A Comprehensive Guide To The Geography And Significance Of Tyne And Wear
A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography and Significance of Tyne and Wear
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography and Significance of Tyne and Wear
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography and Significance of Tyne and Wear. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography and Significance of Tyne and Wear
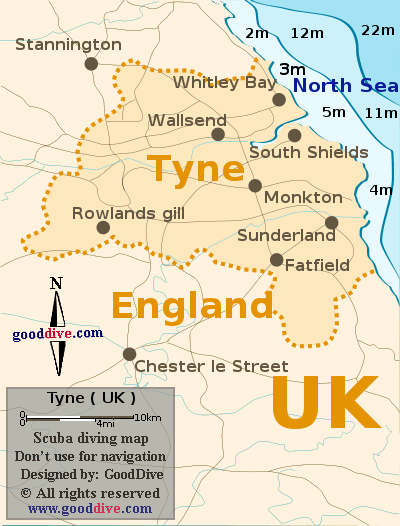
The metropolitan county of Tyne and Wear, located in North East England, encompasses a rich tapestry of history, culture, and industry. Understanding its geographical makeup is crucial to appreciating the region’s unique character and its pivotal role in the national and international landscape.
Geographical Overview:
Tyne and Wear, despite its relatively small size, boasts a diverse geography. The county is bisected by the River Tyne, a major waterway that has historically served as a vital artery for trade and transportation. The river’s estuary forms the northern boundary of the county, opening into the North Sea.
To the west of the Tyne, the landscape gradually rises, transitioning into rolling hills and valleys. This area is characterized by the presence of the Pennine Hills, a prominent range that extends across northern England. The eastern portion of Tyne and Wear, however, features a flatter terrain, dominated by the coastal plain that stretches along the North Sea.
Administrative Divisions:
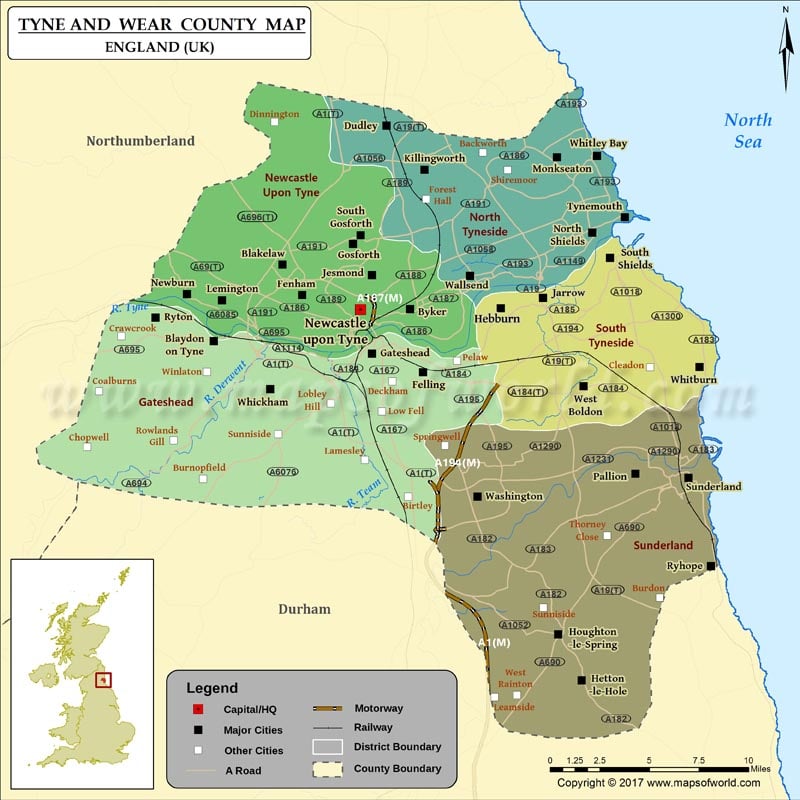
Tyne and Wear is composed of five metropolitan boroughs, each possessing its own distinct identity and administrative functions:
- Newcastle upon Tyne: The largest and most populous borough, Newcastle is the regional center for commerce, culture, and education. It boasts a rich architectural heritage and is home to several universities and research institutions.
- Gateshead: Located across the Tyne from Newcastle, Gateshead is renowned for its cultural offerings, including the iconic Sage Gateshead concert hall and the Baltic Centre for Contemporary Art.
- South Tyneside: This borough encompasses the coastal towns of South Shields and Jarrow, known for their historic shipbuilding industries and vibrant seaside communities.
- Sunderland: A major industrial hub, Sunderland is a center for manufacturing and automotive production. It also boasts a rich maritime history and a thriving cultural scene.
- North Tyneside: Situated to the north of Newcastle, North Tyneside is characterized by its coastal towns, including Whitley Bay and Tynemouth, renowned for their beaches and historic castles.
Historical Significance:
Tyne and Wear’s history is deeply intertwined with its geography. The River Tyne, with its strategic location and navigable waters, played a crucial role in the region’s economic development. From the medieval period onward, the river served as a conduit for trade, facilitating the growth of shipbuilding, coal mining, and other industries.
The region’s industrial heritage is evident in the numerous historic towns and villages that dot the landscape. From the shipbuilding yards of South Shields to the coal mines of Gateshead, these communities bear witness to the region’s past as a powerhouse of manufacturing and innovation.
Contemporary Landscape:
While Tyne and Wear’s industrial past remains a defining feature, the region has undergone significant transformation in recent decades. The decline of traditional industries has led to a shift towards a more diversified economy, with growth in sectors such as technology, healthcare, and tourism.
Newcastle, in particular, has emerged as a vibrant hub for technology and innovation, attracting investment from leading companies in the fields of software development, digital media, and life sciences. The city’s burgeoning cultural scene, coupled with its historic charm, has also contributed to its growing appeal as a tourist destination.
Environmental Considerations:
Tyne and Wear’s geography presents both opportunities and challenges in terms of environmental management. The region’s coastal location makes it vulnerable to the effects of climate change, including rising sea levels and increased storm surges. The River Tyne, while a vital waterway, has also faced pollution issues in the past.
However, Tyne and Wear has made significant strides in environmental protection and sustainability. The region has invested heavily in renewable energy sources, such as wind power, and has implemented measures to improve air quality and reduce waste.
Transportation and Infrastructure:
Tyne and Wear boasts a well-developed transportation network, connecting its various towns and cities. The region is served by a comprehensive bus network, as well as a metro system, known as the Tyne and Wear Metro, which provides efficient and reliable public transport within the county.
The region also benefits from its proximity to major transport hubs, including Newcastle International Airport, which offers connections to destinations across the UK and Europe. The A1, a major north-south motorway, passes through Tyne and Wear, providing access to other parts of England.
Cultural Significance:
Tyne and Wear is renowned for its rich cultural heritage, reflected in its museums, theaters, and art galleries. The region is home to several world-class institutions, including the Great North Museum: Hancock, the Baltic Centre for Contemporary Art, and the Sage Gateshead.
Tyne and Wear is also a vibrant hub for music, theater, and dance. The region boasts a thriving live music scene, with venues such as the O2 Academy Newcastle and the Tyne Theatre & Opera House hosting a diverse range of performances.
Economic Significance:
Tyne and Wear is a significant economic driver for the North East of England. The region boasts a diverse economy, with key sectors including manufacturing, technology, healthcare, and tourism.
The region’s economic performance has been steadily improving in recent years, with a growing number of businesses establishing themselves in Tyne and Wear. The region is attracting investment from both national and international companies, driven by its skilled workforce, competitive business environment, and attractive quality of life.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its economic progress, Tyne and Wear faces a number of challenges, including high levels of deprivation in certain areas, a skills gap in some sectors, and the need to address the impact of climate change.
However, the region also presents a number of opportunities for growth and development. Its strong educational institutions, its skilled workforce, and its vibrant cultural scene provide a solid foundation for future success.
FAQs:
1. What is the population of Tyne and Wear?
The population of Tyne and Wear is approximately 1,025,000.
2. What is the largest city in Tyne and Wear?
The largest city in Tyne and Wear is Newcastle upon Tyne.
3. What are the main industries in Tyne and Wear?
The main industries in Tyne and Wear include manufacturing, technology, healthcare, and tourism.
4. What are the main tourist attractions in Tyne and Wear?
Some of the main tourist attractions in Tyne and Wear include the Tyne Bridge, the Sage Gateshead, the Baltic Centre for Contemporary Art, and the Great North Museum: Hancock.
5. What are the main universities in Tyne and Wear?
The main universities in Tyne and Wear include Newcastle University, Northumbria University, and Sunderland University.
Tips:
- Explore the region’s diverse cultural offerings: From museums and art galleries to theaters and music venues, Tyne and Wear has something to offer everyone.
- Enjoy the region’s natural beauty: Take a stroll along the River Tyne, explore the beaches of South Shields, or hike in the Pennine Hills.
- Sample the region’s culinary delights: From traditional fish and chips to innovative modern cuisine, Tyne and Wear offers a wide range of dining experiences.
- Experience the region’s vibrant nightlife: Newcastle is renowned for its lively nightlife, with a wide range of bars, clubs, and live music venues.
- Learn about the region’s rich history and heritage: Visit historic sites such as the Angel of the North, the Durham Cathedral, and the Beamish Museum.
Conclusion:
Tyne and Wear is a region with a rich history, a diverse geography, and a vibrant culture. Its industrial past has shaped its character, while its present is marked by innovation, creativity, and a commitment to growth. As a major economic hub for the North East of England, Tyne and Wear continues to attract investment and develop its potential. The region’s commitment to sustainability and its focus on improving the lives of its residents ensure that its future is bright.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography and Significance of Tyne and Wear. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!