A Comprehensive Exploration Of The World’s Nations: Understanding The Global Landscape
A Comprehensive Exploration of the World’s Nations: Understanding the Global Landscape
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Exploration of the World’s Nations: Understanding the Global Landscape
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Exploration of the World’s Nations: Understanding the Global Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Exploration of the World’s Nations: Understanding the Global Landscape
The Earth, our shared home, is a tapestry of diverse cultures, languages, and landscapes. Understanding the intricate web of nations that populate our planet is crucial for navigating the complex challenges of the 21st century. This exploration aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the world’s countries, delving into their unique characteristics and highlighting the importance of recognizing their individual identities.
A Global Tapestry of Nations
The world is currently home to 195 officially recognized sovereign states, each with its own rich history, cultural heritage, and political structure. These nations, ranging in size from the vast expanse of Russia to the tiny island nation of Nauru, represent a diverse spectrum of human experience.
Navigating the Global Landscape
To grasp the complexities of the international community, it is essential to understand the geographical, political, and economic factors that shape each nation.
Geographical Diversity:
-
Continents: The world is divided into seven continents, each with distinct geographical features, climates, and ecosystems.
- Asia: The largest and most populous continent, with diverse landscapes ranging from the Himalayas to the vast Siberian plains.
- Africa: Home to the Sahara Desert, the Nile River, and a rich tapestry of cultures and languages.
- North America: From the Rocky Mountains to the Great Lakes, North America boasts a diverse geography and a rich history of indigenous cultures.
- South America: The continent of the Andes Mountains, the Amazon rainforest, and vibrant cultures like the Inca and Maya.
- Europe: A continent of diverse landscapes, from the Alps to the Scandinavian fjords, and a rich history of cultural exchange.
- Australia: A unique continent known for its vast deserts, diverse wildlife, and unique indigenous culture.
- Antarctica: The coldest and windiest continent, covered in ice and home to unique ecosystems.
-
Regions: Within continents, nations are often grouped into regions based on geographical proximity, shared history, or cultural similarities. Examples include:
- The Middle East: A region encompassing countries in Western Asia and North Africa, known for its rich history and diverse cultures.
- Southeast Asia: A region characterized by its tropical climate, diverse cultures, and rapidly developing economies.
- Latin America: A region encompassing countries in Central and South America, known for its vibrant cultures and rich history.
- Sub-Saharan Africa: A region encompassing countries south of the Sahara Desert, known for its diverse cultures and economies.
Political Systems:
- Democracy: A system of government where power is vested in the people and exercised through a system of representation.
- Monarchy: A system of government where a king or queen holds supreme power.
- Republic: A system of government where power is vested in the people and exercised through elected representatives.
- Dictatorship: A system of government where power is held by a single person or a small group, often through force or intimidation.
Economic Systems:
- Capitalism: An economic system characterized by private ownership of the means of production and the pursuit of profit.
- Socialism: An economic system characterized by social ownership of the means of production and the distribution of wealth based on need.
- Communism: A political and economic system characterized by the abolition of private property and the establishment of a classless society.
Understanding the Importance of National Identity
Recognizing the unique characteristics of each nation is vital for fostering understanding, collaboration, and peace.
- Cultural Diversity: Each nation is a treasure trove of cultural heritage, including languages, traditions, art, music, and cuisine.
- Historical Context: Understanding a nation’s history helps us grasp its present-day realities and aspirations.
- Political Systems: Different political systems shape the way nations govern themselves and interact with the international community.
- Economic Development: Each nation has its own unique economic strengths and challenges, influencing its role in the global economy.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a country and a state?
- Country: A sovereign entity with its own government, territory, and population.
- State: A political subdivision within a country, often with its own government and administrative structures.
2. What is the purpose of international organizations?
International organizations, such as the United Nations, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund, facilitate cooperation between nations on issues of global concern, such as peace, development, and trade.
3. How do countries interact with each other?
Countries interact through diplomacy, trade, treaties, and international organizations.
4. What are some of the challenges facing the international community?
The international community faces a range of challenges, including climate change, global poverty, armed conflict, and human rights violations.
Tips for Understanding the World’s Nations
- Engage with different cultures: Travel, explore diverse media, and connect with people from different backgrounds.
- Study history: Understanding the past helps us understand the present and anticipate the future.
- Follow international news: Stay informed about global events and the issues facing different nations.
- Support international organizations: Contribute to organizations working to address global challenges.
Conclusion
The world’s nations, each with its own unique story, contribute to the rich tapestry of human experience. Understanding their individual identities and the challenges they face is essential for building a more peaceful, prosperous, and sustainable future for all. By embracing diversity, fostering dialogue, and promoting collaboration, we can create a world where all nations thrive and contribute to a shared future.


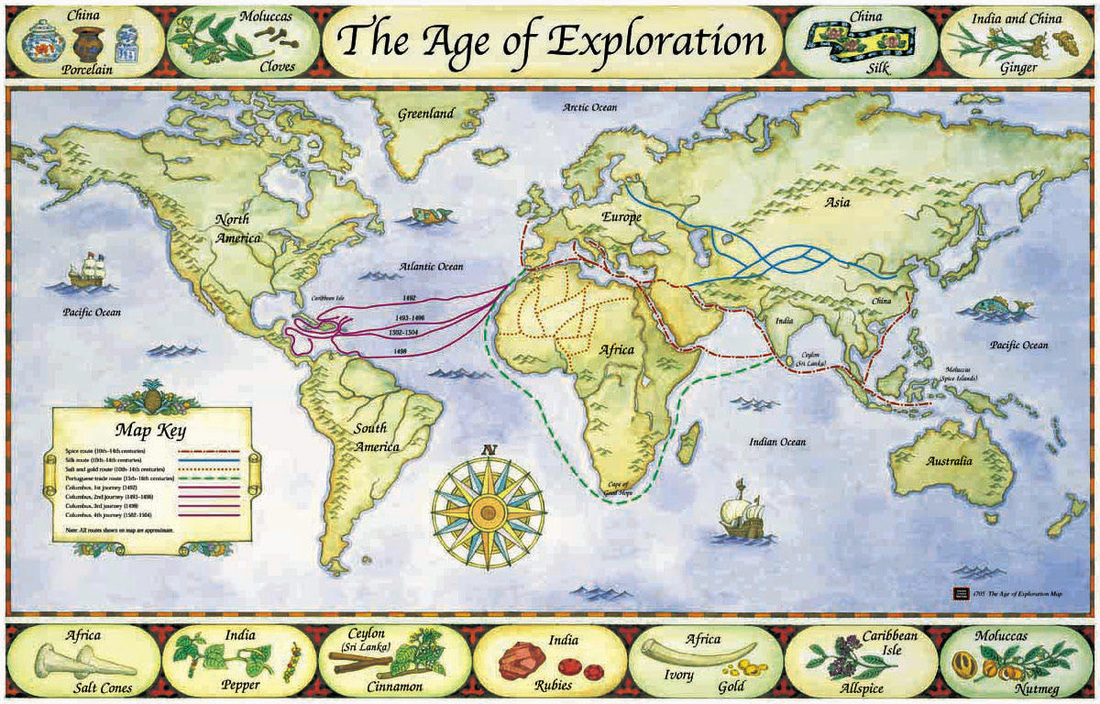
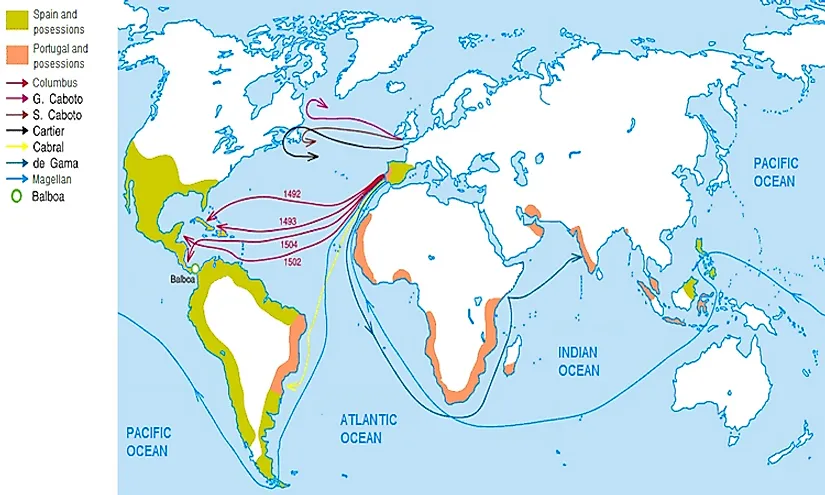
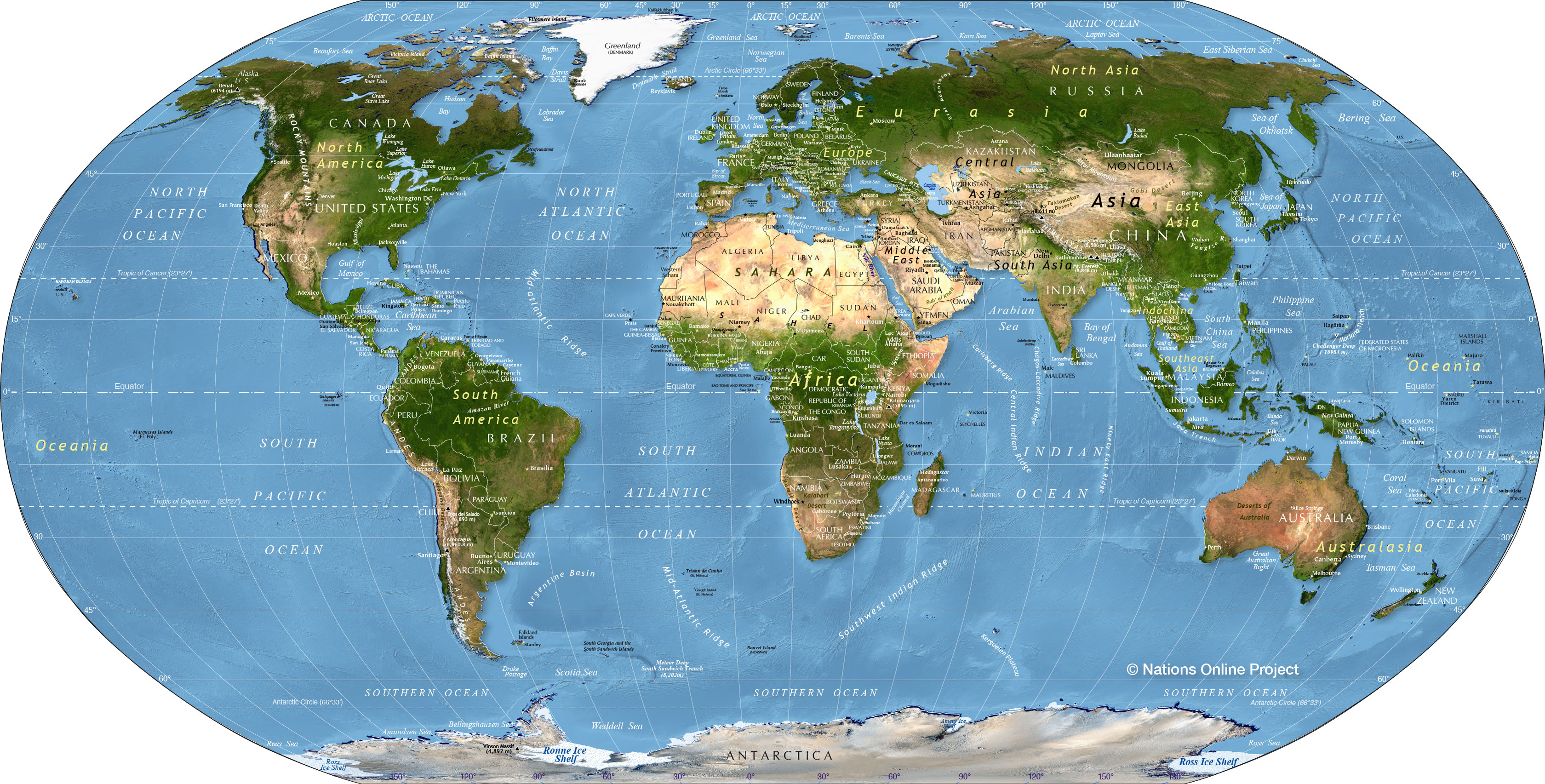
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Exploration of the World’s Nations: Understanding the Global Landscape. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!