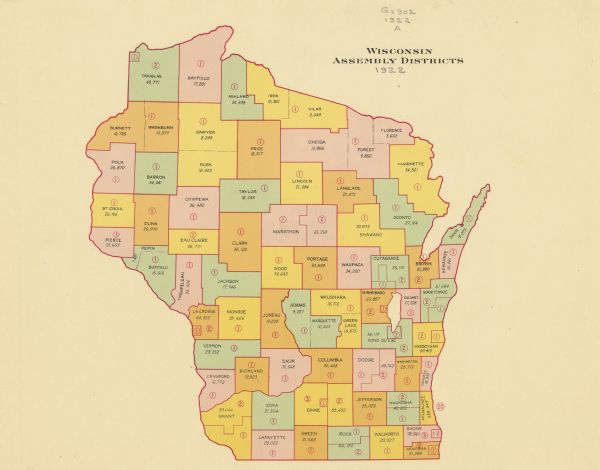
A Historical Perspective on Districting
The process of dividing Wisconsin into Assembly Districts has evolved over time, reflecting shifts in population demographics, political ideologies, and legal interpretations. The state constitution mandates that districts be as equal in population as practicable, with the goal of ensuring fair and equitable representation. However, the application of this principle has been subject to interpretation and debate, leading to various redistricting efforts throughout history.
The 2000s Redistricting Cycle and Its Impact
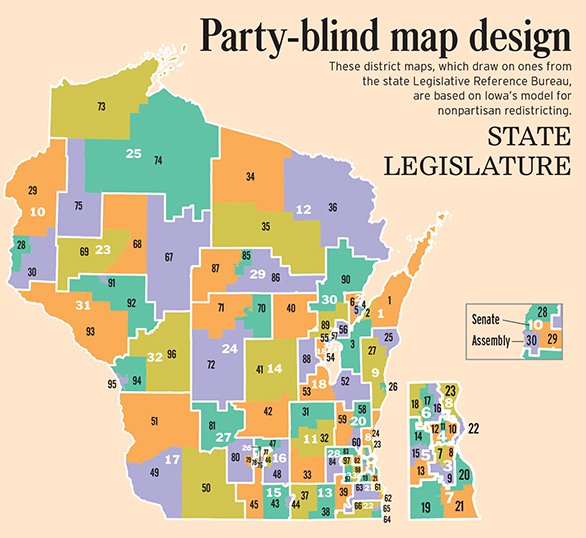
The 2000s saw a significant redistricting cycle in Wisconsin, driven by the 2000 Census. This process led to the creation of the current Assembly district map, which has remained largely unchanged since then. The redistricting process was marked by controversy, with accusations of gerrymandering, the manipulation of district boundaries to favor a particular political party, surfacing. This controversy highlights the inherent tension between the principles of equal representation and political advantage in the redistricting process.
Understanding the Map: Key Features and Implications
The map of Wisconsin Assembly Districts reveals several key features that influence the political landscape:
- Urban vs. Rural Representation: The distribution of Assembly Districts reflects the state’s urban-rural divide. Densely populated urban areas, such as Milwaukee and Madison, are often divided into multiple districts, while rural areas may be grouped together into larger districts. This disparity in district size can impact the relative influence of urban and rural voters.
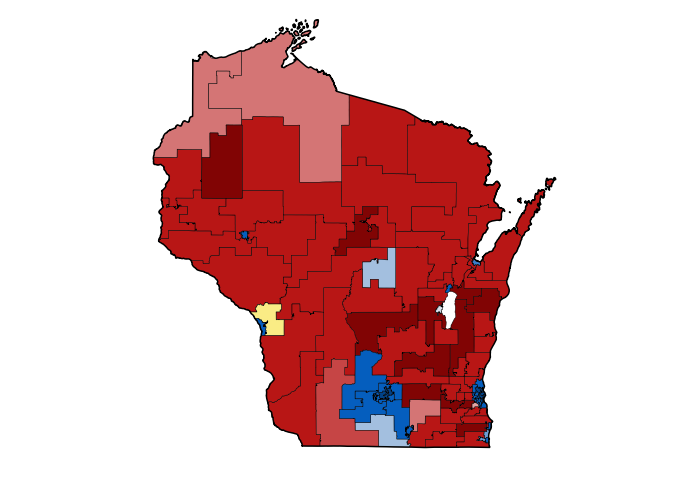
- Party Dominance and Competition: The map also reveals patterns of party dominance and competition across different districts. Some districts are consistently considered safe seats for one party, while others are more competitive, offering potential for shifts in representation.
- Representation of Minority Groups: The map’s design can impact the representation of minority groups. Districts with a high concentration of minority voters may be more likely to elect candidates who represent their interests. However, concerns about the effectiveness of minority representation can arise if districts are designed in a way that dilutes their voting power.
- The Role of Geography: Geographical features, such as rivers, lakes, and major highways, often play a role in shaping district boundaries. This can lead to districts that are geographically diverse, encompassing both urban and rural areas, or districts that are more homogeneous in terms of their population characteristics.
The Importance of the Assembly District Map
The map of Wisconsin Assembly Districts is not simply a geographical tool; it is a fundamental element of the state’s political structure. Its impact extends beyond the immediate allocation of seats in the Assembly, influencing:
- Electoral Outcomes: The boundaries of Assembly Districts directly affect the composition of the electorate and can influence the outcome of elections.
- Policymaking: The representation of different constituencies within the Assembly, as determined by district boundaries, can shape the policy agenda and legislative priorities.
- Public Engagement: The map’s design can influence the level of public engagement in the political process. Residents may be more likely to participate in elections and advocacy efforts if they feel represented by their Assembly member.
FAQs About Wisconsin Assembly Districts
Q: How often are Assembly District boundaries redrawn?
A: Assembly District boundaries are typically redrawn every ten years following the decennial census, to ensure that districts reflect changes in population distribution.
Q: What is the role of the Wisconsin Legislative Redistricting Commission in the redistricting process?
A: The Wisconsin Legislative Redistricting Commission is a bipartisan body responsible for drawing the boundaries of Assembly Districts and other legislative districts. The commission is composed of four members, two from each major political party, and a fifth member, the chairperson, who is selected by the other four members.
Q: What are the main criteria used to draw Assembly District boundaries?
A: The primary criteria used in drawing Assembly District boundaries are:
- Equal Population: Districts must be as equal in population as practicable.
- Contiguity: Districts must be contiguous, meaning that all parts of a district must be connected.
- Compactness: Districts should be as compact as possible, meaning that they should not be unnecessarily stretched or elongated.
- Communities of Interest: Districts should respect communities of interest, such as neighborhoods, towns, and cities, to the extent possible.
Q: What are the potential consequences of gerrymandering?
A: Gerrymandering can have several negative consequences:
- Reduced Competition: It can create districts that are heavily skewed towards one party, reducing competition and making it more difficult for challengers to win elections.
- Diminished Voter Choice: It can limit voter choice by creating districts where one party’s candidates are virtually guaranteed to win.
- Underrepresentation: It can lead to the underrepresentation of certain groups, such as minorities, by diluting their voting power.
Tips for Understanding Wisconsin Assembly Districts
- Consult the Official Map: The Wisconsin Legislative Redistricting Commission provides an official map of Assembly Districts on its website.
- Explore District Demographics: Resources like the U.S. Census Bureau website offer demographic data for each Assembly District, providing insights into the population characteristics of each area.
- Follow Redistricting Updates: Stay informed about upcoming redistricting cycles and the processes involved.
- Engage in Public Comment: Participate in public hearings and comment periods during the redistricting process to share your views on district boundaries.
Conclusion
The map of Wisconsin Assembly Districts serves as a vital tool for understanding the state’s political landscape and the representation of its diverse population. While the process of drawing district boundaries is often subject to debate and controversy, it remains a fundamental element of the democratic process. By understanding the historical context, key features, and implications of the map, citizens can better engage in the political process and ensure that their voices are heard in the halls of government.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Wisconsin Assembly Districts: Understanding the Building Blocks of Representation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!